- IB
- Metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (HL)
Practice Metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (HL) with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The image shows part of a plant cell with a chloroplast in close proximity to mitochondria.
State two structural similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Compare and contrast mitochondria and chloroplasts in terms of the substrates they use and the products they produce.
Outline how the compounds produced by chloroplasts are distributed throughout the plant.
The electron micrograph shows part of a cell including a mitochondrion. 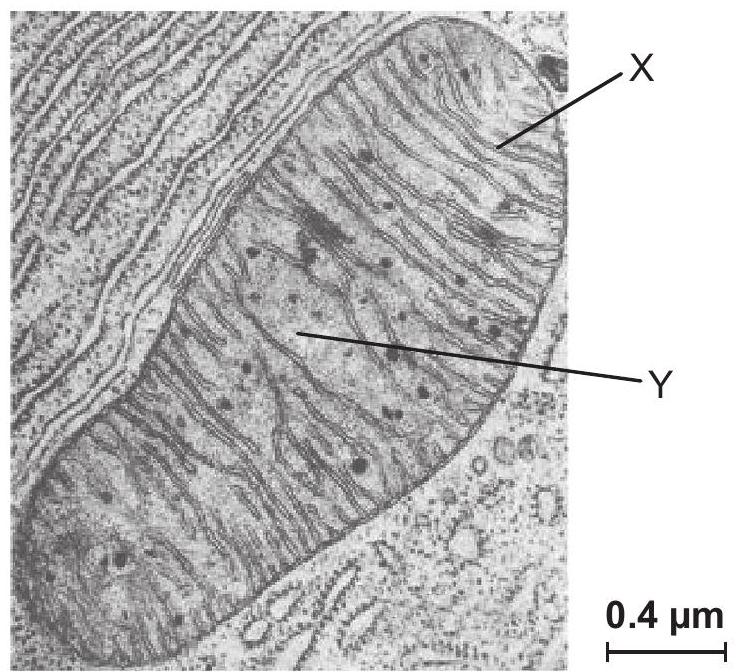
Outline how the structures labelled X and Y are adapted to carry out the function of the mitochondrion.
Explain how ATP is generated in mitochondria by chemiosmosis.
This reaction occurs in mitochondria.
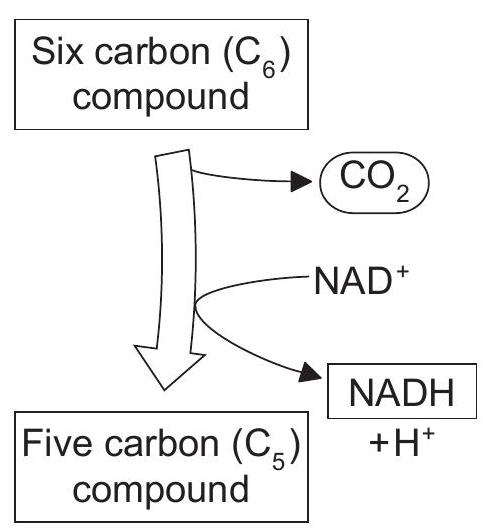
What explains that this reaction enables energy to be converted into a usable form?
The electron micrograph shows a section through part of an animal cell.
