- IB
- 3.2 Impacts of changing trends in resource consumption - the Water-Food-Energy nexus
Practice 3.2 Impacts of changing trends in resource consumption - the Water-Food-Energy nexus with authentic IB Geography exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like physical geography, human geography, and geospatial analysis. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
SECTION B
Answer the following question. Refer to the graph below The graph shows the total food waste (kg per person) around the world
Source: Eurobarometer, EPRS, FAO Using examples from the chart, analyse how the distribution of food waste per capita may reflect broader inequalities in consumption and resource efficiency.
Using examples from the chart, analyse how the distribution of food waste per capita may reflect broader inequalities in consumption and resource efficiency.
Suggest two structural or systemic factors that could contribute to persistently high food waste in high-income economies. Support your answer with examples or reasoning.
Suggest two structural or systemic factors that could contribute to persistently high food waste in high-income economies. Support your answer with examples or reasoning.
The diagram shows the projected changes in global water, food, and energy consumption from 2020 to 2050.
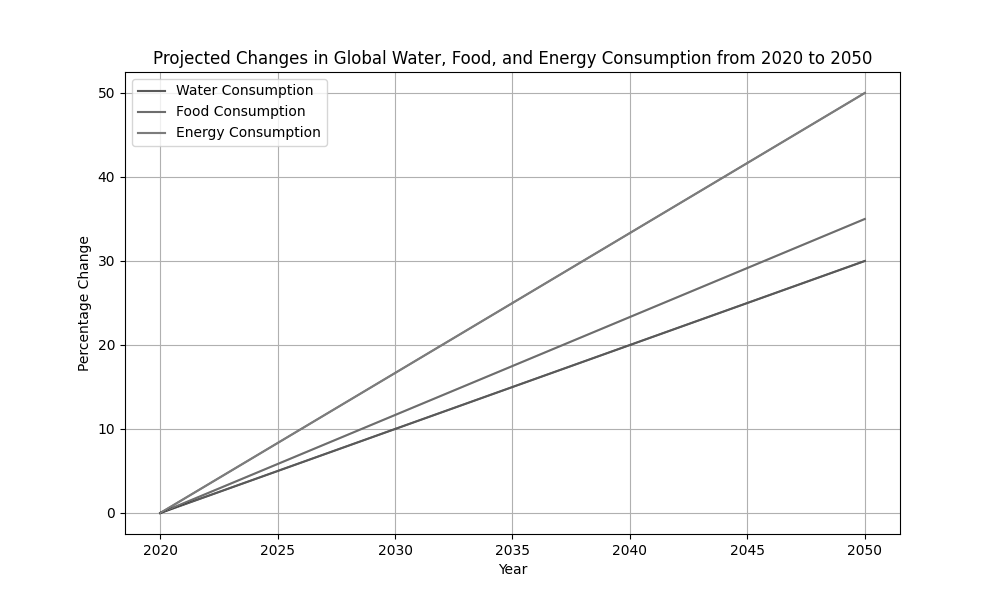
Describe the trends in global water, food, and energy consumption from 2020 to 2050 as shown in the diagram.
Explain two possible reasons for the rapid increase in global energy consumption compared to water and food consumption.
Discuss the potential impacts of the interconnected rise in water, food, and energy consumption on global sustainability.
Evaluate the effectiveness of one integrated approach that could help manage the interconnected consumption of water, food, and energy to promote sustainability.
The diagram shows the projected global water demand and supply from 2020 to 2050.
