Practice Humanitarian crises with authentic MYP MYP History exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like historical sources, cause and effect, and continuity and change. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of MYP examiners.
What specific conditions in post-war Iraq, according to the text, contributed to the creation of a power vacuum that extremist organizations later exploited?
Which of the following is a frequently cited reason for why global institutions may hesitate to intervene in a crisis?
1
After capturing territory across Syria and Iraq by filling a power vacuum, the extremist group ISIS took control of major cities such as __________.
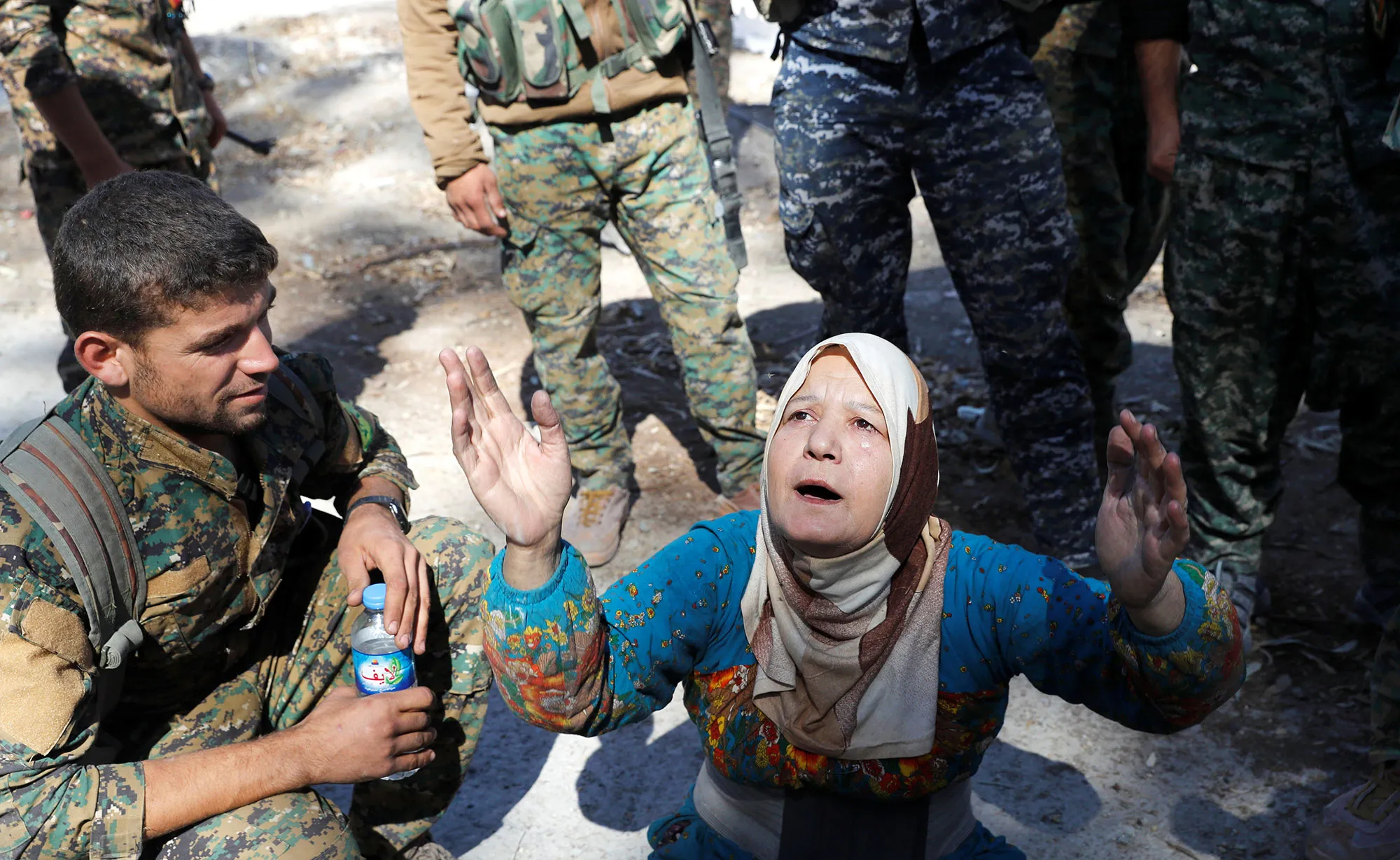

The institutional collapse in Yemen resulted in the largest modern outbreak of which disease, affecting over 2 million people?
