Practice 9.1 Transport in the xylem of plants with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Outline how the properties of water make it an effective coolant for the body.
Describe how changes in weather conditions affect the transport and loss of water in plants.
Explain how water balance is restored in mammals when they are dehydrated.
Which graph represents the effect of humidity on the transpiration rate in plants?
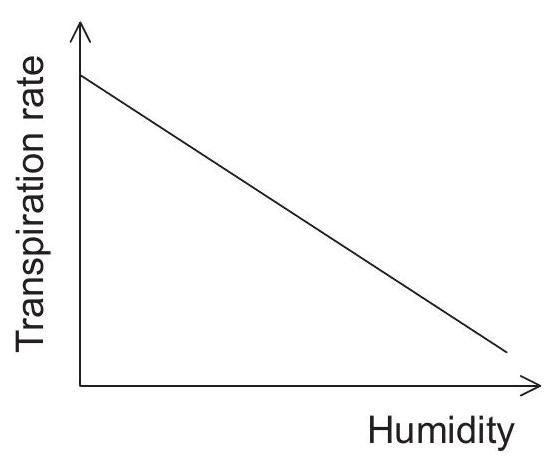
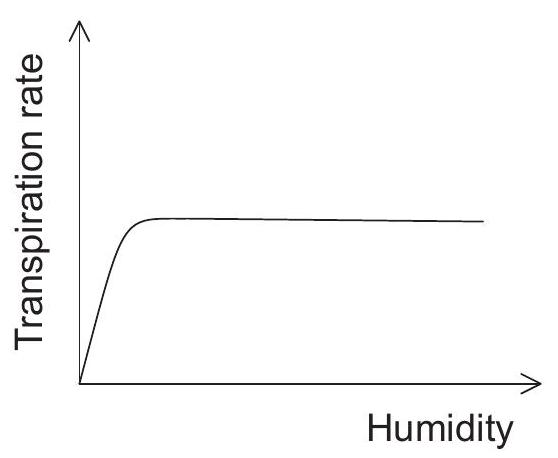
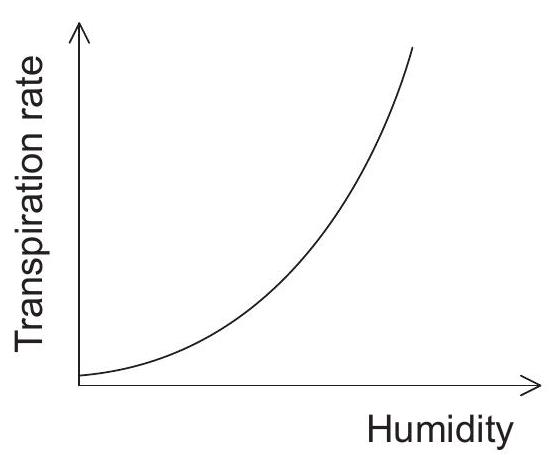
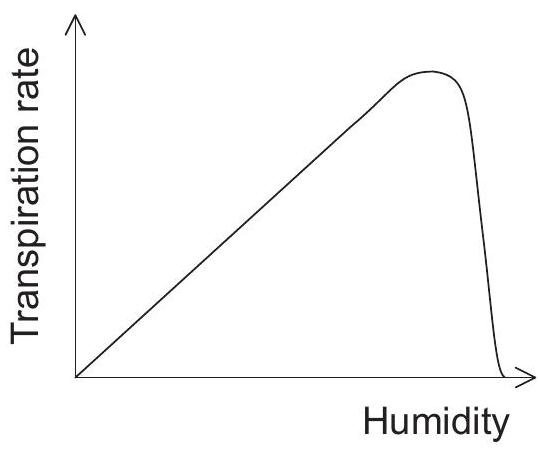
Which process is most responsible for movement of water from roots to leaves of a plant on a hot sunny day?
What is a role of xylem?
Cobalt chloride paper is blue when dry but turns pink with water. Blue cobalt chloride paper was fastened to the upper and lower surfaces of a plant leaf. After 20 minutes, many small pink dots were observed on the paper on the lower surface, and a few pink dots were seen on the upper surface. What conclusions can be drawn?
I. There are more stomata on the lower surface than on the upper surface.
II. Stomata on the upper surface are blocked by the waxy cuticle.
III. More transpiration occurs through the lower surface than through the upper surface.
What is the apoplastic route for water from the soil to the endodermis of roots?
What is a difference between cohesion and adhesion?
The following electron micrograph shows part of a palisade mesophyll cell. Which of the labelled structures controls the exchange of substances to and from the cell?
