- IB
- Question Type 3: Finding the quartiles using the cumulative frequency graph
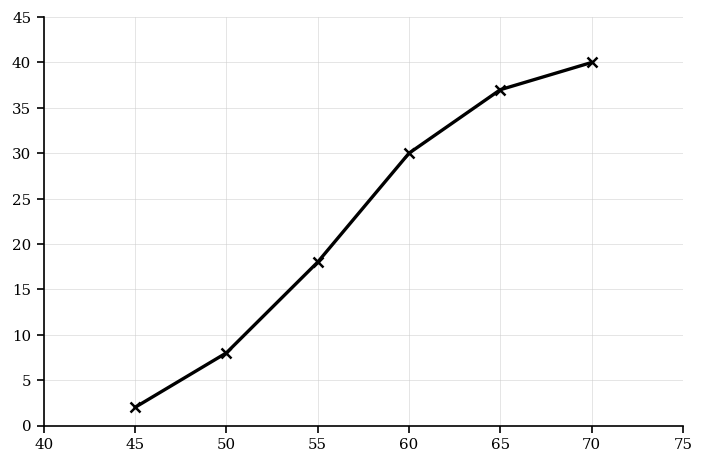
Heights (cm) of 48 seedlings are displayed with a cumulative frequency graph through the points below.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency graph):
| Upper height (cm) | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 54 | 4 |
| 58 | 12 |
| 62 | 24 |
| 66 | 34 |
| 70 | 42 |
| 74 | 48 |
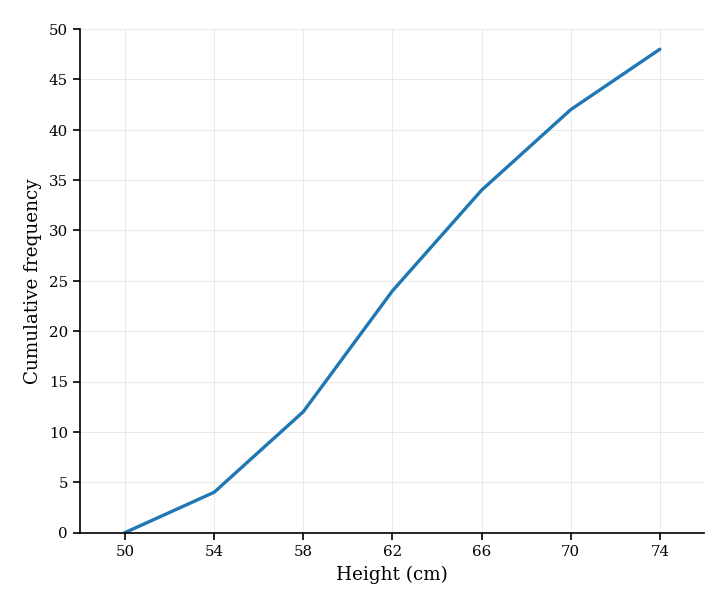
Estimate , median, , and the IQR. Give answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
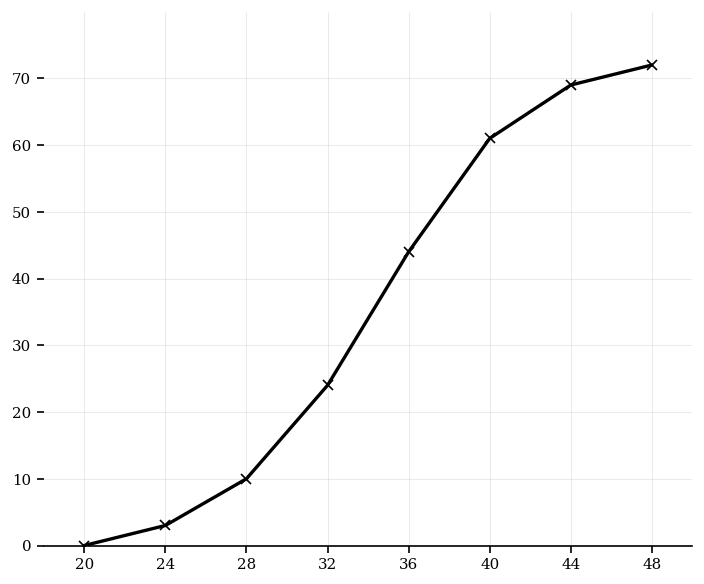
[5]Leaf lengths (cm) for 60 leaves were grouped and a cumulative frequency curve was drawn through the points below.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper length (cm) | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 14 |
| 8 | 30 |
| 10 | 44 |
| 12 | 54 |
| 14 | 60 |
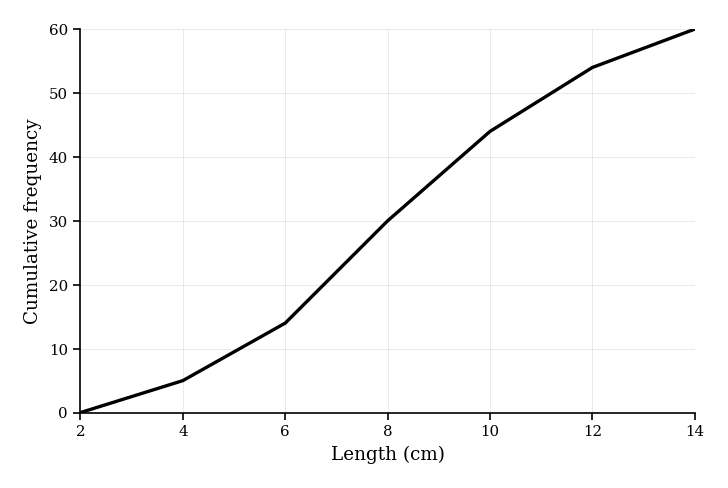
