- IB
- SL 3.3—Angles of elevation and depression, bearings
Practice SL 3.3—Angles of elevation and depression, bearings with authentic IB Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (AA) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like functions and equations, calculus, complex numbers, sequences and series, and probability and statistics. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A hiker runs 620 m in the direction to a checkpoint, and then 360 m in the direction to the finish. To find :
- Direct distance from the starting point to the finishing point.
- Bearing of the finishing point from the starting point.
Direct distance from the starting point to the finishing point.
Bearing of the finishing point from the starting point.
A ship leaves port A on a bearing of . It sails a distance of 25 km to point B . At B , the ship changes direction to a bearing of . It sails a distance of 40 km to reach point C . A second ship leaves port A and sails directly to C . To find :

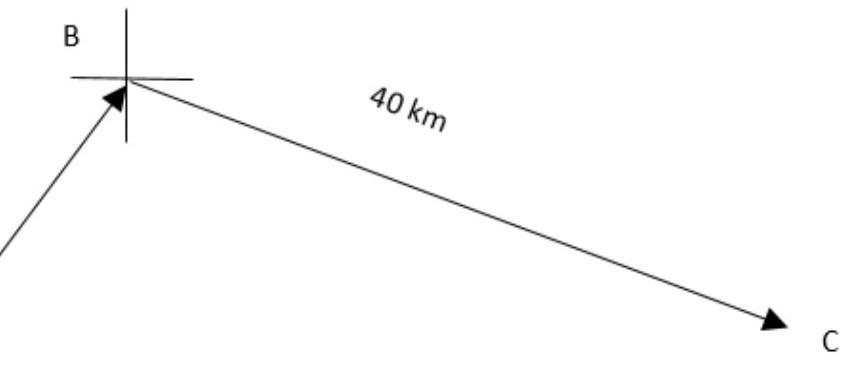
Distance the second ship will travel.
Bearing of the course taken by the second ship.
[Maximum Mark : 20] [With GDC]
Given the cuboid of dimensions as shown in the figure below. To find:
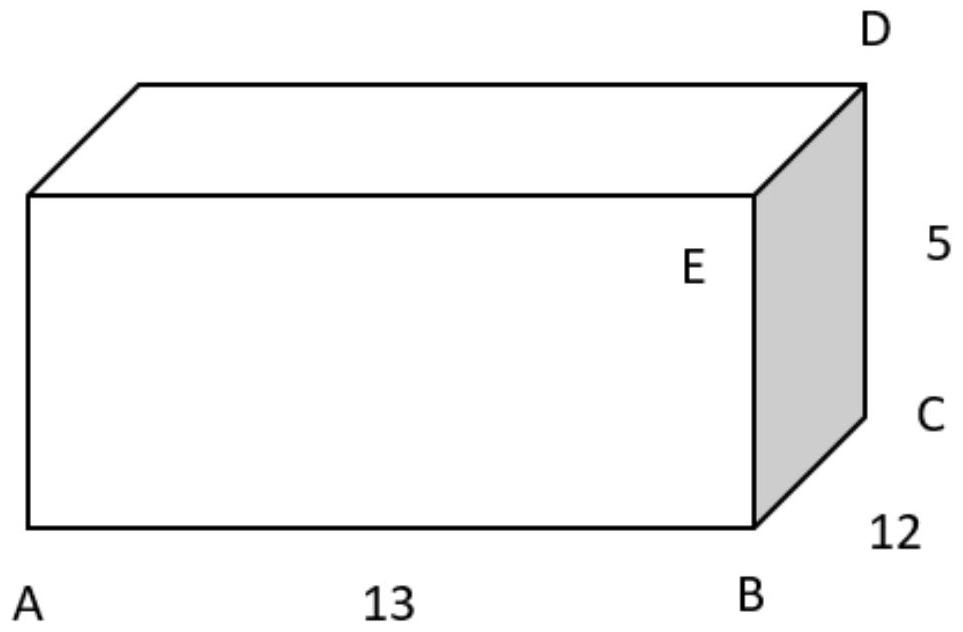
- Length of AC .
