Practice A2.3 Viruses (HL) with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
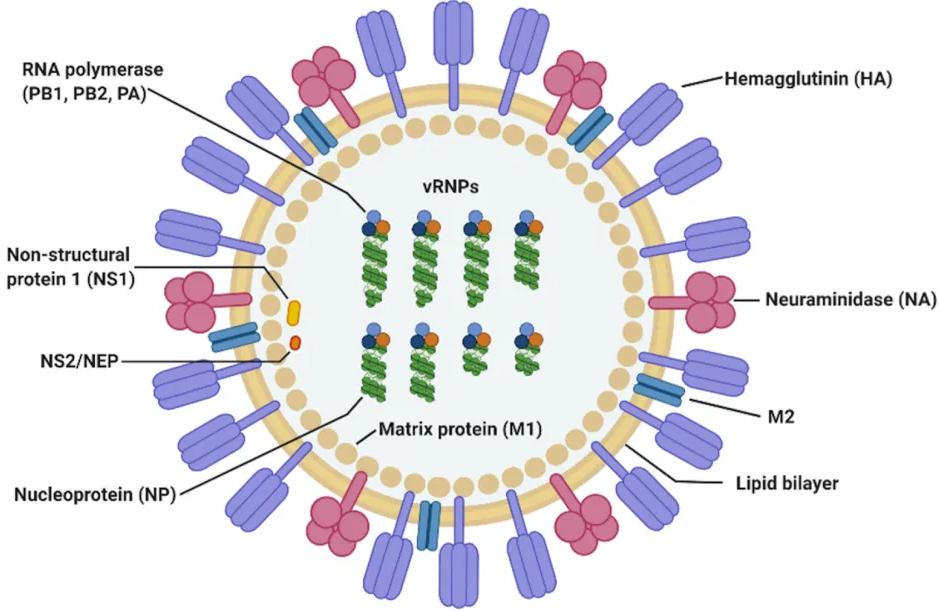
Which feature distinguishes the influenza virus shown in the image from bacteriophage lambda?
The diagram shows the life cycle of a virus. Which step involves the virus entering the host cell?
The graph shows the concentrations ( particles/ml) of E. coli host cells (solid line) and phage particles (dashed line) over time during bacteriophage lambda infection.
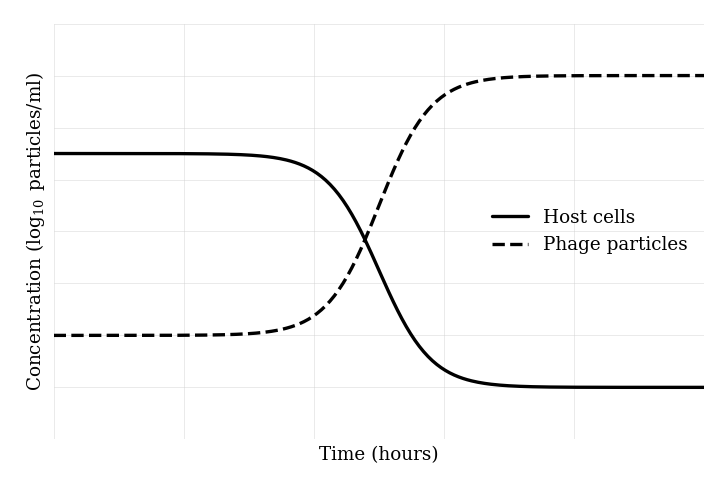
Based on the trends shown, which conclusion is most strongly supported?
Explain how reverse transcriptase allows retroviruses to replicate within a host cell.
What is the function of the viral RNA?
The following electron microscope image shows the structure of a virus:
Additionally, the table below compares key characteristics of viruses and living cells:
| Feature | Virus | Living Cell |
|---|---|---|
| DNA or RNA | Yes | Yes |
| Metabolism | No | Yes |
| Ability to Reproduce | Only inside host cell | Yes (independent cell division) |
| Ribosomes | No | Yes |
| Response to Antibiotics | No | Yes (for bacteria) |
Based on the image and data, explain why viruses are considered non-living organisms.
Describe one method by which viruses reproduce inside a host cell.
Focusing on the effects on the host cell and the timing of viral replication, compare and contrast the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of viruses.
Explain how the envelope helps viruses evade the host immune system and enhance their infectivity.
Discuss the impact of viruses on global health, providing examples of major viral pandemics and the strategies used to control viral outbreaks.
Outline the impact of viruses on global health.
Describe the key characteristics of a major viral pandemic, including its impact on global health and at least one strategy used for its control.
Discuss the strategies used to control viral outbreaks.
Explain how RNA viruses synthesize proteins and replicate their genomes within a host cell.