Estimate the interquartile range (IQR). Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
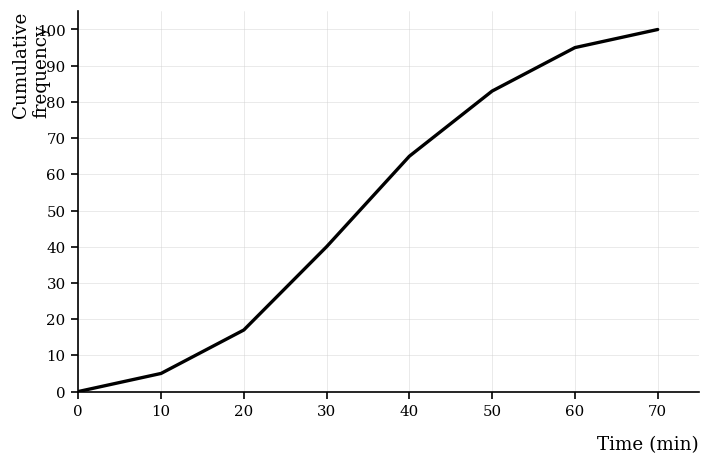
[5]The cumulative frequency graph of test scores (out of 60) is drawn by plotting the points below and joining them with straight segments.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper score | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 10 | 4 |
| 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 20 |
| 40 | 32 |
| 50 | 42 |
| 60 | 50 |
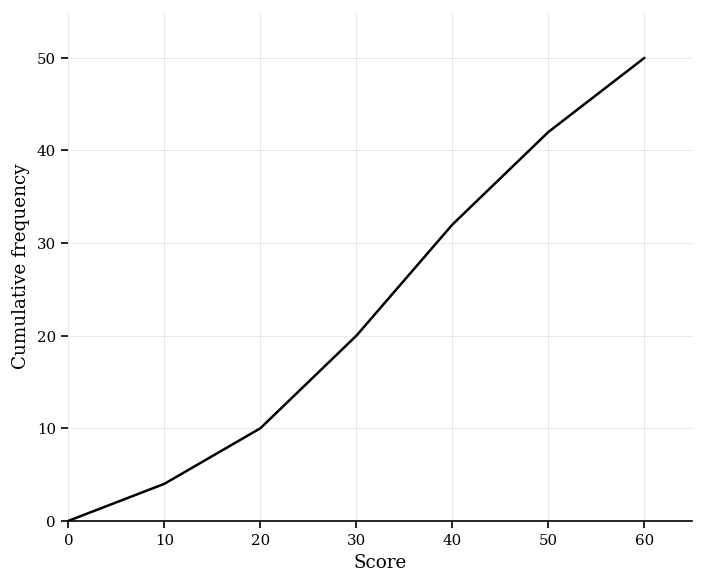
Estimate , the median, , and the interquartile range (IQR). Give answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
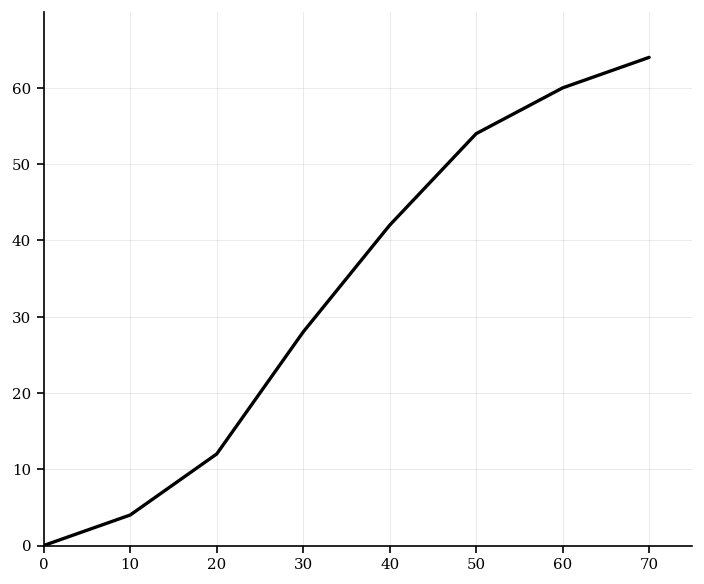
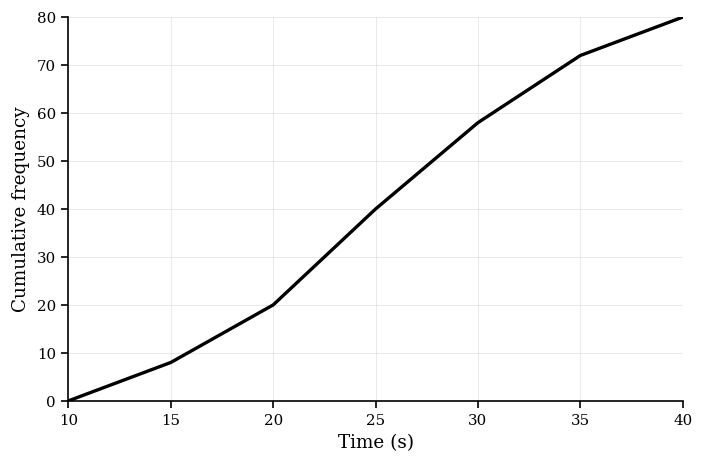
[6]A cumulative frequency graph for 50 task completion times (minutes) includes a zero-frequency class. The graph connects the points below with straight line segments.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency graph):
