Practice D4.3 Climate change with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
What human action could have an impact on the whole biosphere?
What is the impact of lower ocean pH on coral reefs?
Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback cycle related to global warming?
Which characteristic of water vapour classifies it as a greenhouse gas?
Which statement about the greenhouse effect is true?
Which substances increase the greenhouse effect the most?
Which activity directly contributes the most to recent increases in atmospheric CO₂ concentrations?
Researchers studied the impact of increased atmospheric on global primary production and nutrient density of plants.
Image A maps the rate of GPP (gross primary production) change with rising .
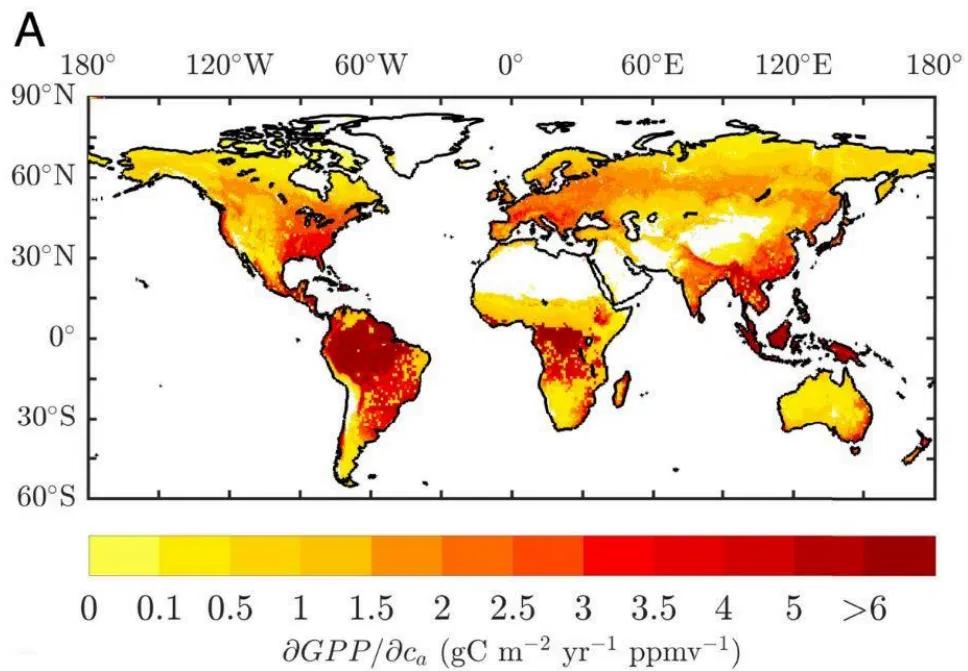
