Practice 1.2 The mole concept with authentic IB Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
When this equation is balanced correctly, the coefficient, , for is
The temperature in Kelvin of of an ideal gas is doubled and its pressure is increased by a factor of four. What is the final volume of the gas?
28 g of metal M reacted with 8 g of oxygen to form an oxide with the formula MO . What is the relative atomic mass of M ?
Two 1.00 dm3 containers A and B each contain 2.00 g of the gas indicated at 25.0°C 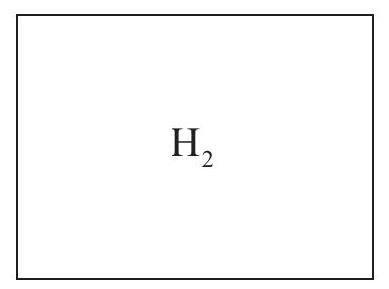 A
A 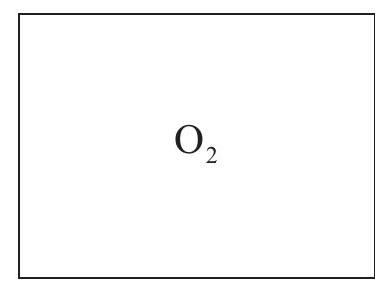 B
B
Calculate the pressure in container B.
Deduce without calculation whether the pressure in A is higher or lower than container B and explain your answer.
Which statement about the kinetic theory is not correct?
A student was asked to make some copper(II) sulfate-5-water (CuSO₄·5H₂O) by reacting copper(II) oxide (CuO) with sulfuric acid.
Calculate the molar mass of copper(II) sulfate-5-water.
Calculate the amount (in mol) of copper(II) sulfate-5-water in a 10.0 g sample.
Calculate the mass of copper(II) oxide needed to make this 10.0 g sample.
5.0 cm³ of 2.00 mol dm⁻³ sodium carbonate solution, , was added to a volumetric flask and the volume was made up to 500 cm³ with water. What is the concentration, in mol dm⁻³, of the solution?
What is the empirical formula of a hydrocarbon with 75 % carbon and 25 % hydrogen by mass?
Hydrogen and chlorine react according to the equation above. What will be the result of the reaction of 2.0 moles of and 1.5 moles of ?
At which temperature, in K , assuming constant pressure, is the volume of a fixed mass of gas at doubled?