| Upper time (min) | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 5 | 6 |
| 10 | 20 |
| 12 | 20 |
| 20 | 40 |
| 30 | 50 |
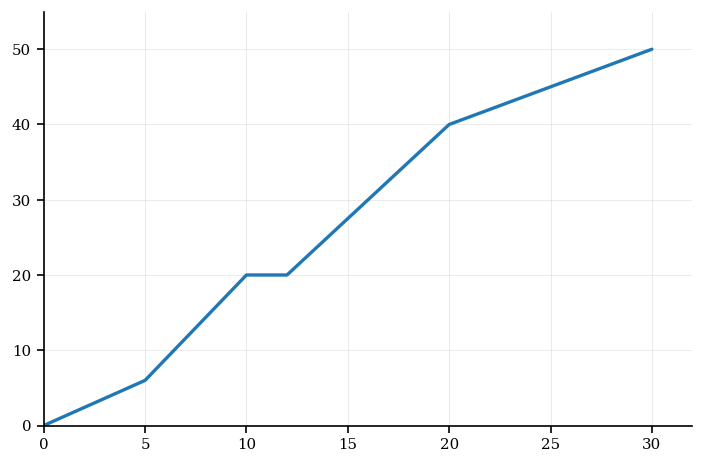
Estimate the median and the interquartile range (IQR). Give your answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
[7]Reaction times (ms) for 200 participants are summarized by the cumulative frequency curve through the points below.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper time (ms) | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 150 | 8 |
| 200 | 30 |
| 250 | 80 |
| 300 | 140 |
| 350 | 178 |
| 400 | 194 |
| 450 | 200 |
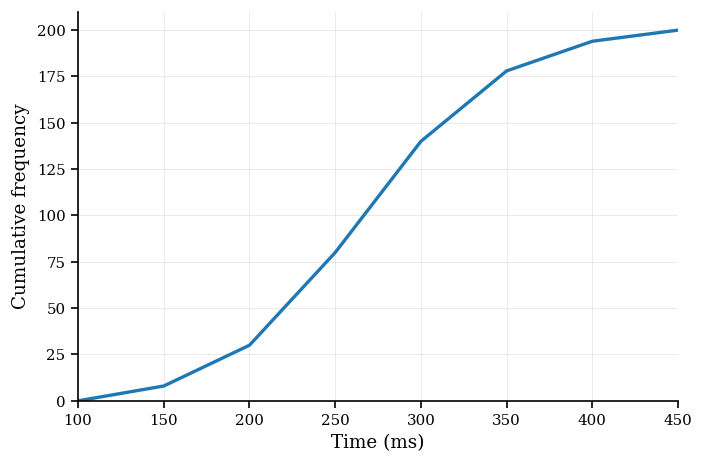
Estimate the median and the IQR. Give answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
[6]The cumulative frequency graph for car speeds (km/h) is based on unequal class widths and passes through the points below.