Image B shows this GPP response across major biomes.
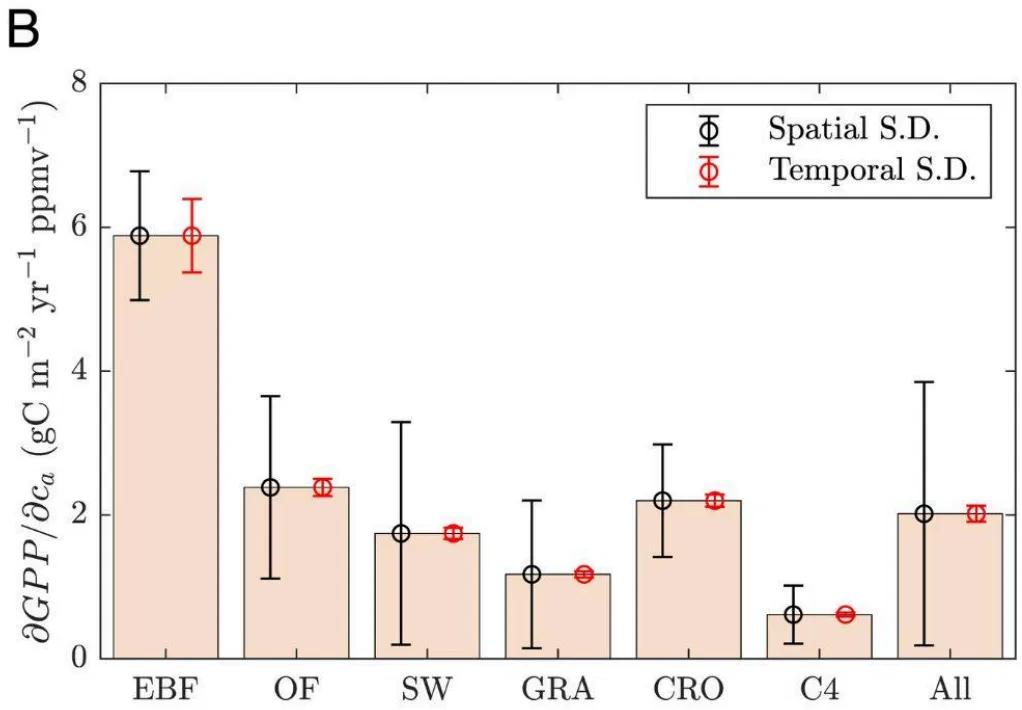
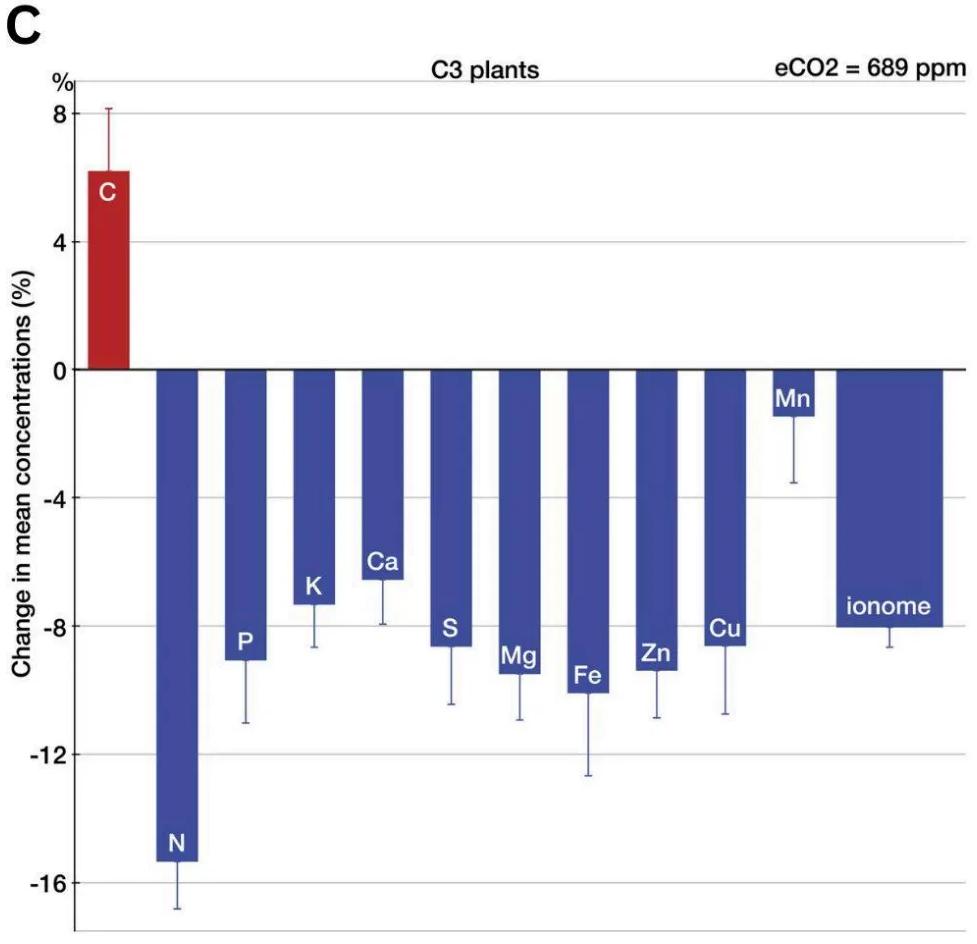
Image C shows changes in essential nutrient concentrations in crops grown at elevated CO2 (689 ppm).
Using Image A, identify two regions with the highest rates of carbon accumulation through GPP.
Explain how GPP data reflect variations in primary production across biomes, using Image B.
Based on Image C, explain how declining plant nutrient content could reduce secondary production in food webs.
Suggest how this might affect trophic efficiency and biomass transfer in ecosystems.
Explain why the CO₂ fertilization effect, although increasing GPP, might contribute to positive feedback in the climate system over time. Refer to at least two figures.
