Practice AHL 3.12—Vector definitions with authentic IB Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (AA) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like functions and equations, calculus, complex numbers, sequences and series, and probability and statistics. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Let and . Let be a vector that is perpendicular to both and .
Find a vector that is perpendicular to both and .
Consider the plane given by the equation and the plane given by the equation .
Find a vector equation of the line of intersection of the planes and .
Verify that the line of intersection found is perpendicular to the normal vectors of both planes.
In this question, all lengths are in metres and time is in seconds. Consider two particles, and , which start to move at the same time. Particle moves in a straight line such that its displacement from a fixed point is given by , for .
Find an expression for the velocity of at time .
Particle also moves in a straight line. The position of is given by . The speed of is greater than the speed of when . Find the value of .
In 3D space, the points are
Find the vectors and .
Compute and hence find to 3 s.f.
Find the unit vector in the direction of .
Find the perpendicular distance from to the line .
In the following diagram is a square of side 5 cm while is a rectangle of length 10 cm and width 5 cm. Let and .
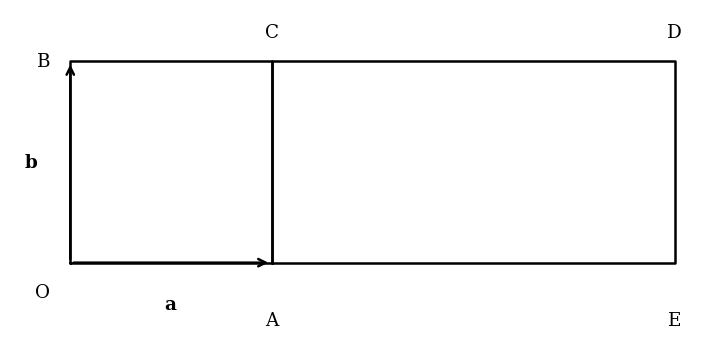
Express the following vectors in terms of and
Let and .
Find the magnitude of .
Find the magnitude of .
Find the unit vector in the direction of .
Find the unit vector in the direction of .
Find the vector from to the point dividing in the ratio (start at ) for and .
Consider two vectors and
Calculate
A construction company is analyzing the forces acting on a beam supported by two cables. The forces exerted by the cables are represented by vectors. Forces are measured in Newtons (N). The company needs to ensure that the angle between the two force vectors is within a safe range to prevent structural failure.
Given the force vectors and , calculate the dot product .
Using the dot product calculated, determine the cosine of the angle between the two vectors and .
Determine if the angle between the two vectors is within the safe range of to .
Consider a circle with a diameter , where has coordinates and has coordinates . The circle forms the base of a right cone whose vertex has coordinates .
Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle.
Find the radius of the circle.
Find the exact volume of the cone.