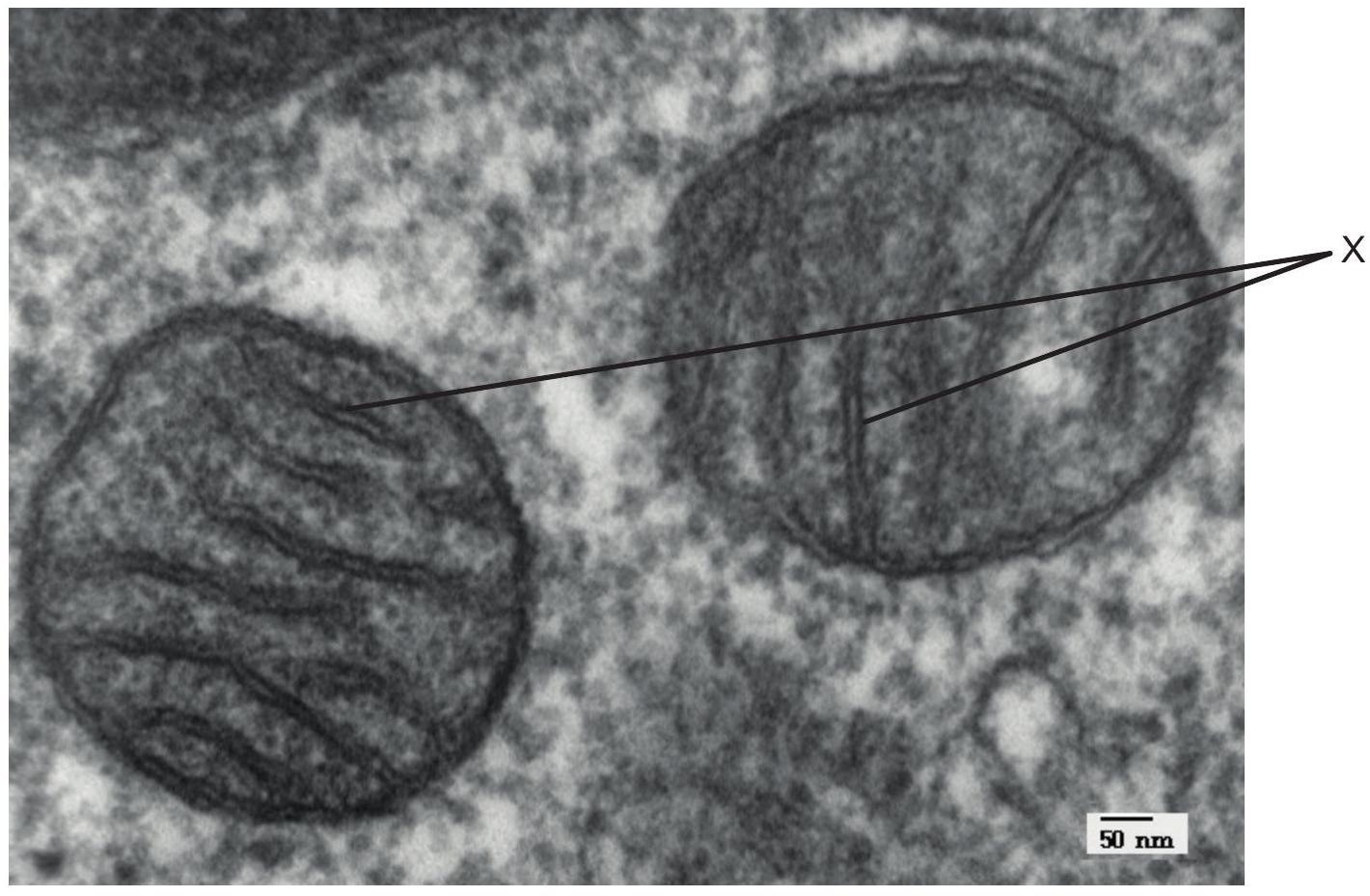
Which process is occurring on the structures labelled X ?
Which of the following processes occurs during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
Describe the structure of triglycerides (fats).
Outline the use of fats in cell respiration.
