Price is not the only factor that affects the supply of an individual firm or the market. These other factors are referenced to as the non-price determinants of supply.
Non-Price Determinants of Supply
Factors, other than price, that can affect the supply of a firm (or multiple firms) and shift (change position) the supply curve.
The most important thing to note in this topic is that:
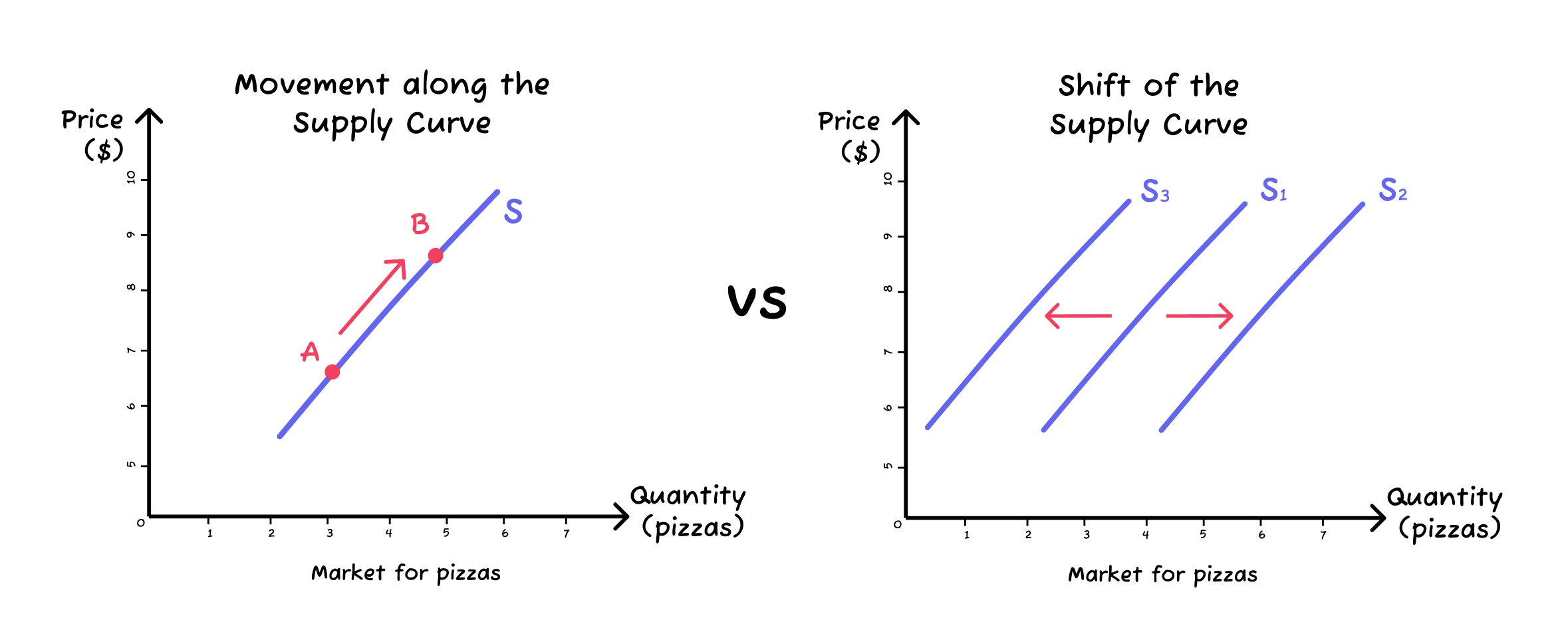
- Changes in price changes the amount of a good or service supplied (causing a movement along the supply curve).
- Changes in the non-price determinants of supply change the supply in the market (causing a shift of the supply curve).
- A rightward shift means that for a fixed given price, supply increases and more is supplied.
- A leftward shift means that for a fixed price, supply decreases and less is supplied.
The non-price determinants of supply covered in the IB curriculum:
- Changes in costs of factors of production.
- Price of related goods.
- Indirect taxes and subsidies.
- Future price expectations.
- Changes in technology.
- Number of firms in the market.
Changes in costs of factors of production (FOPs)
Factors of production
All resources or inputs used to produce goods and services.
Increased costs of factors of production → leftwards shift
- When the costs of FOPs rise (such as higher wages, increased rent, or pricier raw materials) production becomes more expensive.
- This increase in costs reduces the quantity that the firm (or firms) is willing and able to supply for every given price.
Decreased Costs → rightwards shift
- Alternatively, If FOPs costs fall, production becomes cheaper and more profitable.
- This reduction in costs means the firm (or firms) is willing and able to supply more for a given price
Prices of related goods: competitive and joint supply
Competitive supply
Competitive Supply
Goods or services in Competitive Supply are alternate use of resources of each other where they compete for the use of the same resources.
