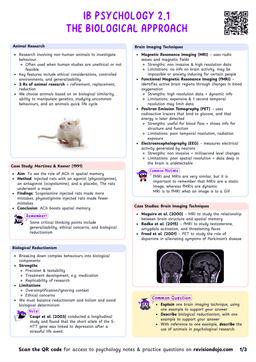
Correlation vs Causation
Correlation
- Correlation describes a statistical relationship between two variables.
- When one variable changes, the other tends to change in a predictable way.
Height and Weight
- Positive Correlation: Taller people tend to weigh more.
- As height increases, weight tends to increase.
Hours Studied and Test Scores
- Positive Correlation: Students who study more hours tend to score higher on tests.
- As study time increases, test scores tend to increase.
Correlation does not imply that one variable causes the other to change.
Causation
- Causation means that one variable directly influences another.
- A change in one variable causes a change in the other.
Causation: A relationship where one variable directly influences another, causing a change in the second variable.
Smoking and Lung Cancer
- Causal Relationship: Smoking causes lung cancer.
- The chemicals in cigarettes damage lung tissue, leading to cancer.
Alcohol Consumption and Reaction Time
- Causal Relationship: Alcohol slows reaction time.
- Alcohol affects the central nervous system, reducing alertness.
Causation requires evidence that one variable directly influences the other.
Key Differences Between Correlation and Causation
- Directionality: Correlation does not specify which variable influences the other, whereas causation identifies a clear direction of influence.
- Third Variables: Correlation can be influenced by a third variable that affects both variables, whereas causation rules out third variables as the primary cause.
- Predictability vs. Explanation: Correlation allows for prediction but does not explain why the relationship exists, whereas causation provides an explanation for the relationship.
The Third Variable Problem
If ice cream consumption and crime both increase in the summer, someone may infer that ice cream consumption causes crime.
However, both variables may increase due to the warmer weather.
Thus, weather is the third variable in this situation.
Think of correlation as two lines rising together on a graph, while causation is like one domino knocking over another.
Establishing Causation
- To establish causation, researchers use experimental methods.
- This involves manipulating one variable (the independent variable ) and observing its effect on another variable (the dependent variable).
Drug Trials
- Researchers test a new drug by giving it to one group and a placebo to another.
- If the drug group shows improvement, researchers can infer causation.
When Experiments Aren't Possible
- In some cases, experiments are not ethical or practical.
- Researchers rely on correlational studies to identify relationships.
Childhood Trauma and Mental Health
- Researchers cannot ethically expose children to trauma.
- Correlational studies examine the relationship between trauma and mental health outcomes.
Why Correlation is Still Valuable
- Prediction: Correlation allows researchers to predict outcomes. For example, knowing that exercise correlates with lower stress can inform health recommendations.
- Hypothesis Generation: Correlational studies help generate hypotheses for future research. Researchers can test these hypotheses in experimental studies.
- Ethical Considerations: Correlation is often the only option when experiments are unethical or impractical.
Reflection
- Can you explain the difference between correlation and causation?
- Why is correlation valuable in psychological research?
- How can researchers avoid the trap of assuming correlation implies causation?