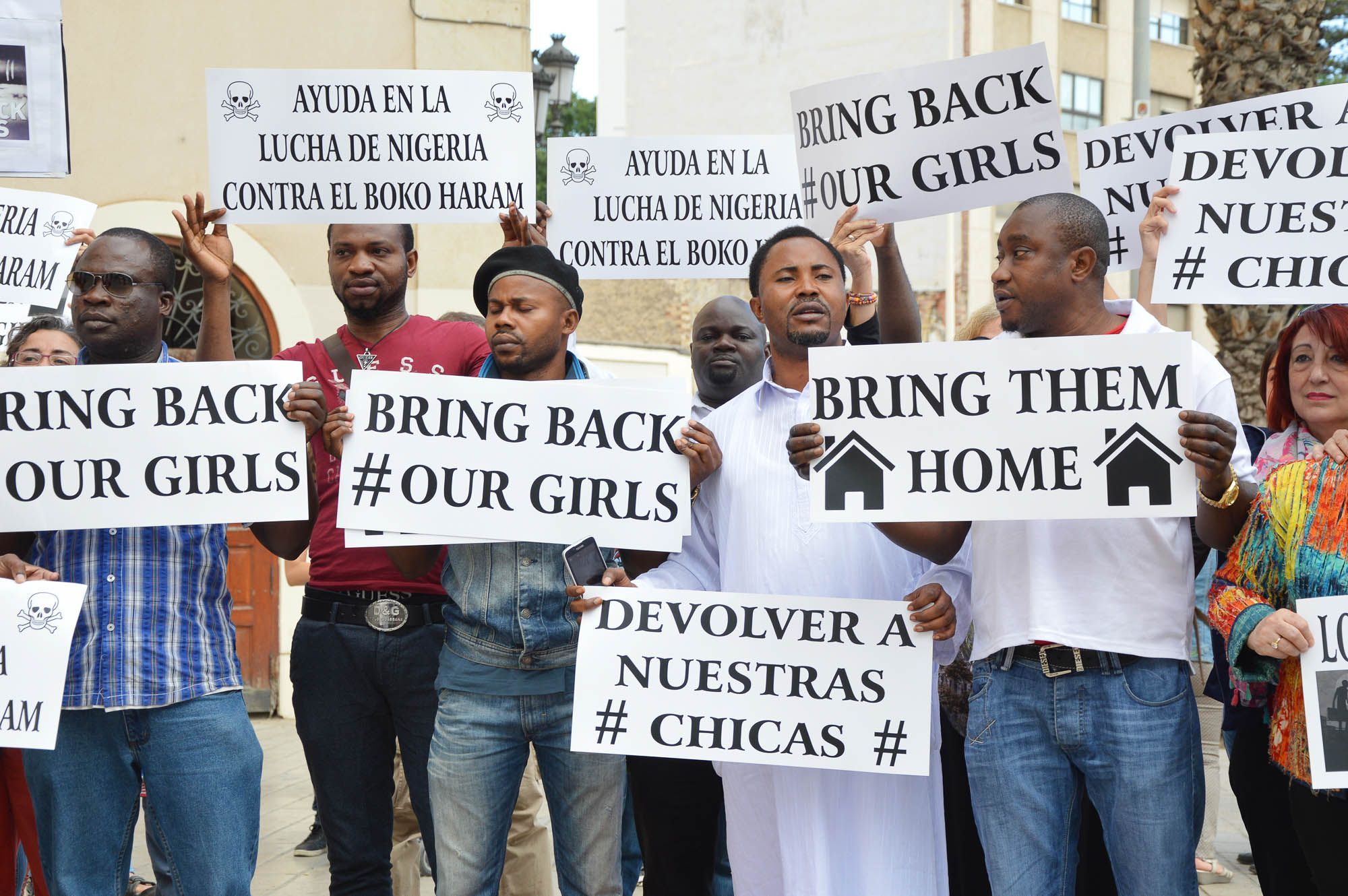Organized Civil Society and Non-Governmental Organizations
- Organized civil society refers to the network of groups and institutions that operate independently of the government to represent diverse interests and values. It includes:
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs): Independent organizations focused on specific issues like human rights, environmental protection, or poverty alleviation.
- Community-Based Organizations (CBOs): Local groups addressing community-specific needs.
- Faith-Based Organizations: Religious groups involved in social and humanitarian work.
- Advocacy Groups: Organizations that lobby for policy changes on issues like climate change or gender equality.
- Organized civil society plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between individuals and the state, providing a platform for collective action and advocacy.
