- IB
- S3.2 Functional groups: Classification of organic compounds
Practice S3.2 Functional groups: Classification of organic compounds with authentic IB Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A section of an organic compound is shown.
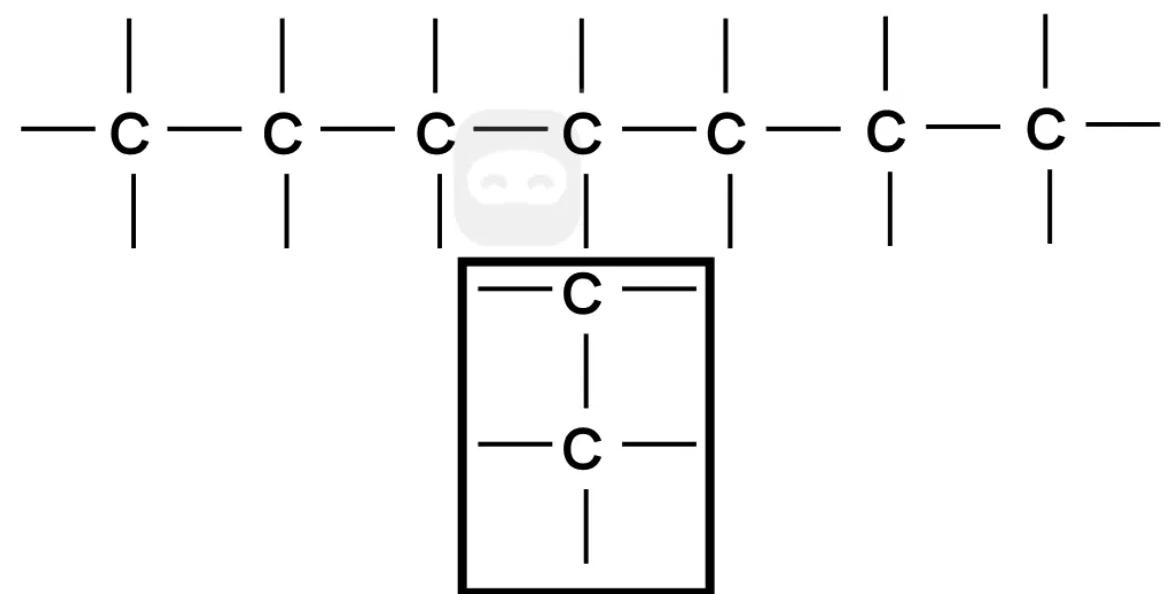
Which is the correct substituent name for the branch section?
Which compound can be oxidised when heated with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
The full structural formula of an organic compound is shown.
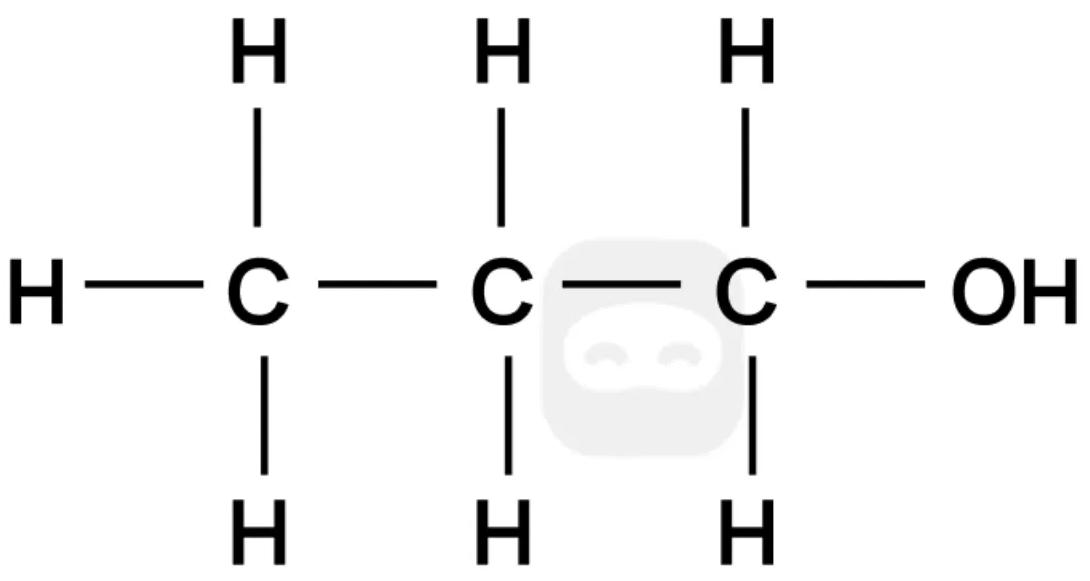
Which of the following is an isomer of the compound?
