Practice D.1 Geophysical systems with authentic IB Geography exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like physical geography, human geography, and geospatial analysis. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The map below shows The Global Distribution of Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries.
Source: BBC
Identify the tectonic plate with the highest concentration of volcanoes.
State the type of plate boundary where most volcanoes are located.
Outline one reason why volcanoes are often located near plate boundaries.
Explain two reasons why volcanic hazards vary in severity depending on tectonic settings.
Examine the relationship between plate boundary types and the occurrence of volcanic hazards.
Evaluate the extent to which human vulnerability contributes to the impact of volcanic hazards.
The diagram shows the structure of the Earth's interior and the movement of tectonic plates.
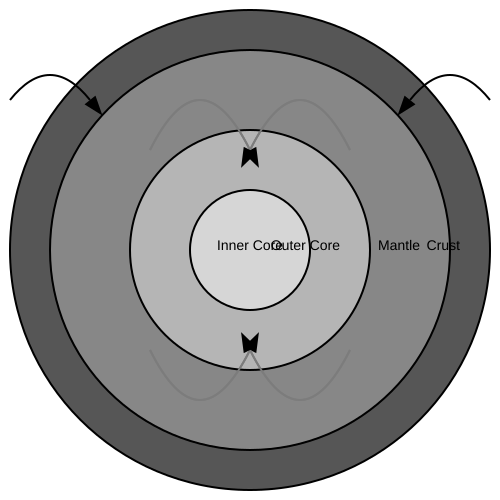
- Describe the structure of the Earth's interior as shown in the diagram.
- Explain the role of convection currents in the mantle in the movement of tectonic plates.
- Discuss the differences between oceanic and continental crust and their interactions at plate boundaries.
- Using the diagram, explain the formation of mid-ocean ridges and ocean trenches.
- Evaluate the impact of tectonic plate movements on human societies, providing specific examples.
The map below shows Cities’ Risk of Exposure to Natural Disasters.
Source: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs
Identify one city shown to be at high risk from three or more types of natural disasters.
State the continent with the largest number of high-population cities (over 10 million) exposed to multiple hazard risks.
Outline one reason why urban areas are often more exposed to multiple natural hazards than rural areas.
Explain two ways in which multi-hazard exposure can increase the vulnerability of megacities.
Examine the challenges of managing geophysical hazards in cities located in multi-hazard zones.
Discuss the extent to which population size is the most important factor in determining urban vulnerability to geophysical hazards.
The map shows global seismic hazard zones, indicating the probability of ground shaking caused by earthquakes.
Source: Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Program (GSHAP)
Identify one country that is located in a high seismic hazard zone.
Identify one country that is located in a low seismic hazard zone.
Outline one reason why seismic hazard is higher along plate boundaries.
Explain two reasons why the impacts of earthquakes differ between countries.
Discuss the extent to which earthquake hazards can be managed through prediction and preparation.
Evaluate the reasons why some locations experience more serious consequences from earthquakes than others.
The map shows global tectonic plates, the locations of volcanoes and earthquakes, and selected tectonic events since 2000.
Source: Oxford University Press (Adapted)
Identify one tectonic plate where there is a high concentration of both earthquakes and volcanoes.
State the type of plate boundary most commonly associated with both earthquakes and volcanoes.
Outline one reason why destructive plate boundaries are associated with high geophysical hazard risk.
Explain two ways in which the characteristics of different plate boundaries influence the severity of geophysical hazards.
Examine how different types of plate boundaries contribute to the occurrence of volcanic and earthquake hazards around the world.
Evaluate the extent to which the impacts of geophysical hazards are influenced more by the characteristics of the hazard than by human vulnerability.
The map shows global seismic hazard zones, indicating the probability of ground shaking caused by earthquakes.
Source:
Identify the type of plate boundary most commonly associated with active volcanoes.
Identify one region where volcanoes have been active since 1900.
Outline one reason why volcanic activity is concentrated along convergent plate boundaries.
Explain two challenges posed by volcanic hazards to communities living near active volcanoes.
Discuss the reasons why some regions are more vulnerable to volcanic hazards than others.
Evaluate the effectiveness of strategies used to manage volcanic hazards.
The diagram shows the water cycle and its various components.