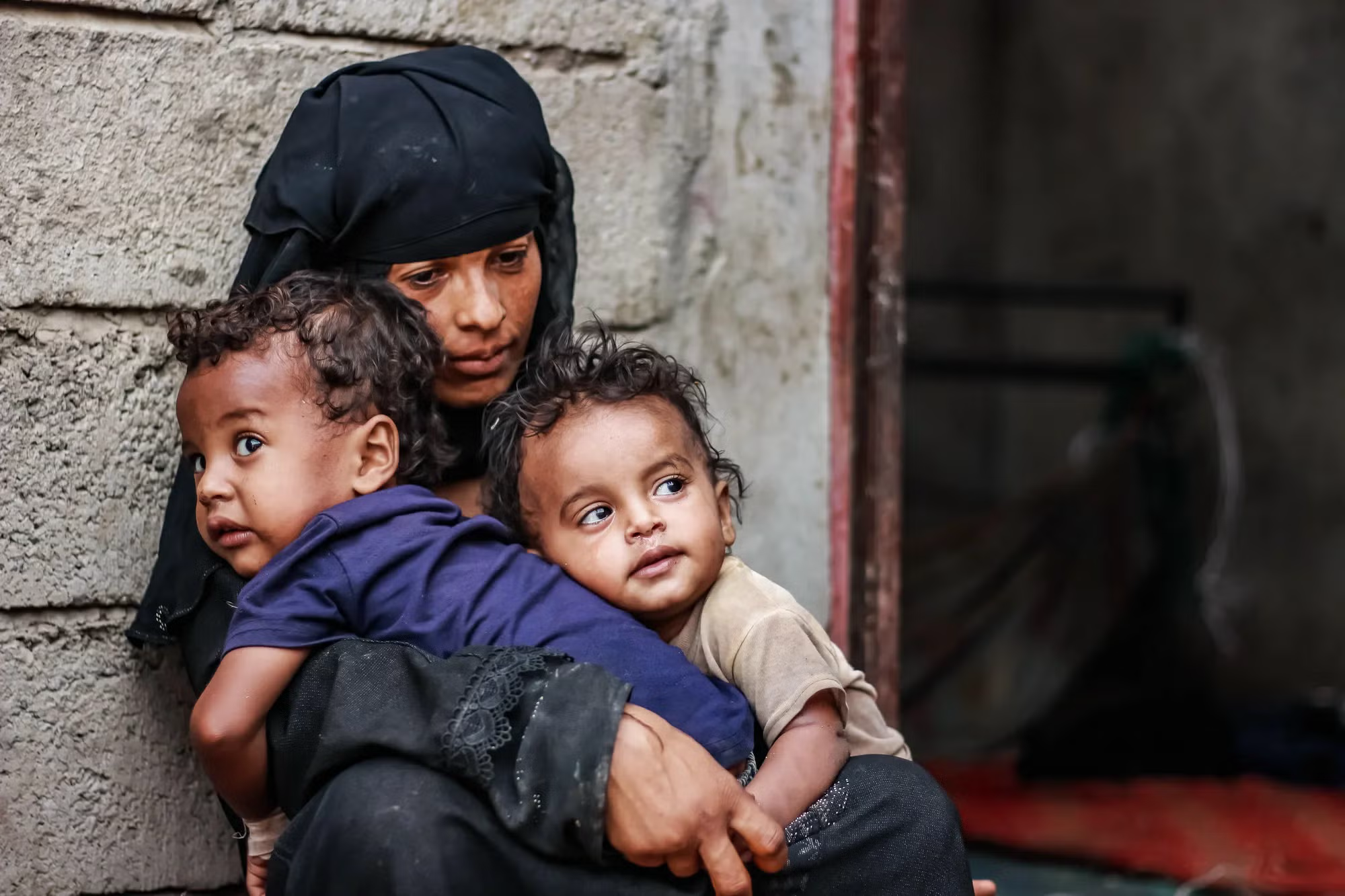

Which specific indicator of organized violence in Rwanda was reported by UN peacekeepers before the genocide actually began?
