Practice SL 5.3—Introduction to derivatives with authentic IB Mathematics Applications & Interpretation (AI) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A local bakery is analyzing the profit from its signature pastry, which is modeled by the function , where represents the number of hours after opening and represents the profit in hundreds of dollars.
Calculate the derivative to determine the rate of change of the profit with respect to time.
Find the critical points of the function by solving . These points will help the bakery understand when the profit is at a local maximum or minimum.
Determine whether the profit is increasing or decreasing on the intervals defined by the critical points.
Identify any local maximum or minimum points and justify your answer.
A technology company is analyzing the performance of its new software product. The function representing the profit from the software is given by:
Find the derivative .
Solve for the critical points where .
Determine the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing.
Determine the -coordinates of the local maximum and minimum points.
Sketch the graph of the function, clearly labeling the critical points and behavior.
A student is studying the decay of a chemical reactant over time in a laboratory experiment. The concentration of the reactant can be modeled by the exponential decay equation: where is the concentration at time , is the initial concentration, and is a positive constant representing the decay rate.
Show that the rate of change of concentration, , is always negative.
Evaluate the limit of as and interpret the result.
Sketch the graph of against . Label the key features, including the initial concentration .
In the following graph, and as an example:
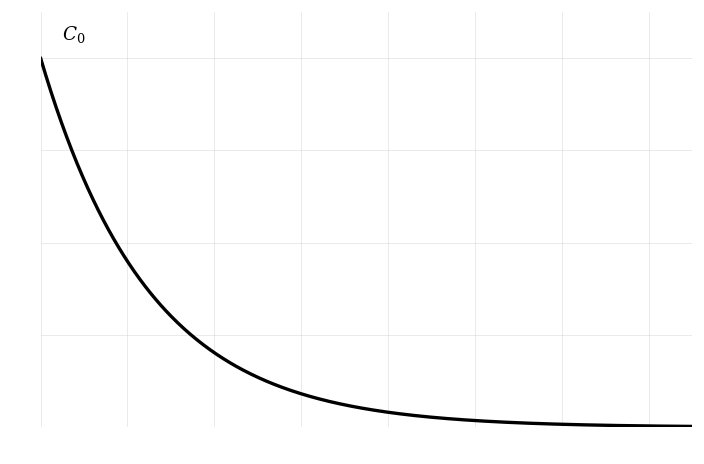
Find the half-life of the concentration, , in terms of .
Rewrite the equation in the form and identify the gradient and intercept of the line.
Use the rewritten equation to determine the values of and if the data plotted shows a straight line with slope and intercept .
A bakery's daily profit, , in hundreds of dollars, is modeled by the function , where is the production level in hundreds of units.
Calculate the derivative to find the rate of change of profit with respect to the production level .
Determine the critical points of for by setting .
Use the second derivative test to classify the nature of the critical points found in Part 2. This helps the bakery decide whether to adjust production levels.
State the intervals where the profit function is increasing and where it is decreasing for .
A startup company is analyzing its profit growth over time to make strategic decisions. The rate at which the company's profit is changing over time is given by:
where represents the company's profit (in thousands of dollars), and is the time in years since the company was founded ().
Find the values of for which the rate of change of profit is zero.
Determine the intervals of time for which the profit is increasing and decreasing.
Interpret the meaning of these intervals in the context of the company's profit.
Let
Evaluate the limit:
Find the derivative ()
Determine the value of .
State the interpretation of in terms of the rate of change of .
The surface area of an open box with a volume of and a square base with sides of length cm is given by where .
Find .
Solve .
Interpret your answer to part 2 in context.
A tech company is analyzing the performance of a new software application, represented by the function , where is the number of updates released.
Calculate the derivative to find the rate of change of performance with respect to updates.
Find the critical points of to identify when the performance is at a stationary point.
Determine whether these points correspond to local maxima or minima using the second derivative test.
Find the instantaneous rate of change of the function at .
Using your result from Part 2, explain what these values of tell us about the slope of the function.
Consider the function $g(x) = \frac{x^4}{4}$.
Find $g'(x)$.
Find the $x$-coordinate of the point at which the normal to the graph of $g$ has gradient $-\frac{1}{8}$.
Find the gradient of the graph of $g$ at $x = -\frac{1}{2}$.
A local government is evaluating the cost function of a new public transportation initiative represented by the function , where represents the number of buses in operation.
Find the derivative .
Determine the critical points by setting .
Identify the intervals on which the function is increasing or decreasing.
Identify any local maxima or minima, if they exist.