Describe one scenario in which increased plant growth might shift to a net carbon source.
The figure shows the effect of increasing atmospheric on ocean pH and the availability of carbonate ions, which are essential for the formation of calcium carbonate shells and skeletons in marine organisms such as corals and mollusks.
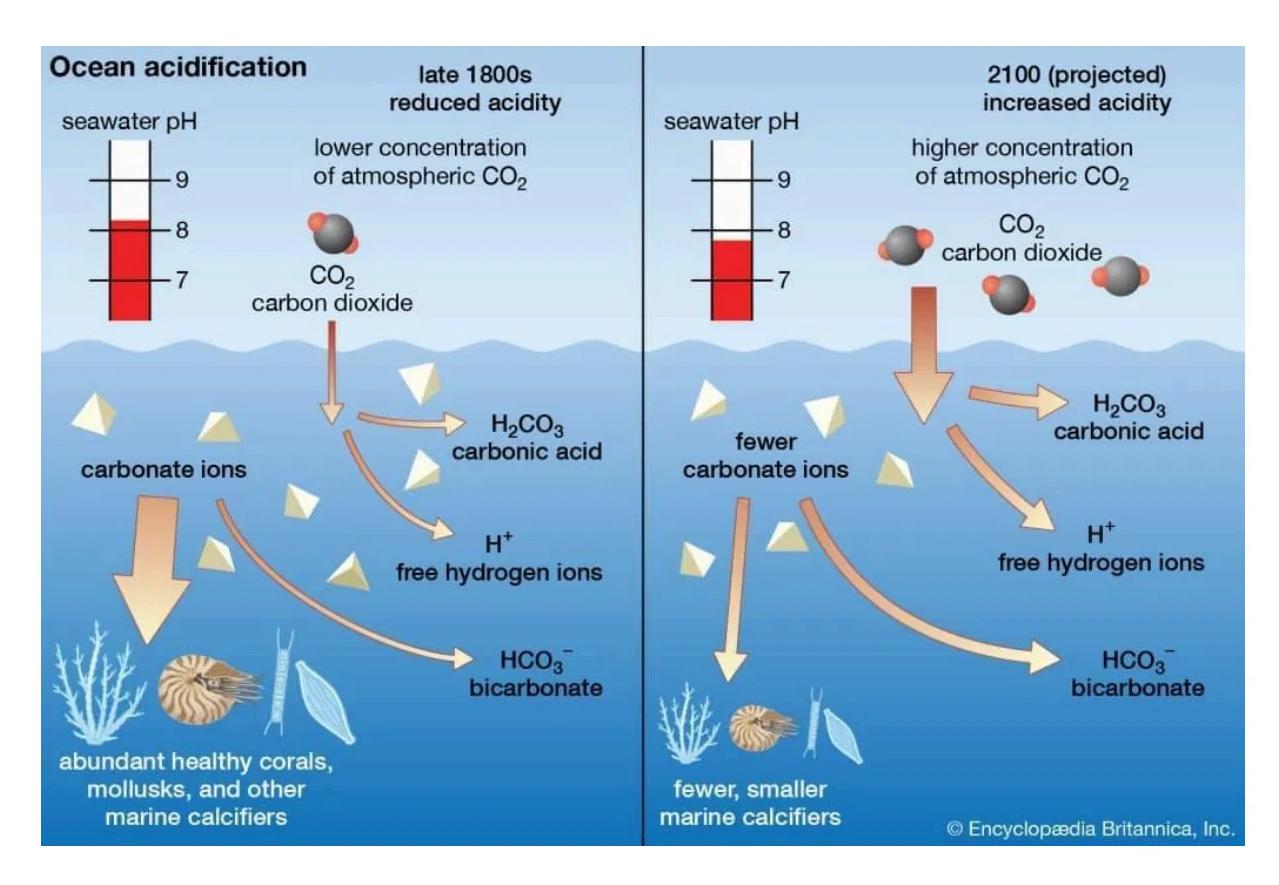
Identify the compound that forms when carbon dioxide dissolves in seawater.
Compare the pH levels and availability of carbonate ions in the late 1800s and the projected 2100 conditions.
Explain why an increase in atmospheric causes a reduction in marine carbonate ion concentration.
Outline the correlation between atmospheric CO and methane concentrations since the industrial revolution and global temperatures.