Practice 9.2 Transport in the phloem of plants with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Plants have developed efficient methods for transport and for synthesis of foods.
Compare and contrast between the xylem and phloem of plants.
Explain how the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis rely on the light-dependent reactions.
Outline how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium in plants.
In the cross-sectional diagram of a dicotolydenous root below, which letter indicates the location of cambium?
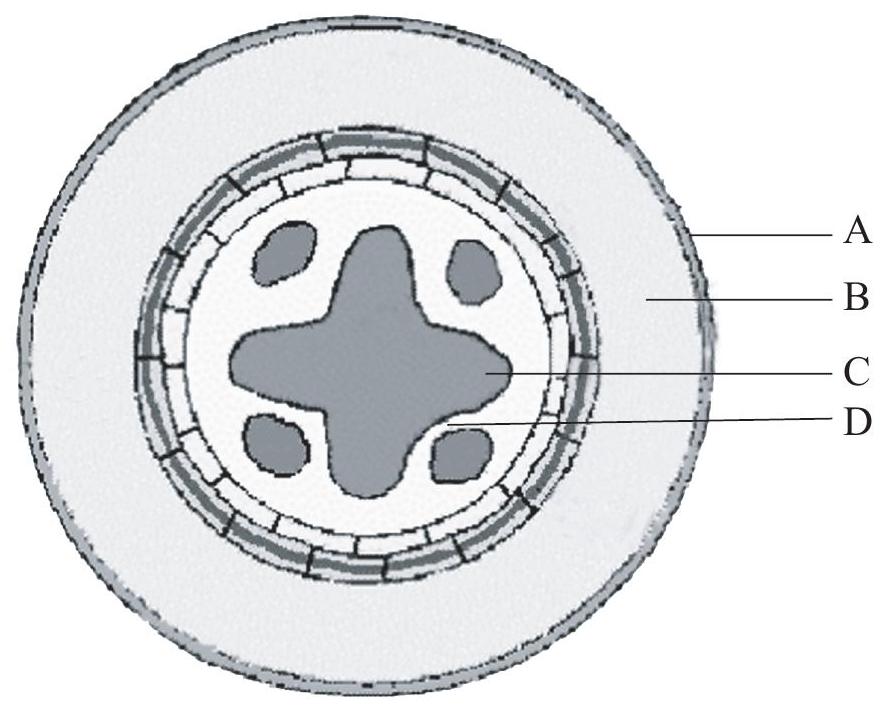
[Source: Biology Department, University of Arkansas at Little Rock (2004),
Biology 2402 - Introduction to Botany Cross Section of a Typical Dicot Root, www.ualr.edu/~botany/root_diagram.gif]
Which is a function of sucrose in plants?
The diagram shows the longitudinal section of phloem tissue at a plant source.
Companion cells Sieve tube elements
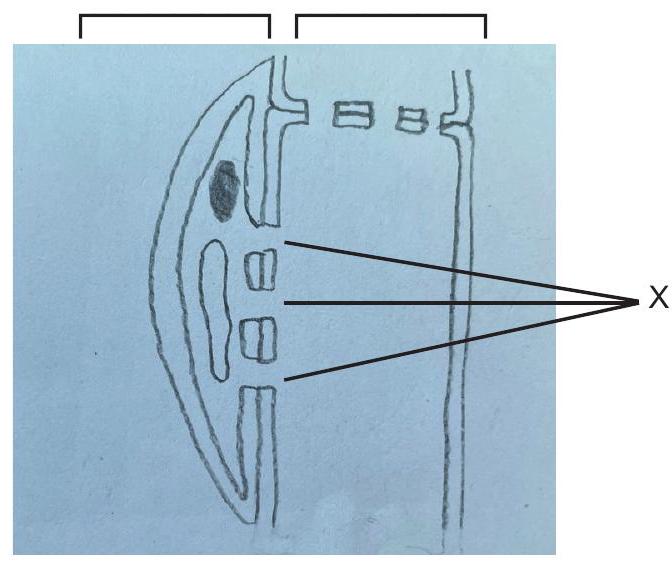
What is a function of the structures labelled X?
The diagrams represent cross sections of the stem and root of a plant.
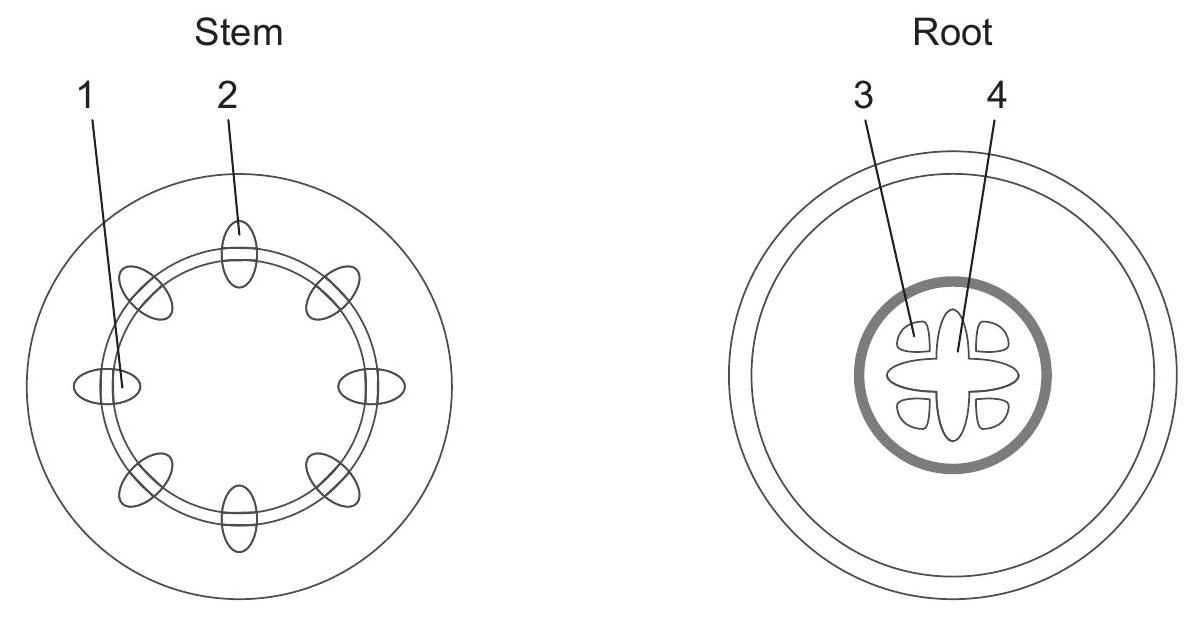
Which tissues transport water in the stem and the root?
| Stem | Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
What could be used in a technique for measuring flow rates in phloem?
I. Potometers II. Aphid stylets III.
Draw a labelled diagram of the internal structure of a seed.
Explain the process of water uptake and transport by plants.
How do water molecules enter root cells?
Which abiotic factors affect transpiration in plants?