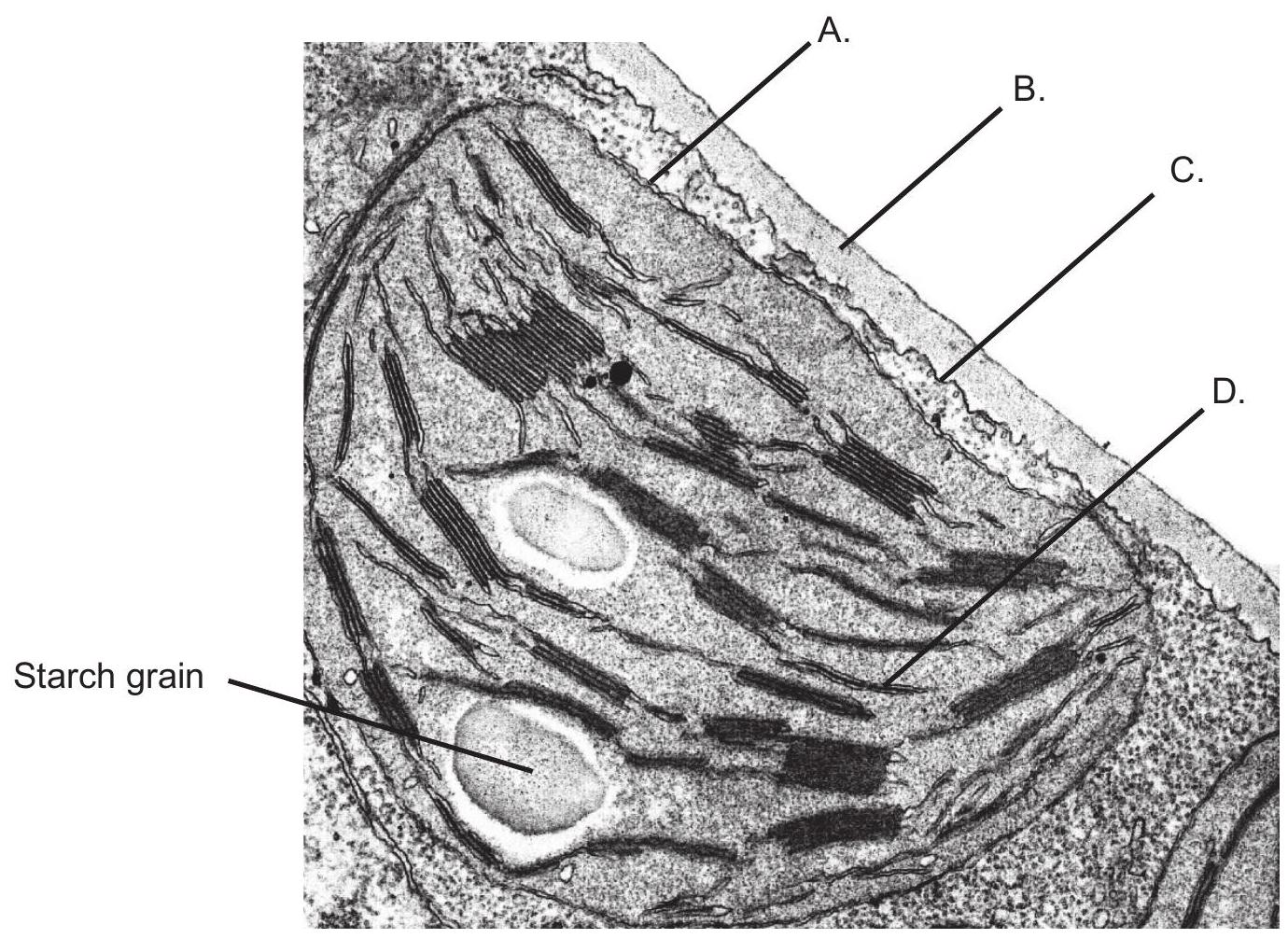
[Source: adapted from Eldon Newcomb, http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/about.html]
Plants have developed efficient methods for transport and for synthesis of foods.
Compare and contrast between the xylem and phloem of plants.
Explain how the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis rely on the light-dependent reactions.
Outline how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium in plants.
Draw a labelled diagram of a eukaryotic plant cell as seen in an electron micrograph.
Outline how the energy flow through food chains limits their length.
In hot, dry conditions plants lose water rapidly due to transpiration. Explain how the structures and processes of the plant allow this water to be replaced.