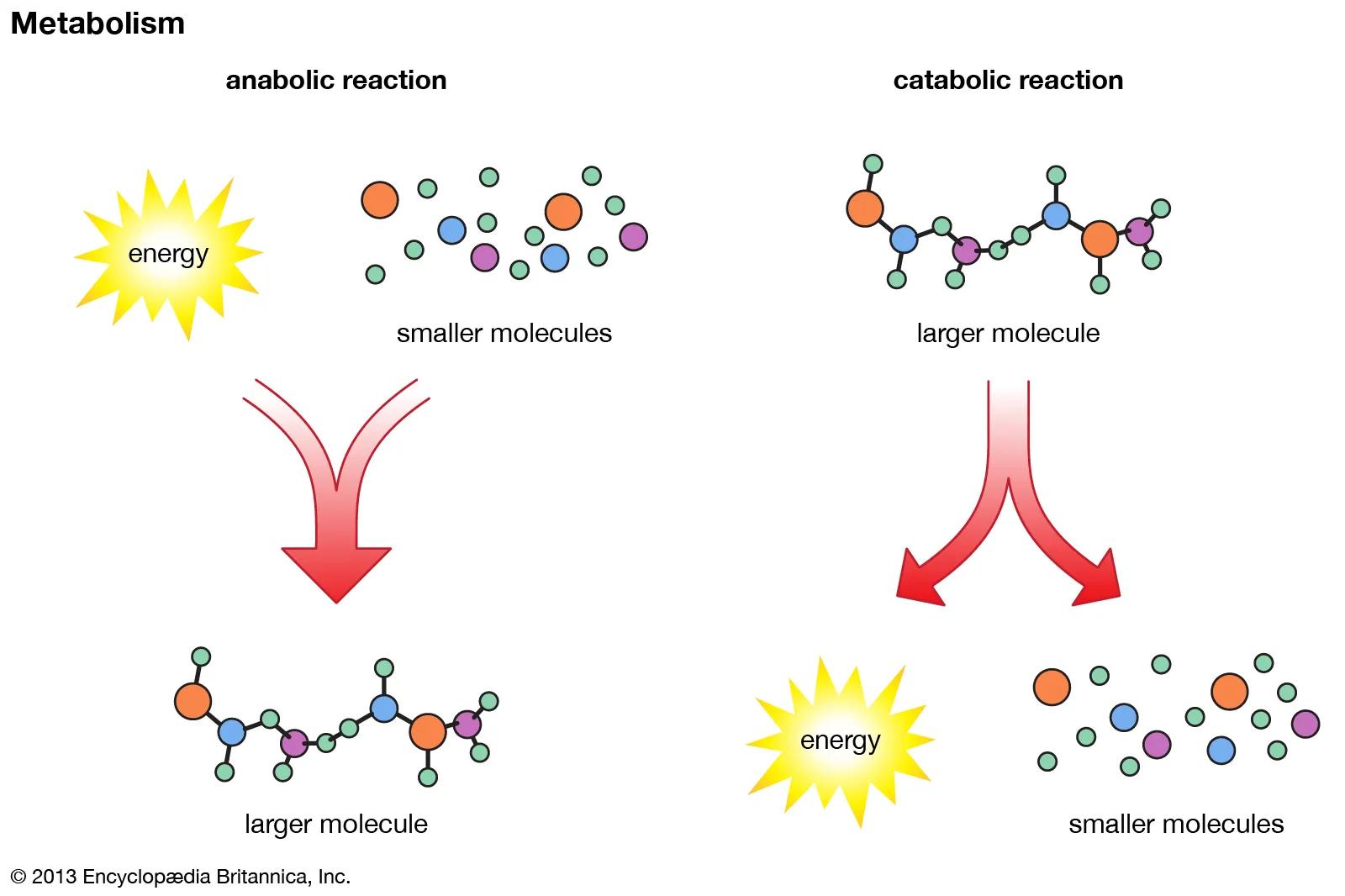
Anabolic and Catabolic Reactions
- Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism, divided into two categories:
- Anabolic reactions: Build larger molecules from smaller ones, requiring energy.
- Catabolic reactions: Break down larger molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy.
Anabolic Reactions: Building Up
Anabolic Reactions
Anabolic reactions are metabolic processes in which smaller molecules are built into larger, more complex molecules using energy.
- Anabolic reactions create complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
- These reactions are often condensation reactions, where water is a byproduct.
- Below are some examples of anabolic reactions;
Protein Synthesis
- Amino acids are linked together by ribosomes to form polypeptides.
- This process occurs through condensation reactions, where a water molecule is released for each peptide bond formed.
- The polypeptides fold into functional proteins, essential for cellular structure and function.
- Insulin, a protein hormone, is synthesized by linking amino acids in a specific sequence.
- This process is critical for regulating blood sugar levels.
Glycogen Formation
- Glycogen is a polysaccharide stored in liver and muscle cells.
- It is formed by linking glucose molecules through condensation reactions.
- Enzymes like glycogen synthase catalyze the formation of α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds, creating a branched structure.
- After a meal, excess glucose is converted into glycogen for storage.
- This process ensures a readily available energy source during fasting or exercise.
Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is an anabolic process where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- This process occurs in the chloroplasts and requires light energy, which is captured by chlorophyll.
- The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which are used in the Calvin cycle to synthesize glucose.
Remember, anabolic reactions require energy, often in the form of ATP or light (as in photosynthesis).
Catabolic Reactions: Breaking Down
Catabolic reactions
Catabolic reactions are metabolic processes in which larger molecules are broken down into smaller molecules, releasing energy in the process.
- Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
- These reactions often involve hydrolysis, where water is used to break bonds.
- Below is an example of a catabolic reaction:
- Remember, catabolic means breaking down.
- Remember it as "cat" as in "cutting."
Digestion of Macromolecules
- Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are broken down into their monomers during digestion.
- Enzymes like proteases, amylases, and lipases catalyze these reactions.
- For example, proteases break down proteins into amino acids, while amylases convert starch into glucose.
In the small intestine, pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into maltose, which is further hydrolyzed into glucose by maltase.
Cellular Respiration
- Cellular respiration is a catabolic process where glucose is oxidized to produce ATP.
- This process occurs in three stages:
- Glycolysis: Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH.
- Krebs Cycle: Pyruvate is further oxidized in the mitochondria, generating ATP, NADH, and FADH₂.
- Electron Transport Chain: NADH and FADH₂ donate electrons, driving ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation.
Unlike Anabolic reactions, Catabolic reactions release energy, which is often captured in the form of ATP to power cellular processes.
Don’t confuse hydrolysis and condensation. Hydrolysis breaks bonds using water (catabolic), while condensation forms bonds and releases water (anabolic).
Why Anabolism and Catabolism Matter
- Growth and Repair: Anabolism builds proteins and other macromolecules for tissue growth and repair.
- Energy Production: Catabolism provides ATP for cellular activities.
- Homeostasis: The balance between anabolism and catabolism maintains stable internal conditions.
- How does the balance between anabolic and catabolic reactions relate to homeostasis?
- Can disruptions in this balance lead to diseases like obesity or muscle wasting?
- What is the main difference between anabolic and catabolic reactions?
- Give an example of a condensation reaction and a hydrolysis reaction.
- How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration interconnected?
- If an enzyme is involved in the breakdown of glucose, what type of reaction is it most likely involved in