Practice R2.2 How fast? The rate of chemical change with authentic IB Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The experiment focuses on investigating the relationship between temperature and the rate of evaporation of three different volatile liquids: methanol, ethanol, and propan-1-ol.
Three identical Petri dishes are labelled A, B, and C, each containing 3.0 cm³ of a different alcohol: methanol (A), ethanol (B), propan-1-ol (C). Each dish is placed inside a temperature-controlled chamber (e.g. warm water bath or incubator) at 60 °C. A digital balance is used to measure mass loss after 5 minutes of heating.
The following data were collected:
| Alcohol | Initial mass / g | Final mass / g | Temperature / °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 2.38 | 0.62 | 60 |
| Ethanol | 2.40 | 1.15 | 60 |
| Propan-1-ol | 2.55 | 1.98 | 60 |
Calculate the average rate of evaporation of methanol in .
Describe the relationship between molecular size and evaporation rate based on the data.
Suggest why propan-1-ol evaporates more slowly than ethanol, despite being under identical conditions.
State the main intermolecular force present in alcohols and explain its origin.
Identify the functional group common to all three alcohols.
Draw a full structural formula of ethanol.
Sketch and label a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve for the ethanol sample at 60 °C. Indicate the activation energy for evaporation and the fraction of particles with enough energy to overcome it.
The reaction between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid forms a precipitate:
Describe a method to determine the rate of this reaction.
Suggest how temperature affects the time for the cross to disappear.
Explain this effect in terms of activation energy.
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes slowly at room temperature:
State one way to measure the rate of this reaction.
State how the rate of reaction changes as the reaction proceeds.
Explain your answer to part 2.
For the reaction between A and B, the rate is first order with respect to A and second order with respect to B. Which experiment would give the fastest rate?
| Experiment | [A] / | [B] / |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| 3 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 4 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
Several reactions of calcium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid are carried out at the same temperature.
Which reaction has the greatest rate?
| Concentration of | Surface area of same mass of | |
|---|---|---|
| A | higher | larger |
| B | lower | smaller |
| C | lower | larger |
| D | higher | smaller |
of large pieces of calcium carbonate are reacted with of at . The volume of produced against time was plotted and curve Q was produced on the graph shown.
Which of the following changes would produce curve P?
Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when is added to excess ?
Ammonia is formed by the Haber process:
The diagram below shows the energy profile of this reaction.
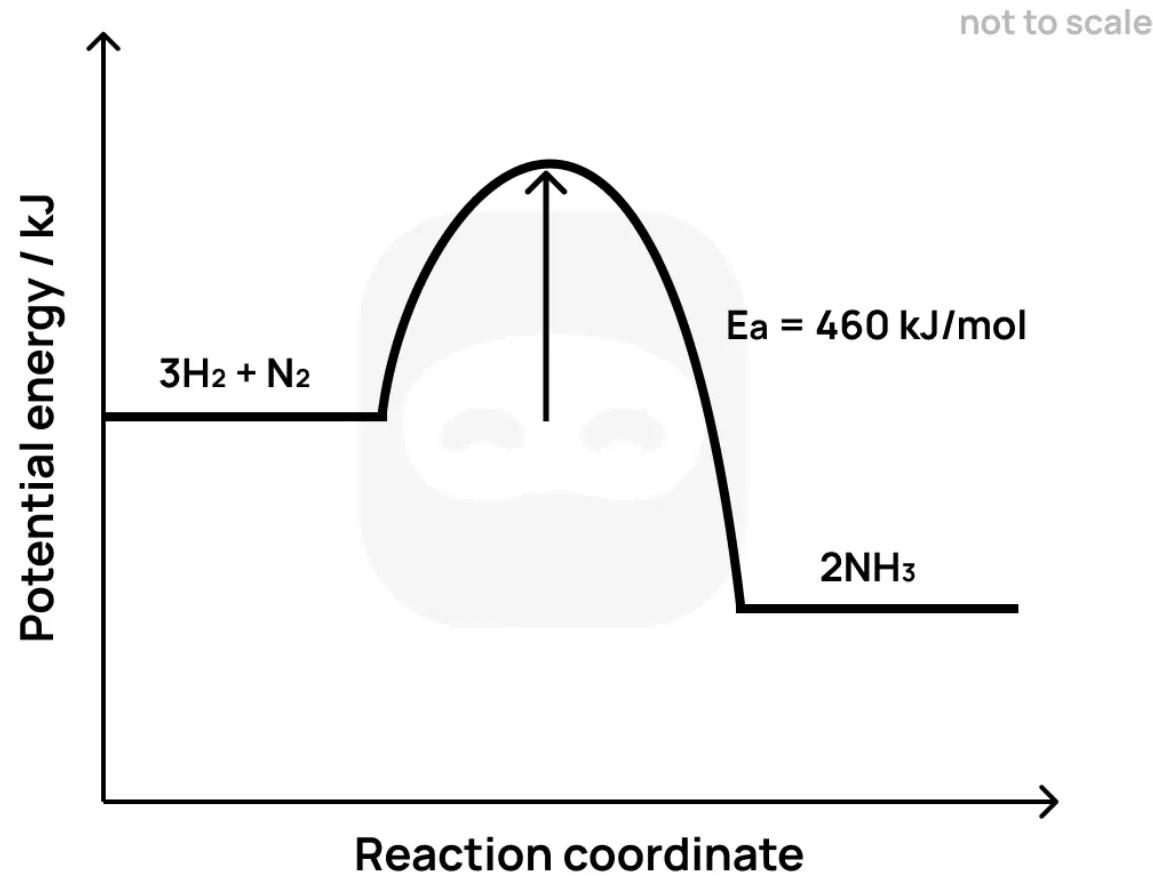
State what is meant by the term activation energy.
Identify whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic and justify your answer using the diagram.
Suggest one reason why a high temperature is required for this reaction to proceed at a practical rate.
Explain how the use of a catalyst would affect the energy profile diagram.
The Haber process is a reversible reaction. State and explain one condition used in industry to increase the yield of ammonia.
Copper catalyses the reaction between zinc and dilute sulfuric acid.
Why does copper affect the reaction?
Which of the following statements about a proposed reaction mechanism are true?
I. The rate-determining step is the slowest step.
II. The sum of the elementary steps must give the overall balanced equation.
III. Intermediates appear in the overall rate equation.