Practice 9.3 Growth in plants with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
What is the role of in plants?
The graph shows how the mass of a bean seed from which all water has been removed (dry mass) changes during germination.
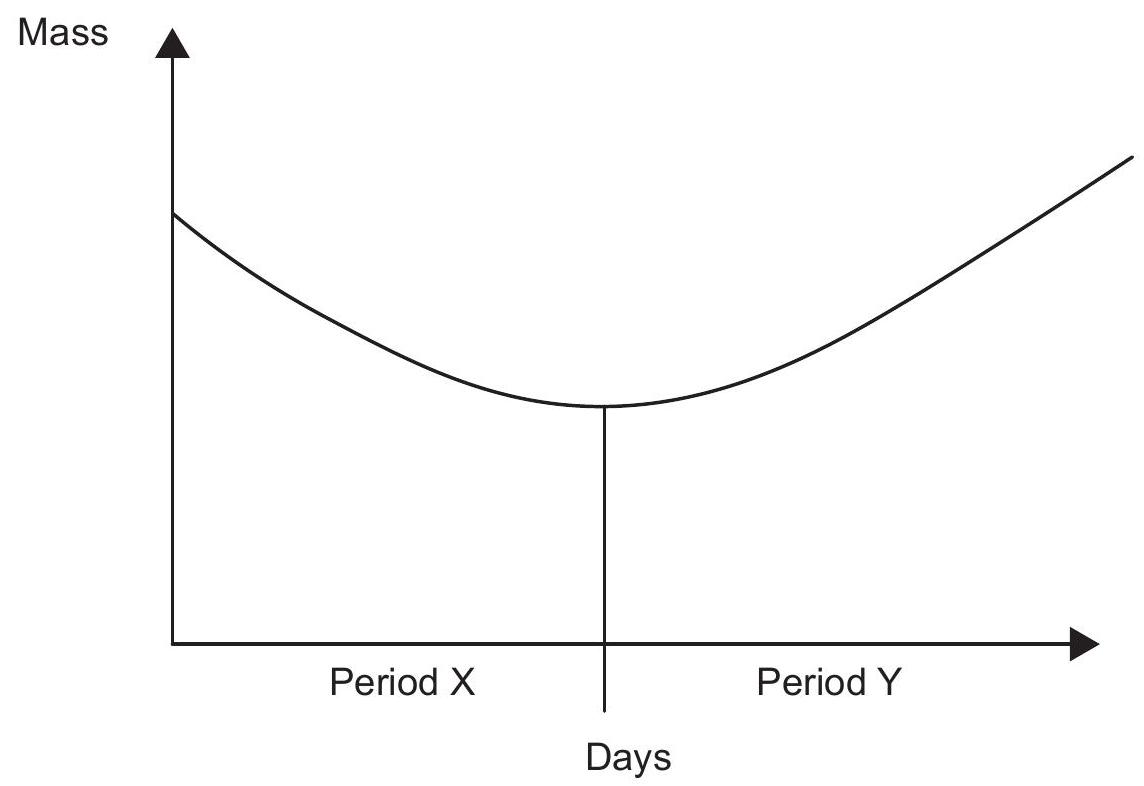
What can be deduced from the graph?
A man attaches a bird box to the trunk of a dicotyledonous tree. A few years later he returns to the tree and finds that his bird box is still attached and the tree is much taller. How high will his bird box be from the ground?
Draw a labelled diagram of a eukaryotic plant cell as seen in an electron micrograph.
Outline how the energy flow through food chains limits their length.
In hot, dry conditions plants lose water rapidly due to transpiration. Explain how the structures and processes of the plant allow this water to be replaced.
What is/are the effect(s) of auxin in plants?
I. Increasing the rate of cell elongation in stems
II. Changing the pattern of gene expression in shoot cells
III. Detecting the direction of light
Which is a function of sucrose in plants?
