Practice 2.2 – Forces with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
This question is about the motion of a bicycle. A cyclist is moving up a slope that is at an angle of 19° to the horizontal. The mass of the cyclist and the bicycle is 85 kg.
Calculate the component of the weight of the cyclist and bicycle parallel to the slope.
Calculate the normal reaction force on the bicycle from the slope.
At the bottom of the slope the cyclist has a speed of 5.5 m s⁻¹. The cyclist stops pedalling and applies the brakes which provide an additional decelerating force of 250 N. Determine the distance taken for the cyclist to stop. Assume air resistance is negligible and that there are no other frictional forces.
A uniform rod PQ of weight is attached to a vertical wall at end P by a hinge. A force of magnitude acts on the rod at end Q as shown such that the rod is in equilibrium.
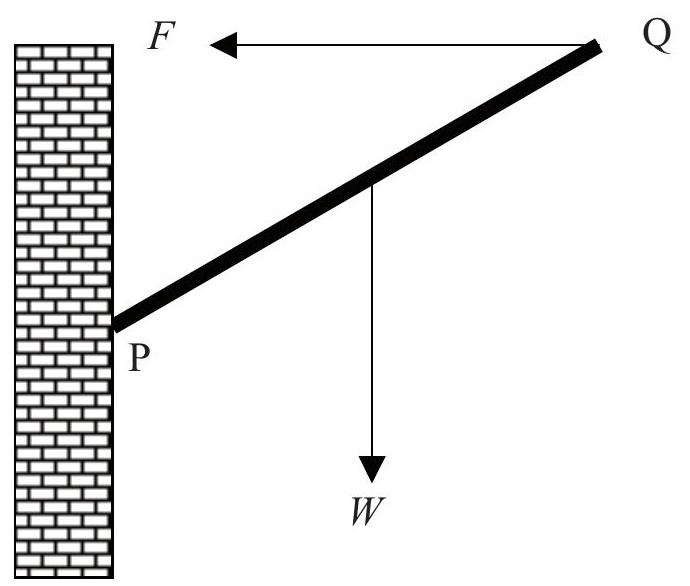
Which of the following diagrams best shows the correct direction of the reaction force at the hinge?
A motorcyclist is cornering on a curved race track.
Which combination of changes of banking angle and coefficient of friction between the tyres and road allows the motorcyclist to travel around the corner at greater speed?
A force directed up a plane, of angle to the horizontal, prevents a block of mass from slipping down, as shown in the diagram.
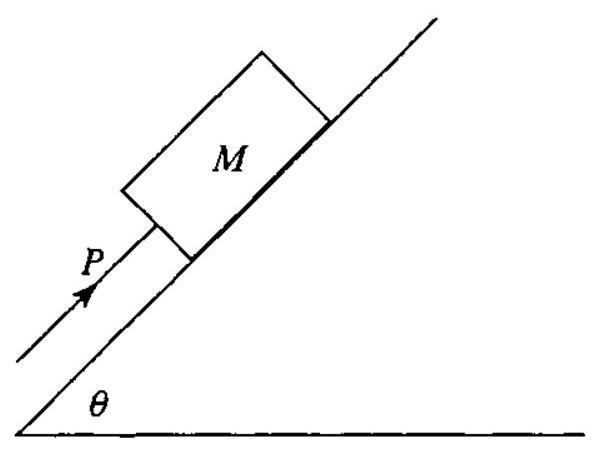
If the coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is , the minimum magnitude of force required, is
An object of mass rests on a horizontal plane. The angle that the plane makes with the horizontal is slowly increased from zero. When , the object begins to slide. What are the coefficient of static friction and the normal reaction force of the plane at ?
A football is kicked with an initial velocity at an angle to the horizontal and reaches the ground seconds later.