Which statements are correct for the molecule shown?
I. The molecule has a chiral centre
II. The molecule rotates the plane of plane-polarised light
III. The IUPAC name of the molecule is butan-1-ol
Which of the following structures represents an ester with molecular formula ?
The diagram shows a reaction which occurs in the production of a polymer.
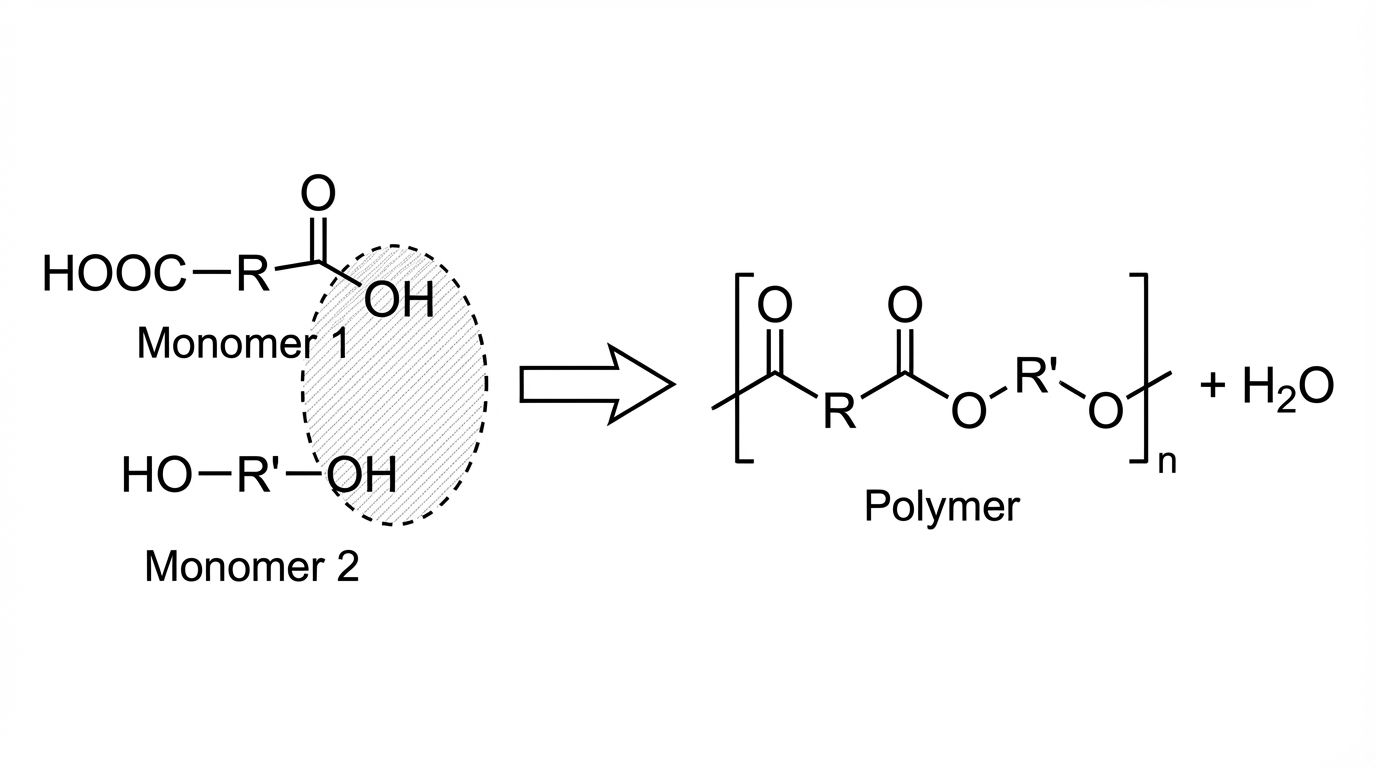
Which type of reaction is this?
What type of reaction is represented by the following equation?
Which of the following compounds is not an isomer of ?
Which technique can be used to distinguish between the two isomers, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol?
A student is analyzing samples of different organic compounds in a school laboratory to identify their functional groups, which determine their chemical properties.
Define the term functional group in the context of organic chemistry.
Identify the functional group present in alcohols.
Name the functional group present in carboxylic acids and draw its displayed structure.