Practice S1.2 The nuclear atom with authentic IB Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Which of the following explains why high-resolution mass spectrometry can distinguish between and ?
Which statement best explains why isotopes of the same element may differ in physical properties but not chemical properties?
What is the symbol for an isotope with 17 protons and 18 neutrons?
Which property of isotopes is always the same?
Which statement correctly describes the relative mass and charge of a neutron?
What is the correct number of subatomic particles in the ion ?
The diagram below shows a simple apparatus used to investigate the properties of sodium chloride and carbon tetrachloride in both solid and molten states.
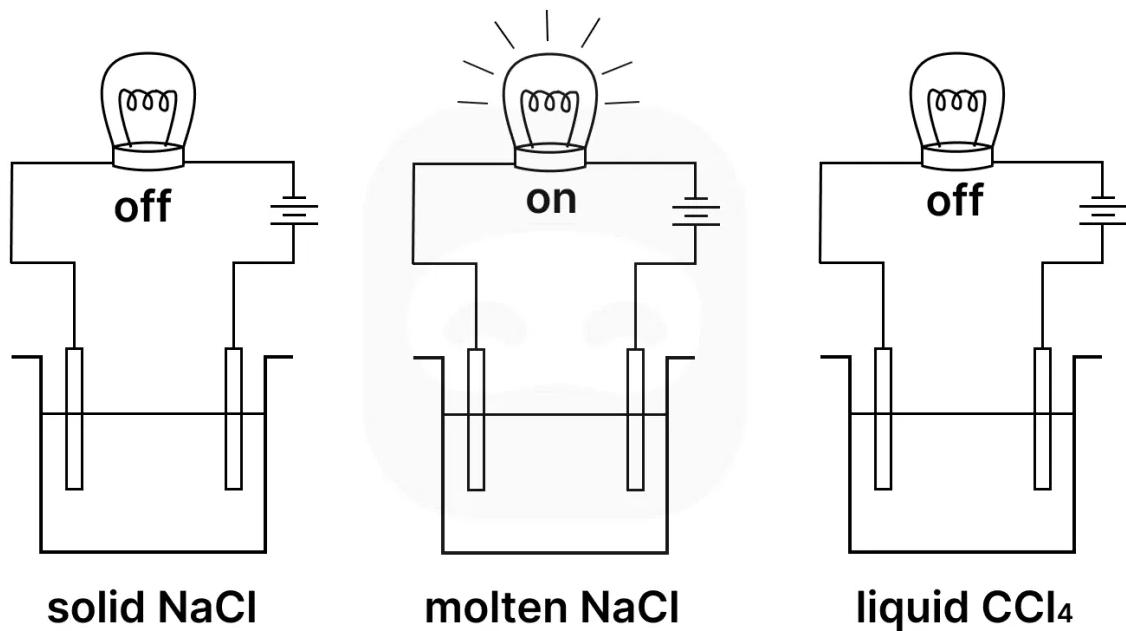
State the type of bonding present in sodium chloride and in carbon tetrachloride.
Explain why sodium chloride does not conduct electricity in the solid state but does when molten.
Suggest why carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity in any state.
Use the diagram and your knowledge of structure and bonding to deduce which substance(s) contain mobile ions.
State and explain the difference in melting point between sodium chloride and carbon tetrachloride.
Explain why carbon tetrachloride is a liquid at room temperature. Justify your answer based on its intermolecular forces.
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structure for the ion and a molecule
The diagram below shows the energy levels of the ion.
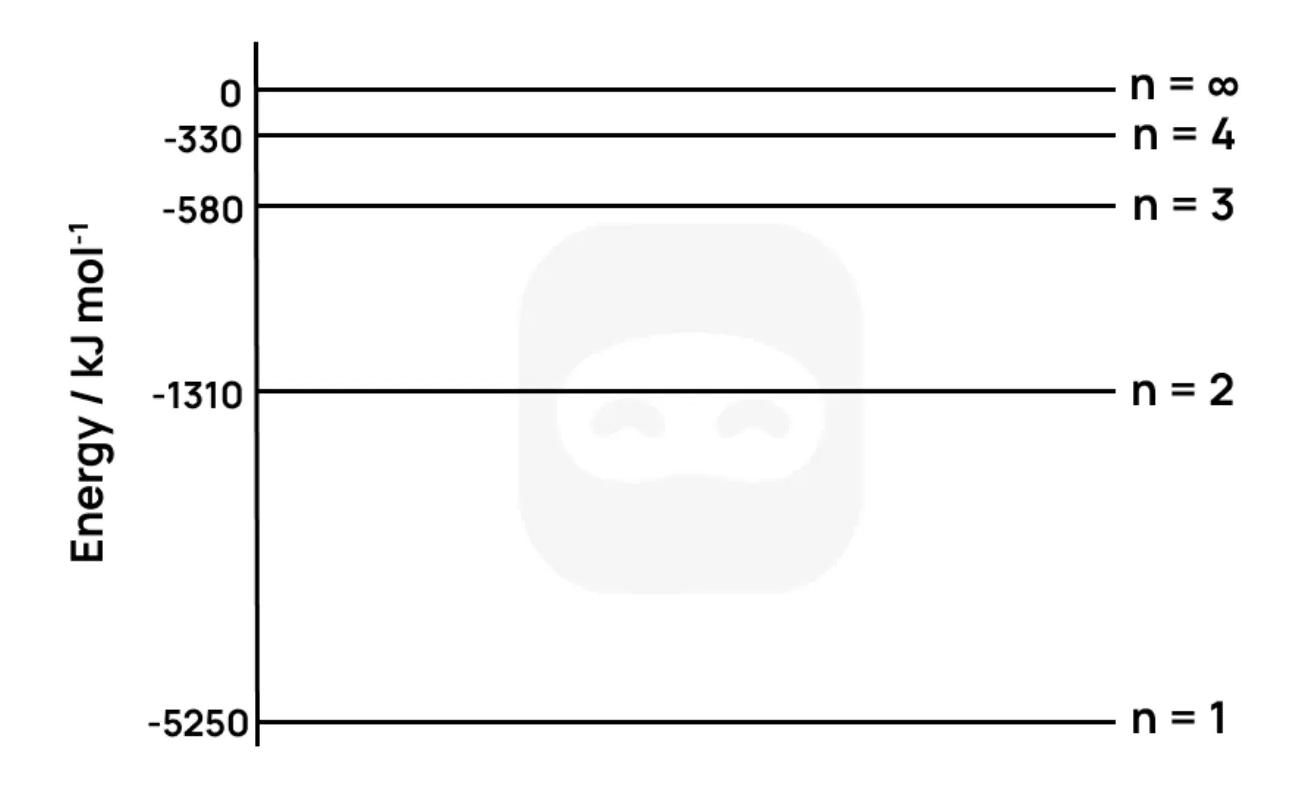
State what the energy value of represents for the ion.
Calculate the wavelength, in nm, of the photon emitted when an electron falls from to . (Planck’s constant , speed of light )
Determine the first ionization energy of the ion in .
Compare the energy required for the electron transitions from to for the ion and the H atom.
Sketch a diagram showing the emission spectrum for corresponding to transitions ending at (Lyman series), indicating the trend in line spacing.
Discuss why the emission lines converge at high frequencies, and how this convergence relates to ionization.
Which is correct for the following species?
A student is studying two isotopes of chlorine: and .
State the number of protons in both isotopes.
Deduce the number of neutrons in each isotope.
Explain why the chemical properties of these two isotopes are almost identical.