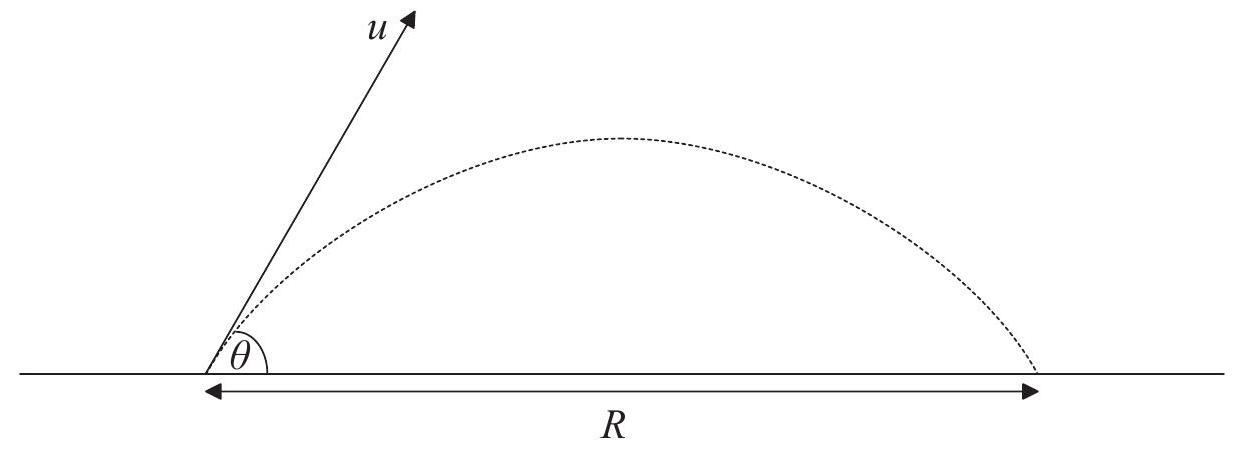
Ignoring air resistance what is the range of the football?
An object of mass 8.0 kg is falling vertically through the air. The drag force acting on the object is 60 N. What is the best estimate of the acceleration of the object?
Which of the following is a fundamental SI unit?
The masses and weights of different objects are independently measured. The graph is a plot of weight versus mass that includes error bars.
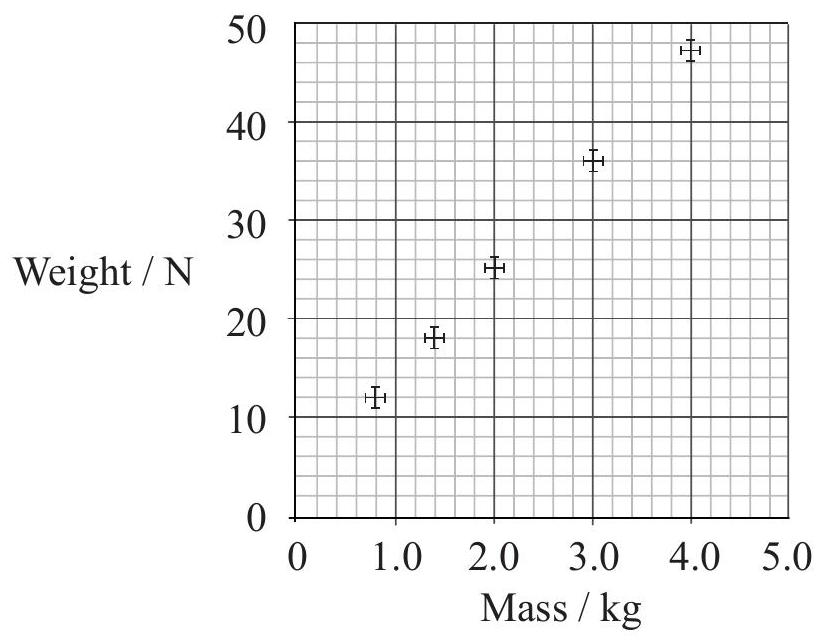
These experimental results suggest that
Two forces of magnitudes 7 N and 5 N act at a point. Which one of the following is not a possible value for the magnitude of the resultant force?