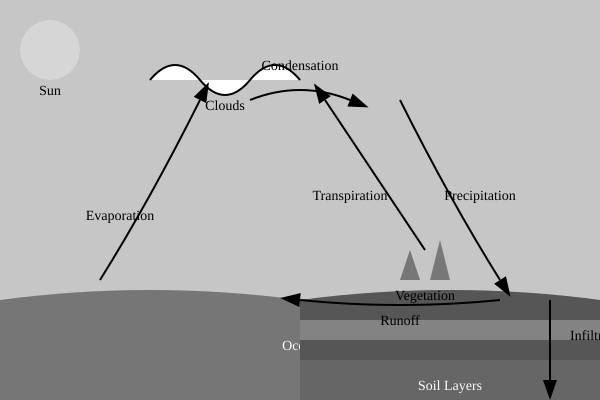
Describe the main processes of the water cycle as shown in the diagram.
Explain how human activities can impact the water cycle.
Discuss the importance of the water cycle in maintaining ecosystem balance.
Evaluate the potential effects of climate change on the water cycle.
The infographic shows The World’s Deadliest Earthquakes.
Source: National Centers for Environmental Information.
Identify the earthquake event with the highest recorded death toll.
Identify one country where more than 50,000 people died due to a single earthquake event.
Outline one reason why the 2010 Haiti earthquake had such a high death toll.
Explain two factors that can influence the death toll of earthquake events.
Examine the physical and human factors that influence the impacts of earthquake disasters.
“The deadliest earthquakes are not always the strongest.”
Discuss this statement.
The diagram shows the different types of plate boundaries and the geological features associated with them.
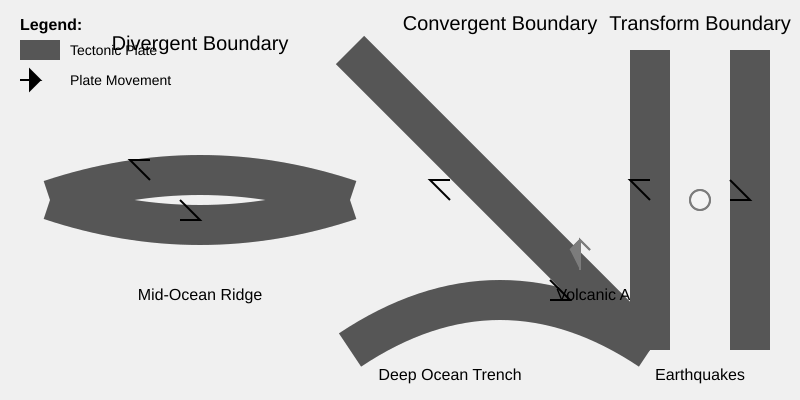
- Describe the geological features associated with each type of plate boundary as shown in the diagram.
- Explain the processes that lead to the formation of mid-ocean ridges at divergent plate boundaries.
- Discuss the role of subduction in the formation of deep ocean trenches and volcanic arcs at convergent plate boundaries.
- Evaluate the impact of transform plate boundaries on human settlements, providing specific examples.
The diagram shows the structure and impact zones of an earthquake on a coastal city.
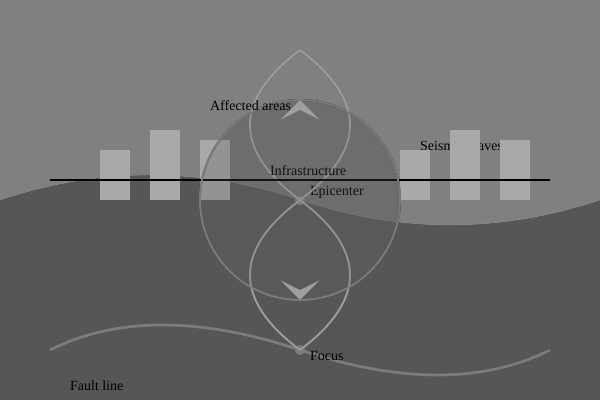
- Explain the processes that lead to the occurrence of an earthquake along a fault line.
- Describe the main features of an earthquake and its impact on a coastal city as shown in the diagram.
- Discuss the potential hazards associated with earthquakes and their impact on human settlements in coastal areas.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies used to mitigate the impact of earthquakes on coastal communities.