In an experiment to measure the acceleration of free fall a student ties two different blocks of masses m1 and m2 to the ends of a string that passes over a frictionless pulley. 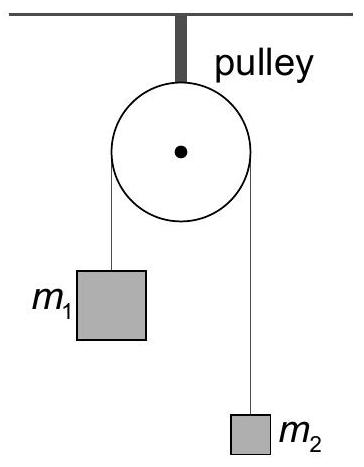 The student calculates the acceleration a of the blocks by measuring the time taken by the heavier mass to fall through a given distance. Their theory predicts that a = g(m1 - m2)/(m1 + m2) and this can be re-arranged to give g = a(m1 + m2)/(m1 - m2).
The student calculates the acceleration a of the blocks by measuring the time taken by the heavier mass to fall through a given distance. Their theory predicts that a = g(m1 - m2)/(m1 + m2) and this can be re-arranged to give g = a(m1 + m2)/(m1 - m2).
Calculate the percentage error in the measured value of g.
error in is OR error in is OR error in a is ✓ adds percentage errors ✓ so error in is OR OR ✓
Deduce the value of g and its absolute uncertainty for this experiment.
«» OR «» ✓ «» OR «» ✓
State and explain the advantage with reference to the magnitude of the acceleration that is obtained.
the acceleration would be small/the time of fall would be large ✓ easier to measure /a longer time of fall reduces the % error in the time of fall and «hence acceleration» ✓