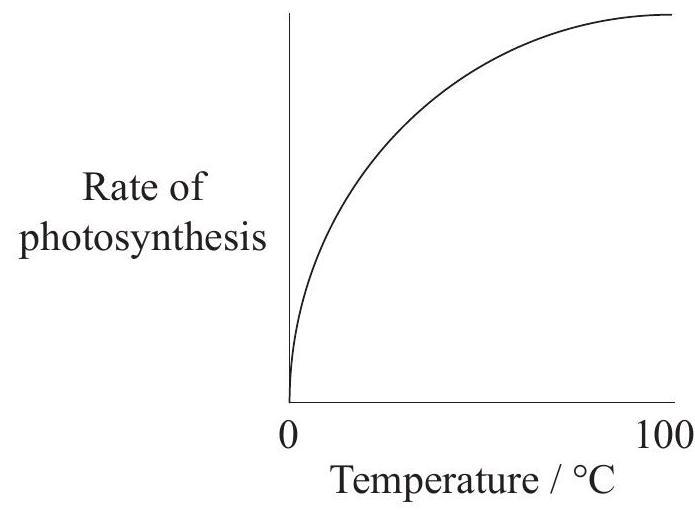
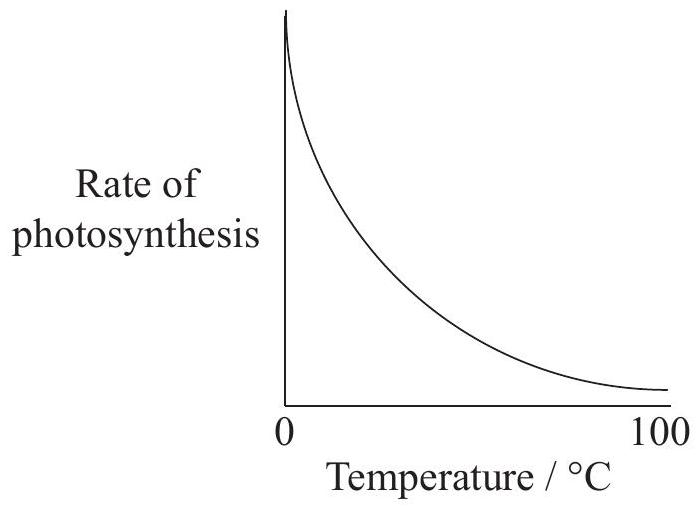
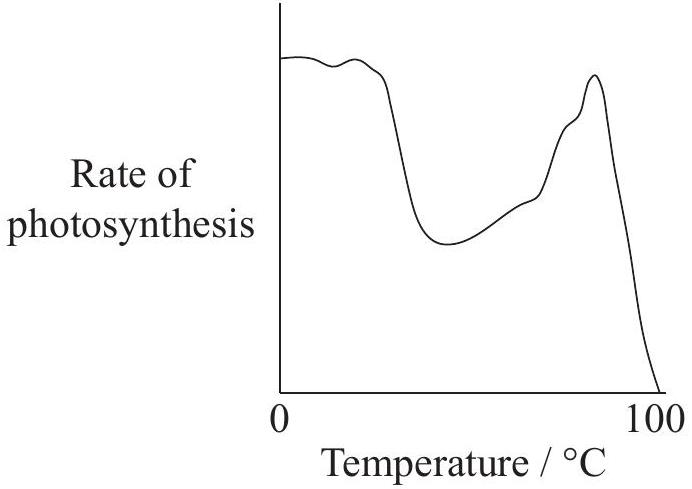
Which graph best represents the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis of a plant?

What conditions will cause the highest rate of transpiration in a well-watered, mesophytic plant?
The main parts of growing plants are roots, stems and leaves. Draw a plan diagram to show the arrangement of tissues in the stem of a dicotyledonous plant.
Outline the adaptations of plant roots for absorption of mineral ions from the soil.
Photosynthesis and transpiration occur in leaves. Explain how temperature affects these processes.
Which hormone causes the closing of stomata?