- IB
- 2.2.9. Define the terms systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Practice 2.2.9. Define the terms systolic and diastolic blood pressure. with authentic IB Sports, exercise and health science (SEHS - Old) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Define systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Include the typical values for a healthy adult at rest.
Explain the physiological mechanisms that lead to changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure during exercise.
Analyse the data in the provided graph showing systolic and diastolic blood pressure at rest and during different intensities of exercise.
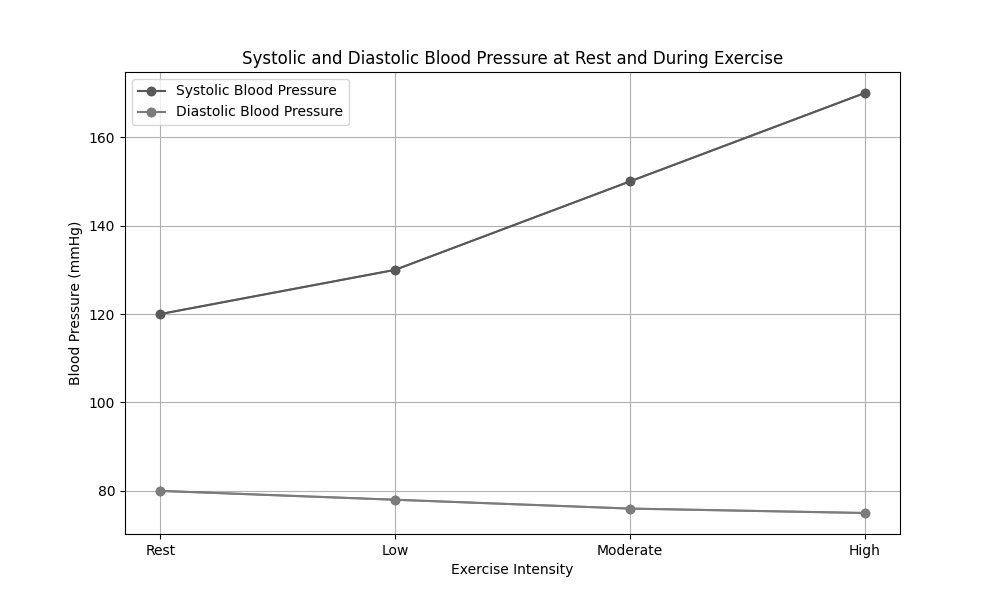
Discuss the potential health implications of abnormal blood pressure responses to exercise, such as excessively high systolic or diastolic blood pressure.
Where does blood exert the force measured as systolic blood pressure?
What does diastolic blood pressure measure?
What action of the cardiac muscle is responsible for the force of systolic pressure as measured on the walls of the main artery?
Which of the following best defines systolic blood pressure?
Predict the effect of a 100 m dash on a runner’s systolic and diastolic arterial pressure.
Define systolic arterial pressure.
Define systolic blood pressure.
Predict the effect of a 100 m sprint on a runner’s systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Explain the redistribution of blood during exercise.
Where does blood exert the force measured as systolic blood pressure?
What does systolic blood pressure measure?
Practice 2.2.9. Define the terms systolic and diastolic blood pressure. with authentic IB Sports, exercise and health science (SEHS - Old) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Define systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Include the typical values for a healthy adult at rest.
Explain the physiological mechanisms that lead to changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure during exercise.
Analyse the data in the provided graph showing systolic and diastolic blood pressure at rest and during different intensities of exercise.

Discuss the potential health implications of abnormal blood pressure responses to exercise, such as excessively high systolic or diastolic blood pressure.
Where does blood exert the force measured as systolic blood pressure?
What does diastolic blood pressure measure?
What action of the cardiac muscle is responsible for the force of systolic pressure as measured on the walls of the main artery?
Which of the following best defines systolic blood pressure?
Predict the effect of a 100 m dash on a runner’s systolic and diastolic arterial pressure.
Define systolic arterial pressure.
Define systolic blood pressure.
Predict the effect of a 100 m sprint on a runner’s systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Explain the redistribution of blood during exercise.
Where does blood exert the force measured as systolic blood pressure?
What does systolic blood pressure measure?