Practice E.2 Quantum physics (HL only) with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is measured as when the incident light frequency is .
Write the equation relating stopping potential , frequency , work function , and Planck’s constant .
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons.
Determine Planck’s constant given the work function . (1 eV = J)
Explain how the photoelectric effect demonstrates the quantized nature of light.
The diagram shows an experimental setup used to investigate the photoelectric effect. Light is incident on a metal surface in a vacuum. A variable potential difference is applied between the collector and emitter. The polarity of the potential difference can be reversed. The current and voltage are measured using an ammeter and voltmeter.
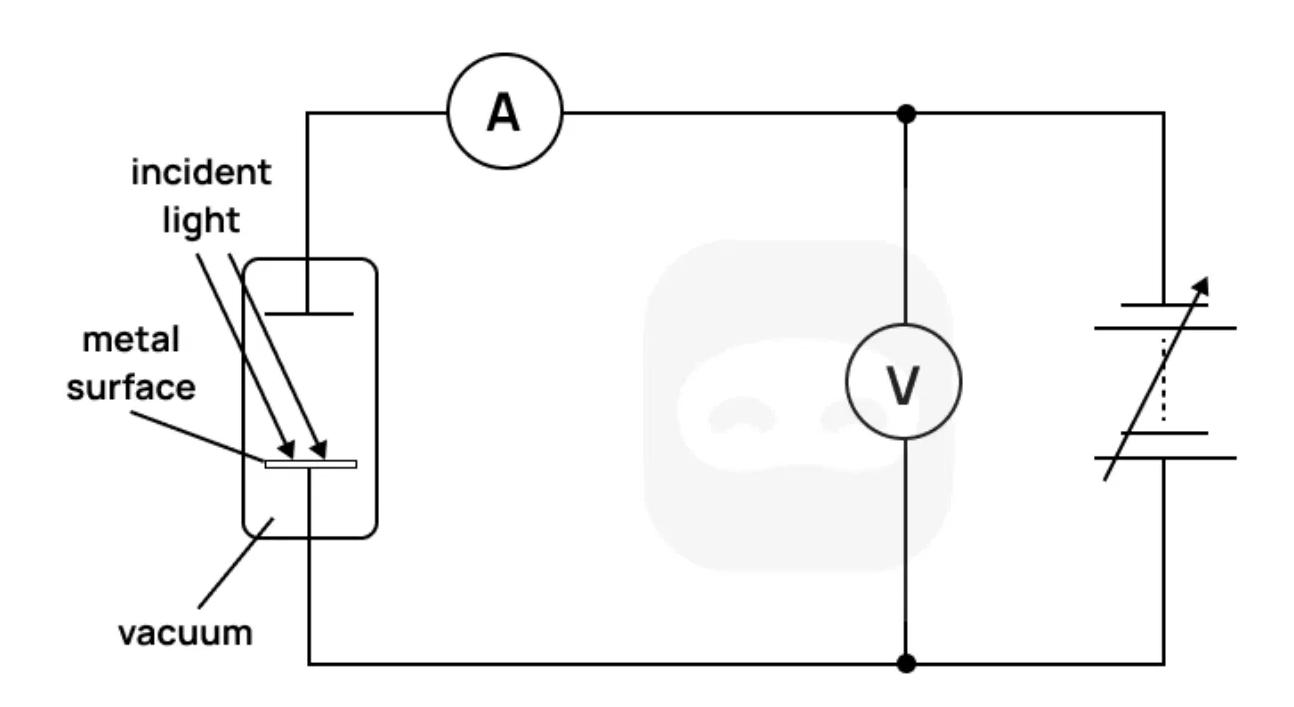
State the observation regarding the timing of emission from the photoelectric experiment that cannot be explained by the wave theory of light.
Explain how this observation supports the photon model of light.
Describe how the stopping voltage is determined in this experiment.
When light of frequency Hz is shone on a metal surface, electrons are emitted. The stopping potential is measured to be 0.85 V. Determine the work function of the metal in eV.
The intensity of the incident light is increased but its frequency remains the same. Discuss the effect of this change on the photoelectric current and the stopping potential.
Outline two assumptions of the photon model used to explain the photoelectric effect.
What is the unit of Planck's constant?
Which experiment demonstrated that light behaves as particles?
Which experiment provided direct evidence for the wave nature of electrons?
Which observation in Compton scattering provides evidence for the particle nature of light?
Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by proposing that light energy is quantized in packets called:
Which change would increase the maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect?
An electron beam is accelerated through a potential difference of . It is directed onto a crystal, producing a diffraction pattern with a first maximum at an angle of .
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons. (Use , , .)
Using Bragg’s law with , calculate the lattice spacing of the crystal.
Explain how the electron diffraction experiment provides evidence for the wave nature of matter.
Which of the following observations in the photoelectric effect provides evidence for the particle nature of light?