- IB
- 5.2.2. Describe Welford’s model of information processing.
Practice 5.2.2. Describe Welford’s model of information processing. with authentic IB Sports, exercise and health science (SEHS - Old) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Define motor program.
Distinguish the three different types of muscle.
Describe the impact of running compared to static exercises like holding a plank on systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
Explain how the concept of motor program can enhance the performance of a gymnastics routine.
Referring to Welford’s model of information processing, describe how information enters the short-term memory (STM).
Explain how the three energy systems support ATP production during an 800-meter run.
The diagram shows Welford’s model of information processing. What does X represent?
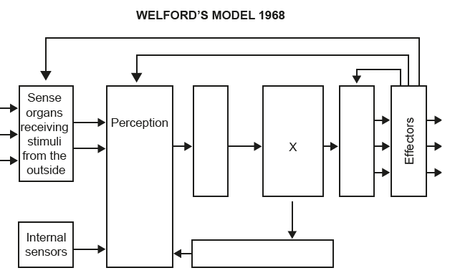
Which feature of Welford’s model of information processing is directly linked to short-term memory?
A goalie anticipates which direction the ball will be kicked. According to Welford’s model, which part of information processing is engaged before the goalie decides which direction to move?
I. Perception
II. Short-term store
III. Effector control
Practice 5.2.2. Describe Welford’s model of information processing. with authentic IB Sports, exercise and health science (SEHS - Old) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Define motor program.
Distinguish the three different types of muscle.
Describe the impact of running compared to static exercises like holding a plank on systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
Explain how the concept of motor program can enhance the performance of a gymnastics routine.
Referring to Welford’s model of information processing, describe how information enters the short-term memory (STM).
Explain how the three energy systems support ATP production during an 800-meter run.
The diagram shows Welford’s model of information processing. What does X represent?

Which feature of Welford’s model of information processing is directly linked to short-term memory?
A goalie anticipates which direction the ball will be kicked. According to Welford’s model, which part of information processing is engaged before the goalie decides which direction to move?
I. Perception
II. Short-term store
III. Effector control