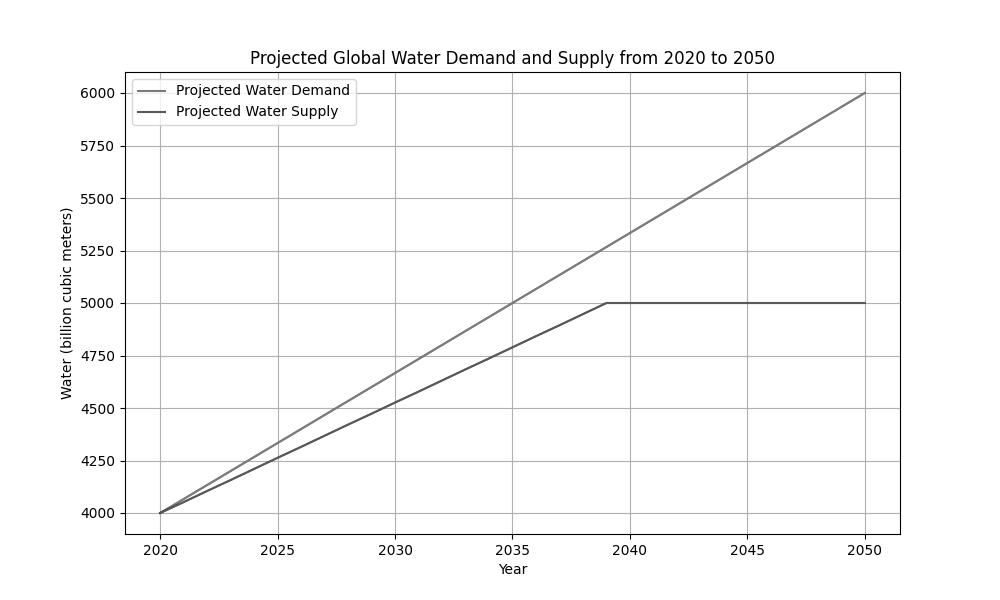
Description: The diagram shows two lines - one representing global water demand (red) and the other representing global water supply (blue) - plotted against time from 2020 to 2050. The demand line shows a steady upward trend, while the supply line increases initially but begins to plateau around 2040, indicating a growing gap between water demand and supply over time.
Describe the trends in global water demand and supply from 2020 to 2050 as shown in the diagram.
Explain two possible reasons why global water supply might plateau around 2040.
Discuss the potential consequences of the growing gap between global water demand and supply for global water security.
Evaluate the effectiveness of one technological and one policy intervention that could help address the projected gap between global water demand and supply.
Suggest two ways in which current global patterns of food consumption are contributing to long-term resource insecurity.
Discuss how energy insecurity can create geopolitical tensions at both regional and global scales.
The map shows the embodied energy trade
Source: Sankey Diagrams
Suggest two reasons why some regions import more energy than they produce domestically.
Using specific examples from the map, examine how energy trade flows reflect patterns of global inequality in production and consumption.
Suggest two reasons why energy-exporting regions may remain economically or politically vulnerable despite their resource advantage.
The diagram shows the projected changes in global food production and population growth from 2020 to 2050. Projected Changes in Global Food Production and Population Growth from 2020 to 2050
Describe the trends in global food production and population growth from 2020 to 2050 as shown in the diagram.
Explain two possible reasons for the slowdown in the rate of increase in global food production after 2040.
Discuss the potential consequences of the mismatch between global food production and population growth for food security.
Evaluate the effectiveness of one technological and one policy intervention that could help address the projected mismatch between global food production and population growth.
Define the term resource security.
Explain two benefits of transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Suggest two reasons why energy demand is increasing globally.
The map shows the Global State of Food Security 2022
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit
Identify one country with a food security index score of 80 or above.
Name one country with a high food security score and one country with a low food security score, based on the map.
Describe the global pattern of food security shown on the map.
Suggest two reasons why countries in Sub-Saharan Africa tend to score lower on the Global Food Security Index.
The diagram shows the global water demand and supply from 2020 to 2050. The y-axis represents the amount of water in cubic kilometers, and the x-axis represents the years from 2020 to 2050. The demand line is shown in red, steadily increasing from 2020 to 2050. The supply line is shown in blue, initially increasing but starting to plateau around 2040.