Data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper speed (km/h) | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 120 | 8 |
| 130 | 20 |
| 150 | 50 |
| 170 | 75 |
| 200 | 90 |
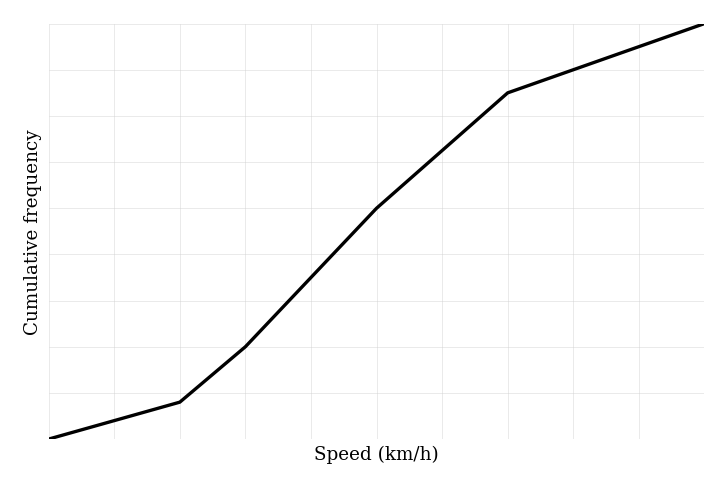
Estimate , the median, , and the IQR. Give answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
[9]Two classes sat the same test. Their cumulative frequency graphs are summarised by the points below.
Class A data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper mark | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 20 | 8 |
| 30 | 22 |
| 40 | 40 |
| 50 | 52 |
| 60 | 60 |
Class B data (points on the cumulative frequency curve):
| Upper mark | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|
| 20 | 5 |
| 30 | 18 |
| 40 | 36 |
| 50 | 54 |
| 60 | 60 |
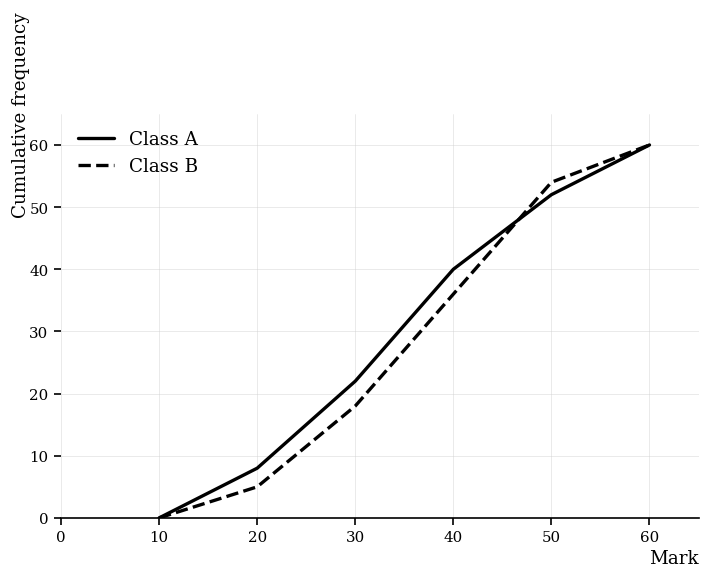
For each class, estimate the IQR, then state which class has the larger IQR. Give answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
[8]