- Length of AD.
- Angle of elevation from A to E.
- Angle of elevation from A to D.
- Angle of depression from E to A .
Length of AC .
Length of AD.
Angle of elevation from A to E.
Angle of elevation from A to D.
Angle of depression from E to A .
A research drone is tethered by two cables, and , attached to points and on level ground. The points and are 80 m apart. The drone is directly above the point on the ground. In the horizontal triangle , the angle at between the lines and is .
At a certain instant, the angle of elevation of the drone from is and from is .
Draw a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all known angles.
Let the horizontal distances m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , show that
Use your results from part 2 and 3 to find the height of the drone above the ground. Give your answer to the nearest metre.
The drone then moves horizontally so that its projection traces out a circular path of radius 80 m centred at . Calculate the angle swept by in radians and the length of the arc of this path when the bearing of from changes from to .
The tension in each cable is proportional to its length. If the tension in is and in is , find the ratio at this instant.
A person standing 60 meters away from a building observes the top of the building at an angle of elevation of .
If the person then moves 20 meters closer to the building, what is the new angle of elevation to the top of the building?
A rescue helicopter hovers above a mountain valley. It is connected by two winch cables to huts and on level ground. The distance between the huts is . The helicopter is vertically above point , and in the horizontal triangle , .
The angle of elevation of the helicopter is from and from .
Sketch a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all given angles.
Let m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , write down an equation relating and .
Use your results to find the height of the helicopter above the ground, correct to the nearest metre.
The point later moves horizontally around a circular path of radius centred at . Find the length of the arc, in metres and radians, when its bearing from changes from to .
If tensions are and , find .
A cyclist can choose between using two ramps. The equations of the ramps with height at horizontal distance are and .
By finding the angle they make with the ground, find the angle created between the two ramps.
Explain which ramp the cyclist should take if they are trying to reach a higher level in the shortest horizontal distance.
A hot-air balloon is anchored by two ropes to points and on level ground. The distance is 75 m. The balloon is vertically above , and in the horizontal triangle .
The angles of elevation of the balloon are from and from .
Draw a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all the given angles.
Let m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , write an equation relating and .
Find the height of the balloon, to the nearest metre.
The projection moves horizontally on a circle of radius centered at . Find the angle subtended by the arc in radians and the length of the arc in metres when the bearing of from changes from to .
If and , find .
A person is flying their kite. The kite is on a string of length and has an angle of elevation of .
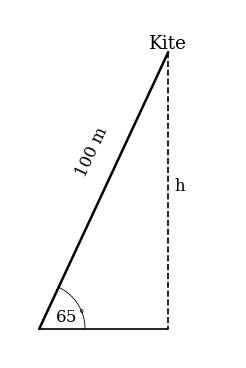
Find the height that the kite is flying at above the point the person is holding it.
Now a second person flies a kite from the same position as the first person. The kite is at the same vertical height as the first kite. The angle between the two strings is and the second kite is further away than the first.
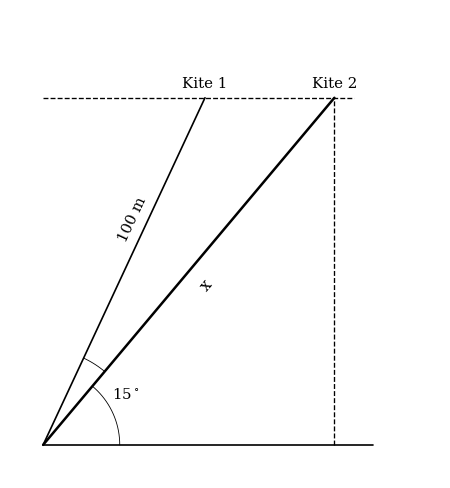
Find the length of the string for the kite flown by the second person.
From a given point, the angle of elevation to the top of the building is . After walking 80 m towards the building, the angle of elevation is now .

Find and in the figure above.