What Are NGOs? (Non-Governmental Organizations)
Non-Governmental Organizations
NGOs are part of civil society but often more structured, they operate independently from governments. Work to solve global/local issues (poverty, health, education, human rights, environment).
Levels of Involvement
- Community NGOs
- City-level NGOs
- National NGOs
- International NGOs
Types of NGOs
- Charitable NGOs: Provide basic needs (e.g. food, shelter), recipients are passive.
- Service NGOs: Deliver services (e.g. education, family planning), recipients engage more.
- Participatory NGOs: Give people tools/resources to help themselves.
- Empowering NGOs: Raise awareness of rights and build long-term agency.
- HL Extension: Environment
- Investigate how civil society influences climate policy at local/national levels.
- Focus: debate around best approaches to global climate crises.
- Great HL case study opportunity.
The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
- Independence: Operate without direct government control.
- Non-Profit Nature: Focus on social, environmental, or humanitarian goals rather than profit.
- Global Reach: Many NGOs operate across borders, addressing transnational issues.
- Tackle poverty, corruption, and inequality.
- Respond to crises (e.g. floods, fires).
- Promote laws, public freedoms, and prevent crime.
- Increase transparency in budgets.
- Protect the environment.
- Empower marginalized communities.
- Advocate for:
- Anti-discrimination
- Women’s and LGBTQ+ rights
- Youth empowerment
- Consumer protection
- Deliver social services (e.g. food kitchens, shelters).
- Greenpeace is a global NGO known for its environmental advocacy, using direct action and campaigns to raise awareness about issues like climate change and deforestation.
Functions of NGOs
- Advocacy and Awareness: NGOs raise awareness about critical issues and advocate for policy changes.
- Service Delivery: Provide essential services such as healthcare, education, and disaster relief, often in areas where governments are unable or unwilling to act.
- Monitoring and Accountability: Act as watchdogs, holding governments and corporations accountable for their actions.
- Capacity Building: Empower communities by providing training, resources, and support.
- When analyzing the role of NGOs, consider their impact at multiple levels: local, national, and global.
- This multi-level approach helps you understand their broader significance in global politics.
Médecins Sans Frontières (Doctors Without Borders)
- Humanitarian Aid: Provides medical care in conflict zones and disaster-stricken areas.
- Advocacy: Raises awareness about humanitarian crises and advocates for policy changes.
- Independence: Maintains neutrality and independence to operate in politically sensitive regions.
- Identify three key functions of NGOs and provide examples of how they operate in different contexts.
Challenges Faced by NGOs
- Funding and Resource Constraints: Reliance on donations and grants can limit their capacity and independence.
- Political Pressure: Governments may restrict NGO activities through legal or bureaucratic means.
- Accountability and Transparency: NGOs must balance their independence with the need for accountability to donors and beneficiaries.
- Security Risks: Operating in conflict zones or authoritarian states can pose significant risks to staff and operations.
- While NGOs are often seen as agents of positive change, they can also face criticism for lacking accountability or imposing external values on local communities.
The Impact of NGOs on Global Politics
- Shaping Policy Agendas: NGOs influence international policy by advocating for issues like climate change, human rights, and global health.
- Fostering Global Cooperation: Collaborate with governments, international organizations, and other NGOs to address transnational challenges.
- Empowering Marginalized Communities: Provide a voice for marginalized groups and promote inclusive development.
- The 2015 Paris Climate Agreement was heavily influenced by NGO advocacy, which helped shape the negotiation process and mobilize public support for climate action.
Critical Perspectives on NGOs
- Neo-Colonialism: Critics argue that some NGOs impose Western values and priorities on developing countries.
- Fragmentation: The proliferation of NGOs can lead to overlapping efforts and inefficiencies.
- Dependency: Reliance on NGO services can undermine local governance and capacity-building efforts.
- To what extent do NGOs represent a universal set of values, and how might this clash with local cultural or political contexts?
The Future of Organized Civil Society
- Digital Advocacy: The rise of digital platforms has transformed how NGOs mobilize support and engage with global audiences.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Increasing collaboration between NGOs, governments, and the private sector to address complex global challenges.
- Focus on Sustainability: Growing emphasis on sustainable development and long-term impact.
- Organized civil society and NGOs play a vital role in global politics by advocating for change, providing services, and holding powerful actors accountable.
- Despite their challenges, NGOs remain essential actors in addressing transnational issues and empowering marginalized communities.
- Understanding the strengths and limitations of NGOs is crucial for analyzing their impact on global governance and international relations.