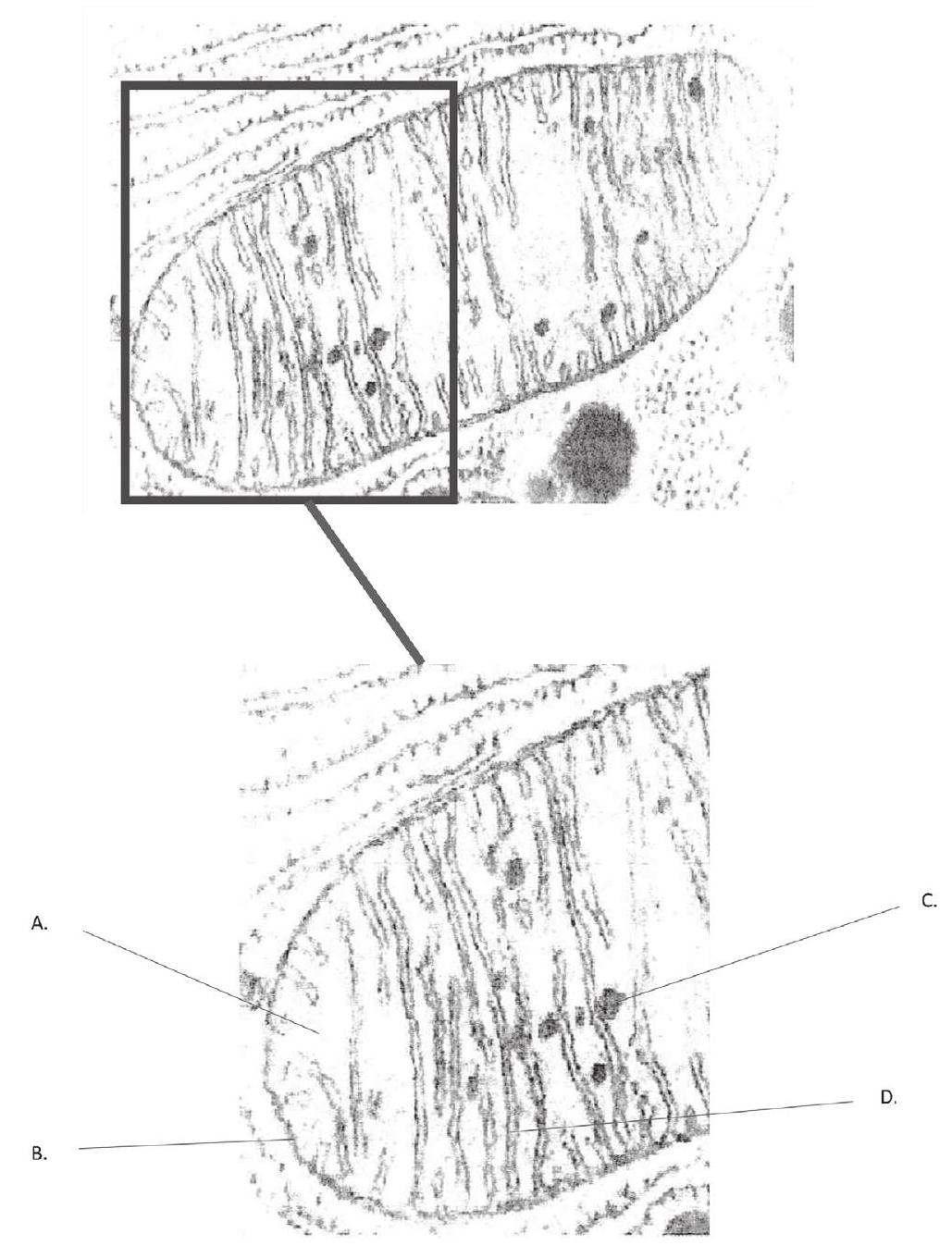
Explain how the structure of the mitochondrion allows it to carry out its function efficiently.
The mitochondrion in the electron micrograph shows some features that make it efficient for its function. Which labelled feature allows a rapid build-up of proton concentration for chemiosmosis?
Identify four examples of proteins that illustrate the wide range of functions of this group of biochemicals in living organisms.
Describe how the structure of the chloroplast is adapted to its function in photosynthesis.
Explain the role of hydrogen ions used in photosynthesis.
Which process requires oxygen in aerobic cell respiration?