- IB
- 1.3 Population challenges and opportunities
Practice 1.3 Population challenges and opportunities with authentic IB Geography exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like physical geography, human geography, and geospatial analysis. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Define the term replacement-level fertility.
State two reasons why some countries have persistently high infant mortality rates despite economic growth.
Discuss three strategies that governments can use to address the challenges of a declining working-age population.
The infographic shows statistics regarding South Sudan’s refugee crisis.
Source: United Nations Refugee Agency and International Organisation for Migration
Describe the two most common nationalities of individuals arriving in South Sudan based on the infographic.
Using the age and sex breakdown, outline one challenge South Sudan might face in meeting the needs of the newly arrived population.
To what extent do the patterns of population inflow into South Sudan reflect the impacts of forced migration?
Explain two reasons why urbanization rates have increased more rapidly in some continents than in others.
Describe a social and an economic impact of rapid population growth in less developed countries.
Outline two challenges that cities may face as a result of increasing ethnic and cultural diversity.
The infographic shows The Countries Losing their Population the Fastest between 2022 and 2023
Source: United Nations Population Division
Identify two European countries from the infographic that experienced a population decrease between 2022 and 2023, and state their percentage decreases.
Using the infographic, describe how population change in Europe compares to that in Africa between 2022 and 2023.
Explain two possible causes of rapid population decline in some countries, and discuss one potential impact of this decline on a country.
Outline one limitation of the Demographic Transition Model when applied to low-income countries today.
Define the term internally displaced person (IDP) and explain how it differs from a refugee.
Explain how migration can lead to changes in the age and sex structure of the origin country.
The infographic shows The Facts on the Global Refugee Crisis.
Source: New Internationalist
State two reasons why most refugees are hosted in developing countries, according to the infographic.
Using evidence from the infographic, outline one way that global responses to refugee displacement are unequal.
To what extent do economic capacity and geopolitical interests shape the global distribution and treatment of refugees?
Compare the approaches to managing population change in a developed and a developing country.
To what extent can migration policies address the challenges of population ageing?
Discuss the potential consequences of gender imbalances in population structure.
Define migration.
Outline two rural push factors.
Define voluntary migration.
Define the term forced migration.
Identify one example of a forced migration movement.
Suggest two consequences of forced migration for the host country.
Explain three possible pull factors that attract people to urban areas.
The infographic shows the Then and Now of Urban Population Worldwide
Source: United Nations Population Division
State two continents that experienced the largest increase in the share of their population living in urban areas between 1950 and 2020, according to the infographic.
State two continents that had more than half of their population living in urban areas in 2020, according to the infographic.
Using evidence from the infographic, explain two reasons why urban populations might have increased in many continents since 1950.
Explain two challenges associated with rapid population growth in developing countries.
The diagram below shows the population pyramid of a country experiencing Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM).
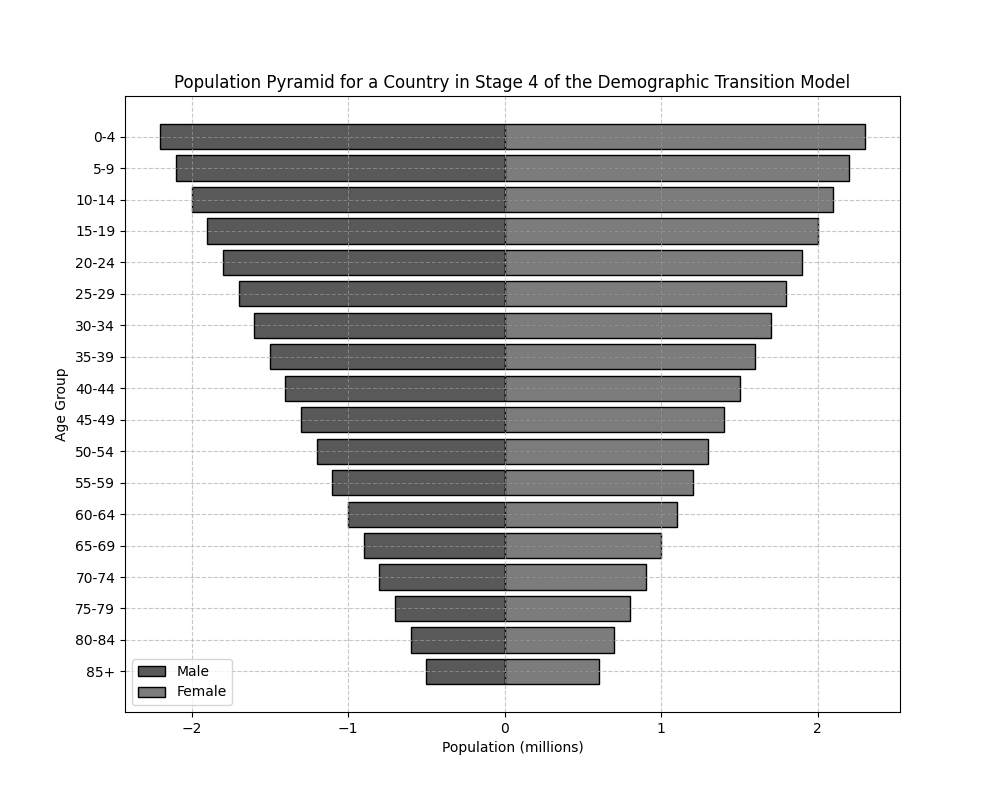
Describe the characteristics of a population pyramid for a country in Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM).
Explain the factors that contribute to the population structure observed in Stage 4 of the DTM.
Discuss the potential social and economic challenges a country in Stage 4 of the DTM might face.