Practice E.3 Radioactive decay with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
In an experiment, a beam of neutrons is used to induce artificial transmutation of stable nuclei, producing radioactive , which undergoes decay with a half-life of 2.25 minutes.
Write an equation for the neutron-induced transmutation reaction.
Write an equation for the subsequent decay of .
Calculate the activity of a sample containing atoms of .
Determine the number of atoms remaining after 6.75 minutes.
Explain the role of neutron activation in nuclear physics and suggest a practical application.
The graph shows the activity of a radioactive sample as a function of time.
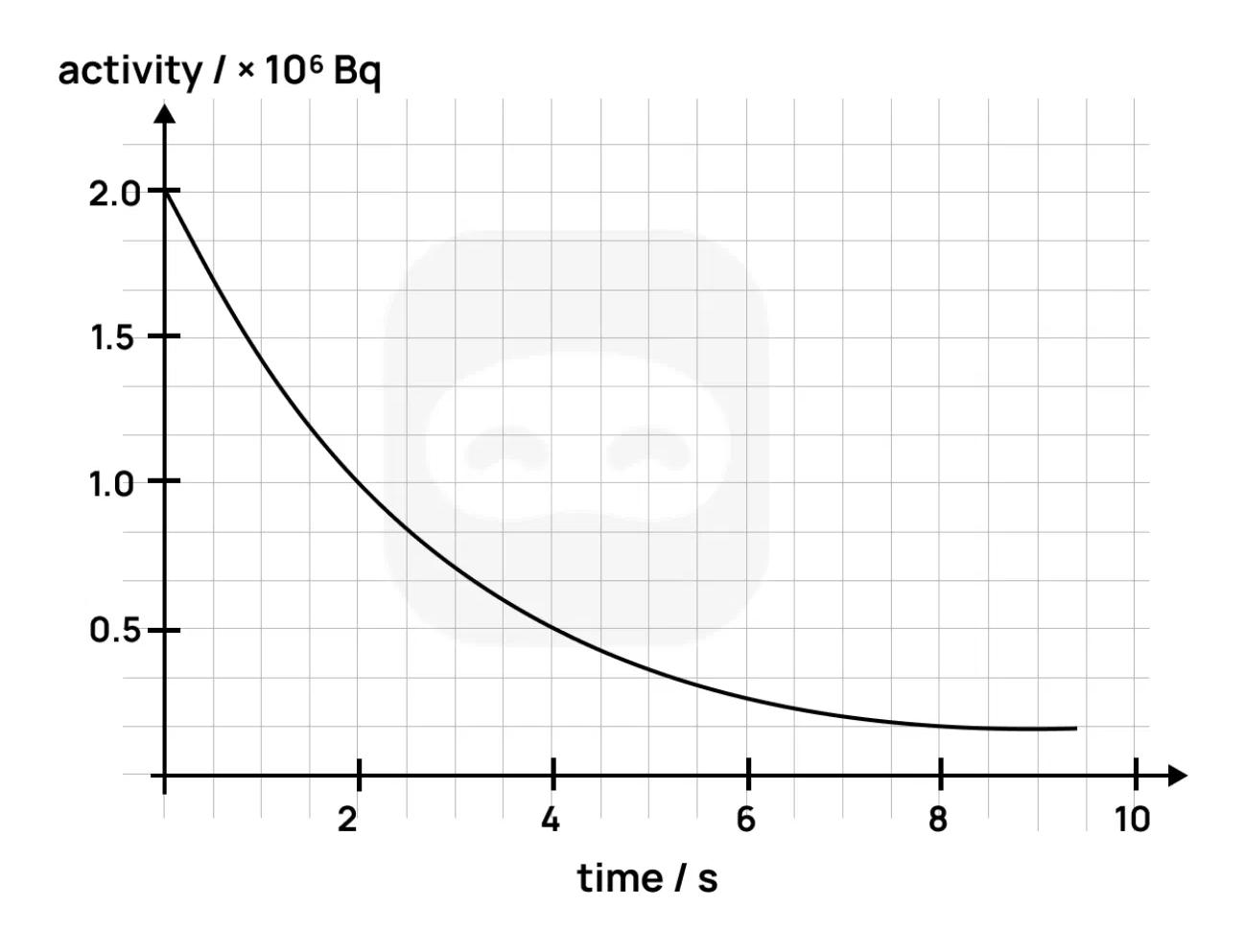
Define the term activity as used in radioactive decay.
Use the graph to determine the half-life of the sample. Show your working.
Calculate the decay constant of the sample using your answer to Part 2.
The number of undecayed nuclei at time is given by . Deduce the expression for the half-life in terms of the decay constant.
A detector used to measure this sample's activity has a uncertainty in its readings. Discuss the effect of this uncertainty on the accuracy of your half-life determination.
Explain how this graph supports the probabilistic nature of radioactive decay.
Which of the following is true about mass-energy changes in nuclear decay?
An isotope of mass number has a binding energy per nucleon of . What is the total energy released if of this isotope is formed from separated nucleons?
In the context of nuclear energy, the principle of mass-energy equivalence plays a crucial role in understanding how energy is released during radioactive decay. This principle is foundational in the development of sustainable energy sources.
Explain the concept of mass defect and its relation to binding energy.
Calculate the energy released if a total mass defect of is converted into energy, using the equation .
Discuss how the mass-energy equivalence principle is applied in the context of nuclear power generation and its implications for sustainable energy.
A pure sample of iodine-131 decays into xenon with a half-life of 8 days.
What is after 24 days?
When the nucleus is bombarded with alpha particles, the following nuclear reaction can occur.
The particle X is a
A graph of the variation of average binding energy per nucleon with nucleon number has a maximum. What is indicated by the region around the maximum?
In a neutral atom there are electrons, protons and neutrons. What is the mass number of the nuclide?
The initial number of atoms in a pure radioactive sample is . The radioactive half-life of the sample is defined as the