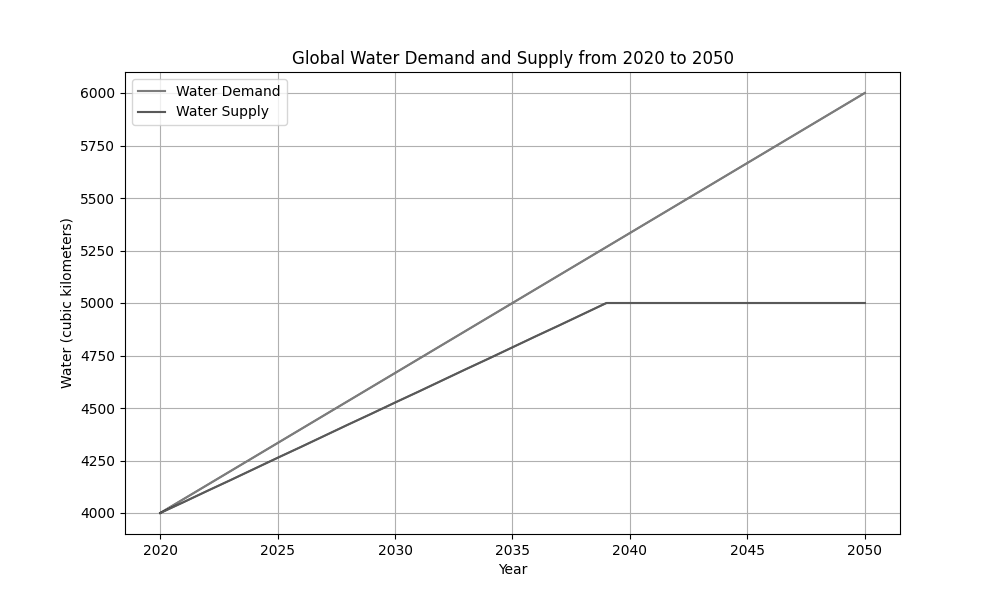
Description: The diagram shows two lines - one representing global water demand (red) and the other representing global water supply (blue) - plotted against time from 2020 to 2050. The demand line shows a steady upward trend, while the supply line increases initially but begins to plateau around 2040, indicating a growing gap between water demand and supply over time.
Describe the trends in global water demand and supply from 2020 to 2050 as shown in the diagram.
Explain two possible reasons why global water supply might plateau around 2040.
Discuss the potential consequences of the growing gap between global water demand and supply for global water security.
Evaluate the effectiveness of one technological and one policy intervention that could help address the projected gap between global water demand and supply.
Describe two ways in which food production affects energy security.
The diagram shows the projected global freshwater availability and demand from 2020 to 2050.
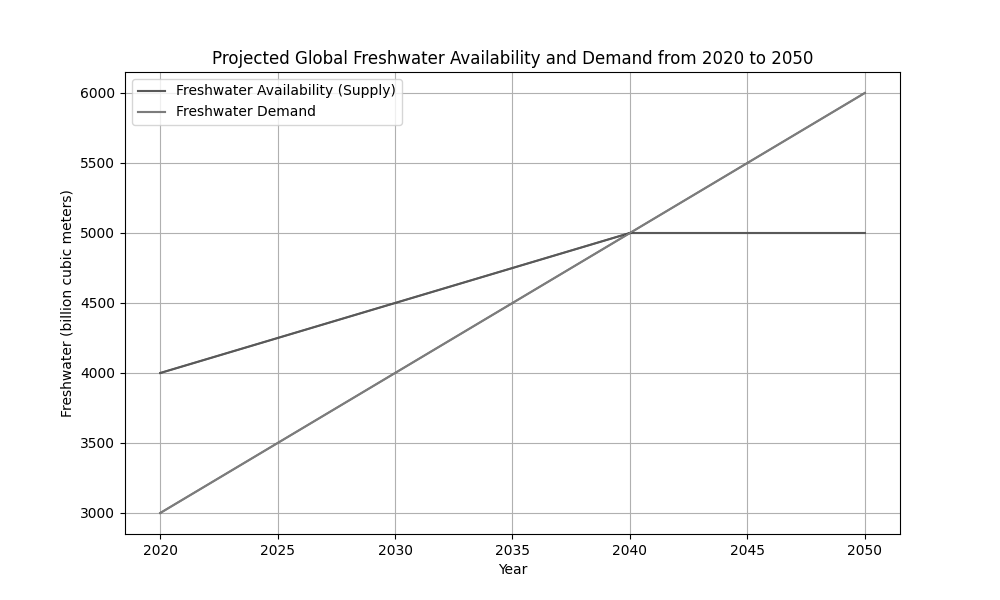
Describe the trends in global freshwater availability and demand from 2020 to 2050 as shown in the diagram.
Explain two possible reasons why global freshwater availability might plateau around 2040.
Discuss the potential consequences of the growing gap between global freshwater availability and demand for global water security.
Evaluate the effectiveness of one technological and one policy intervention that could help address the projected gap between global freshwater availability and demand.
Define the term water scarcity.
Define the term energy security.
Define the term circular economy.
Suggest two reasons why the ecological footprint of a city might be higher than that of a rural area.
The map shows the countries with proven oil reserves (in millions of barrels)
Source: US EIA
Identify one country with over 200,000 million barrels of oil reserves.
Identify one continent where most countries have less than 10,000 million barrels of oil reserves.
Describe the global pattern of oil reserves shown on the map.
Suggest two ways in which having large oil reserves might affect a country’s development.