Practice D3.2 Inheritance with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
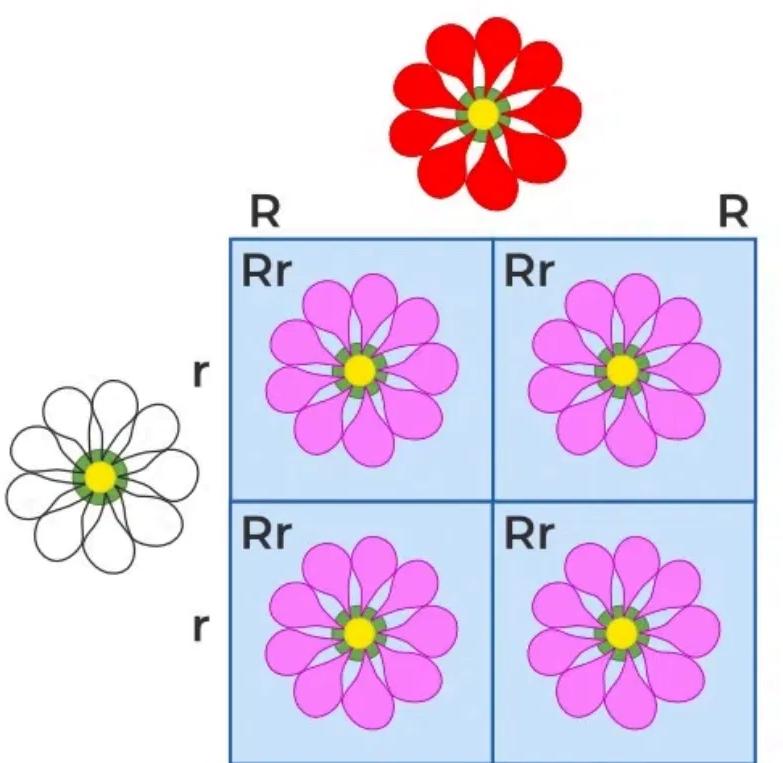
The Punnett square shown represents a cross between a red-flowered plant (RR) and a white-flowered plant (rr), producing all heterozygous offspring (Rr) with pink flowers.
If one of these pink-flowered (Rr) offspring is self-pollinated, what would be the expected phenotypes of the second-generation (F2) offspring and in what proportion?
In a pedigree, two phenotypically normal parents have an affected child for a rare disorder. What conclusion is most likely?
Why can a male never be a carrier for an X-linked recessive condition?
A lizard changes color based on temperature but does not pass this change to offspring. What does this represent?
Which step is essential for a controlled cross in flowering plants?
Which inheritance pattern best describes a trait that is expressed in males who inherit a single copy of the allele, whereas females can carry the allele without expressing the trait?
In Mirabilis jalapa, red flowers (RR) crossed with white (WW) produce pink (RW) offspring. Which best explains why not all RW plants are the same shade of pink?
Which of the following individuals would have the greatest number of expressed traits from heterozygous genotypes?
Which of the following statements is accurate about an individual with genotype ?
In a pedigree chart, which pattern suggests a recessive autosomal disorder?