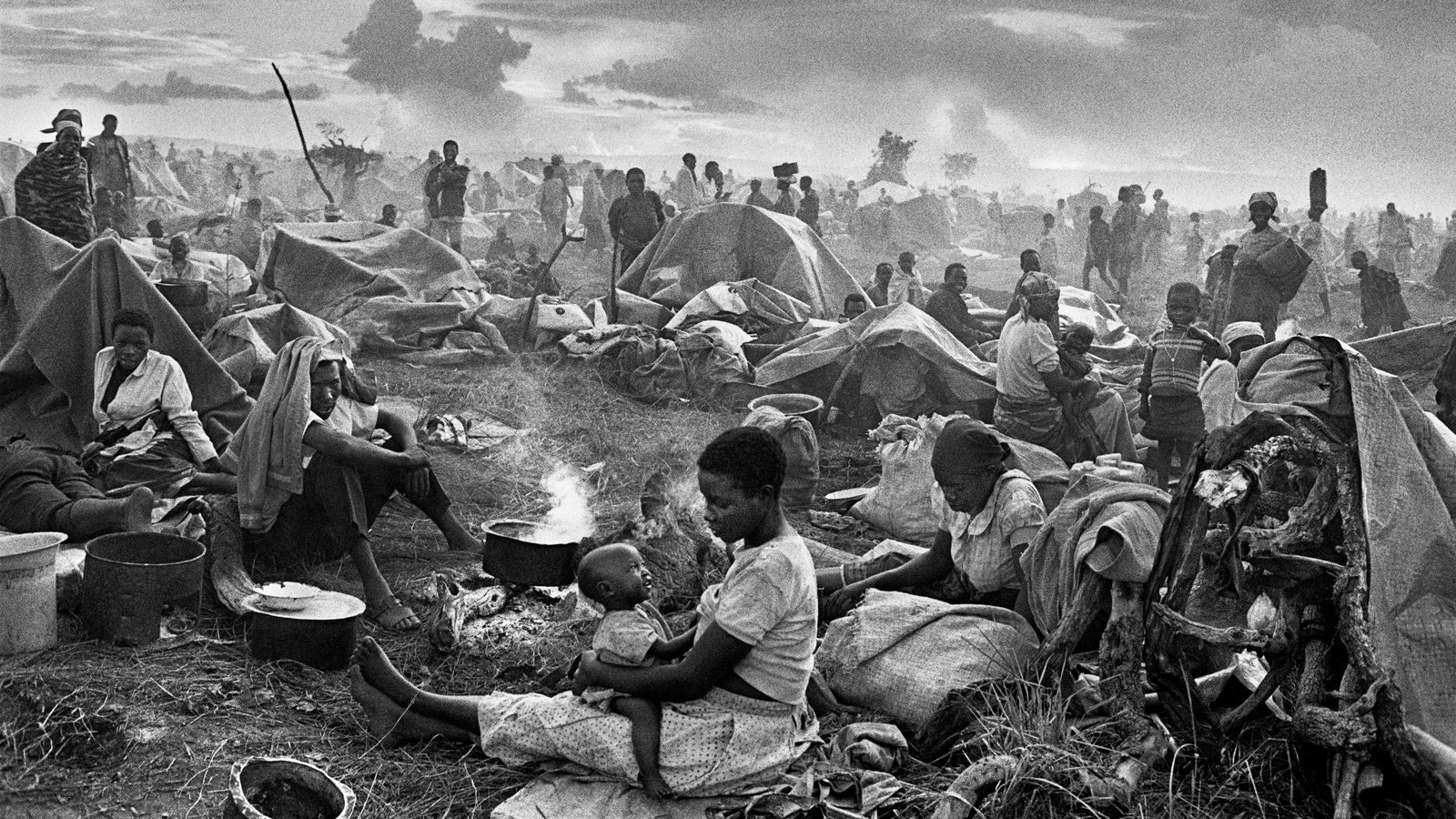

Figure 1 shows the location of the Darfur region in Sudan.
Why did global powers hesitate to intervene during the escalation of atrocities in Darfur, Sudan, in 2003?
Besides political risk and cost, what other factor is mentioned as a reason global institutions like the UN or AU might hesitate to act in a crisis?
According to the 'exam technique' guidance provided in the textbook, which logical sequence should be used to explain the role of inaction in a humanitarian crisis?
Which specific vulnerable groups are often at risk of being 'left behind' as a humanitarian crisis worsens?
Level: SL/HL | Paper: 2
During the 1994 genocide in Rwanda, what term did the hate radio station RTLM use to describe the Tutsi people?