If two goods are in competitive supply, producing more of one means that the production of the other has to be reduced.
ExampleAssume that a company $A$ can use its resources to produce smartphones or smartwatches.
- If the company produces more smartwatches, it has to produce less smartphones.
- If it produces more smartphones, then it has to produce less smartwatches.
Higher prices of a competing good → leftwards shift
- A rise in the price of one good (e.g., smartwatches) incentivises firms to produce more of that good (more smartwatches since their price has increased).
- Therefore, this leads to the supply of the competing goods (e.g., smartphones) to fall because the resources are allocated to the goods in which the prices increased (since firms look to increase their revenue).
Lower prices of a competing good → rightward shift
- Alternatively, a fall in the price of one good (e.g., smartwatches) encourages firms to shift their resources to the other goods (smartwatches cheaper, less profitable).
- Hence, this increases the supply of the competing goods (e.g., smartphones).
Even though we talk about price change here, notice the price only changes of the competing good, not the price of the good itself. For example:
- Price of smartwatches increases
- Quantity supplied of smartwatches goes up
- More resources for smartwatches, less for smartphones
- Supply of smartphones reduces
Notice, the change in supply of smartphones happens due to a change in the price of smartwatches, not the price of smartphones itself.
Hence this is still a non-price determinant since it is concerned with the price of the other competitive good.
You may also note that:
- The change in price of smartwatches affects quantity supplied of smartwatches.
- However, since it is a non-price determinant for smartphones, it affects it's supply.
Joint supply
Joint Supply
Goods or Services in Joint Supply are consequences of each other and derived from a single process or product.
If goods are in joint supply, the production of one good will automatically cause the production of the others.
ExampleAssume that a company uses its resources to product beef.
- By processing the cows, the company also gets leather, which it can also sell.
- If the company produces more beef, it has to utilise more cows, and therefore it gets more of both beef and leather
Increased supply for a main product → rightwards shift
- A rise in supply for the primary product (e.g., beef) means more resources are used to produce that product (more cows used).
- Hence, any joint supply goods or services will also increase in supply since they are made from the same process or product (e.g., leather).
Decreased supply for a main product → leftwards shift
- A fall in supply for the primary product (e.g., beef) means less resources are used to produce that product (less cows).
- Any goods or services in joint supply will also decrease in supply (e.g., leather).
If the demand for beef rises then:
- The firm will increase the production and supply of beef
- Hence automatically increasing the supply of leather
Indirect Taxes and Subsidies
Taxes
Mandatory payments made by households and firms, collected by governments.
Indirect taxes
Taxes levied on spending on goods and services. They are called indirect because while consumers contribute to part or all of the tax, it is the suppliers (firms) who collect and transfer these taxes to the government authorities (consumers pay the taxes indirectly).
Subsidy
Monetary help (direct or indirect payment) offered by the government to firms (sometimes households) to aid in lowering costs of production.
Increase in taxes paid by firms or decrease in subsidy → leftwards shift
- This increases the cost of production the firms face by increasing the payments they have to make to the government (or decreasing the money they receive from the government).
- Therefore, for all given prices, the firms will decrease their supply since it is more expensive to produce.
Decrease in taxes paid by firms or increase in subsidy → rightwards shift
- This decreases the cost of production the firms face by decreasing the payment they have to make to the government (or increasing the money they receive from the government).
- Hence, for all given prices, the firms will increase their supply since it is cheaper to produce than before.
Future price expectations
Producers expect higher prices in the future → leftwards shift
- Firms may withhold some of their goods or services today by not offering it for sale.
- Firms expect that by saving these goods or services for later, they can sell them for a higher price.
- Therefore, the supply of that good or service will fall in the market today.
Even though in the future the idea is to increase the supply, we focus on the short-run.
Producers expect lower prices in the future → rightwards shift
- Firms may increase the supply today so they can utilise the higher prices of today and avoid losing out in the future
- Therefore, the supply of that good or service will increase in the market today.
Changes in technology
NoteTechnological advancements typically improve production efficiency, reducing costs of production.
Technological improvements → rightwards shift
- New technologies allow firms to produce more at lower costs.
- This causes supply to increase.
Technological failures → leftwards shift
- If technology becomes obsolete or breaks down, production becomes more inefficient, which increases costs.
- This causes supply to decrease.
The introduction of automated machinery in car manufacturing reduces costs and increases supply. Conversely, a cyberattack disrupting production systems can decrease supply.
Number of firms in the Market
NoteAs we saw in subtopic 2.2.3, the number of firms in an industry influences the total market supply.
More firms → rightwards shift
- An increase in the number of firms causes the supply to increase, as more producers contribute to market supply.
Fewer firms → leftwards shift
- If firms exit the market, supply decreases.
Remember the main takeaway from this section:
While price affects quantity supplied, non-price determinants affect supply and cause different shifts to the supply curve.