Practice A.4 Rigid body mechanics (HL only) with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A rotating platform in a physics lab has a moment of inertia and is initially rotating at . A student drops a lump of clay of mass onto the platform at a distance of from the axis. The clay sticks to the platform.
Calculate the moment of inertia of the clay relative to the axis of rotation.
Determine the new angular speed of the platform-clay system.
Calculate the change in rotational kinetic energy.
Explain how this experiment demonstrates angular impulse and its relation to angular momentum.
A yo-yo of mass and radius is released from rest and allowed to fall vertically while unwinding. If its moment of inertia is , what is the linear acceleration of its center of mass?
A plank of mass and length rests horizontally on two supports placed from each end. A person of mass walks from the center toward one end. At what distance from the center will the plank begin to tip?
A disc of moment of inertia spinning at angular velocity is placed on a horizontal surface with friction and allowed to roll without slipping. After some time, it transitions into pure rolling motion. What happens to its final angular velocity?
A pulley system consists of a solid disc (mass , radius ) mounted horizontally and free to rotate. A mass is suspended and allowed to fall, causing the pulley to rotate. What is the angular acceleration of the disc?
A flywheel rotates with an initial angular velocity of and comes to rest after 8.0 seconds due to a constant frictional torque. The moment of inertia of the flywheel is .
Calculate the angular acceleration of the flywheel.
Determine the frictional torque acting on the flywheel.
Calculate the total angle (in radians) through which the flywheel rotates before stopping.
Explain the relationship between the angular deceleration and the energy lost by the system.
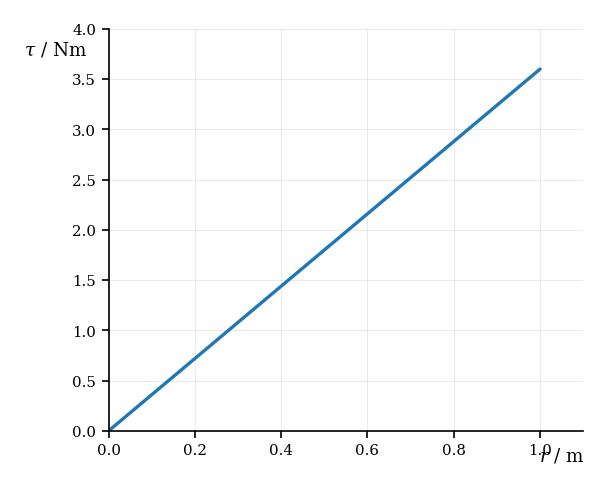
A student investigates the torque produced by applying varying forces at different distances from the pivot of a rigid beam. The following data were recorded:
| Distance from Pivot | Force Applied | Torque |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 3.6 | 0.72 |
| 0.4 | 3.6 | 1.44 |
| 0.6 | 3.6 | 2.16 |
| 0.8 | 3.6 | 2.88 |
| 1.0 | 3.6 | 3.60 |
The relationship between torque, force, and distance is given by:
where:
- is the torque,
- is the perpendicular distance from the pivot,
- is the applied force.
Identify two potential sources of error in the experiment and explain their impact on the measured torque.
Suggest two improvements to minimize these errors.
Using the graph provided, describe the trend in the data and explain how it supports the equation .
Suggest how the value of the applied force at a given distance could be determined graphically.
Using the data point , calculate the applied force . Show all your working.
If the uncertainty in is and the uncertainty in is , calculate the percentage uncertainty in for the same data point.
A billiard ball of radius and mass is struck by a horizontal cue stick at a height above the billiard table. The moment of inertia for a sphere is given by . The cue stick strikes the ball with a force during an interval .
Find an expression for the velocity of the ball after the strike.
Find an expression for the angular velocity of the ball after the strike.
Find the value of for which the ball will roll without slipping. Express your answer in terms of .
A rod of length and mass is pivoted at one end and released from rest in a horizontal position. What is its angular velocity when it reaches the vertical position?
A uniform beam of mass 20 kg and length 6.0 m is supported horizontally by two vertical ropes. One rope is 1.0 m from the left end and the other is 1.0 m from the right end. A 40 kg person stands 1.0 m from the left end. Take . What is the tension in the right rope?