Practice 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The graph below shows the levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle.
Identify hormones I and II.
Outline the roles of FSH in the menstrual cycle.
FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland. During pregnancy, FSH secretion is inhibited. Suggest how FSH secretion could be inhibited during pregnancy.
Skeletal muscle fibres normally respond to insulin by absorbing glucose. Failure of skeletal muscle to respond to insulin is a major factor in the development of type II diabetes. A study was undertaken to investigate the effect of plasma lipids on the process of glucose absorption in response to insulin by muscle fibers. Muscle was bathed in a lipid solution for 5 hours. The lipid was then washed out over the next 3 hours. The graph shows the level of plasma fatty acids and the activity of an enzyme involved in glucose absorption in response to insulin over the period of the study. (Values are means ± standard error) 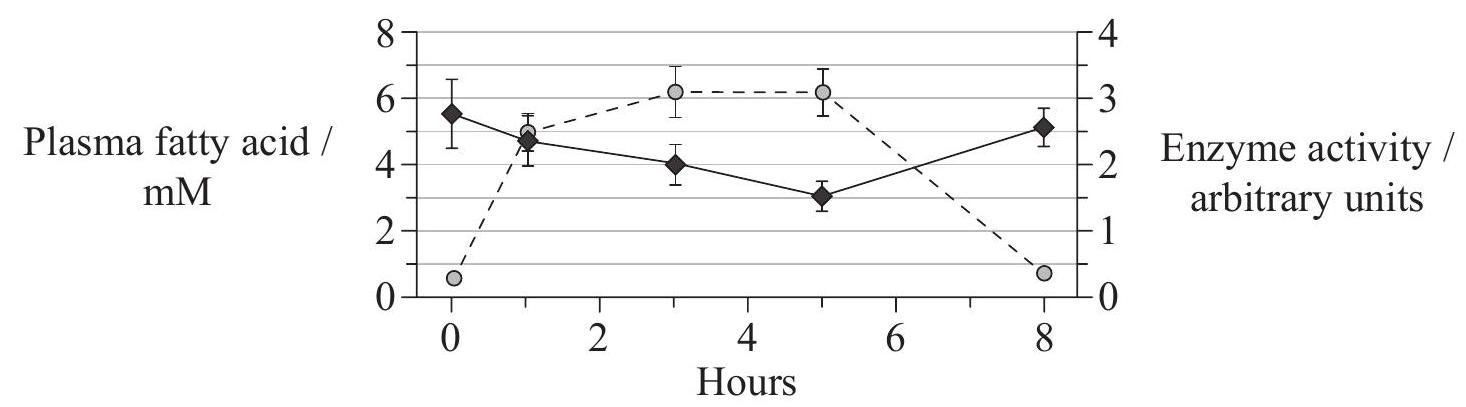 Key: -o- plasma fatty acid → enzyme activity A further study was undertaken to look at the effect of increasing the concentration of insulin on glucose absorption in muscle bathed in lipids. A wide range of insulin concentrations were used in the same type of muscle. Glucose absorption was then measured after 5 hours.
Key: -o- plasma fatty acid → enzyme activity A further study was undertaken to look at the effect of increasing the concentration of insulin on glucose absorption in muscle bathed in lipids. A wide range of insulin concentrations were used in the same type of muscle. Glucose absorption was then measured after 5 hours. 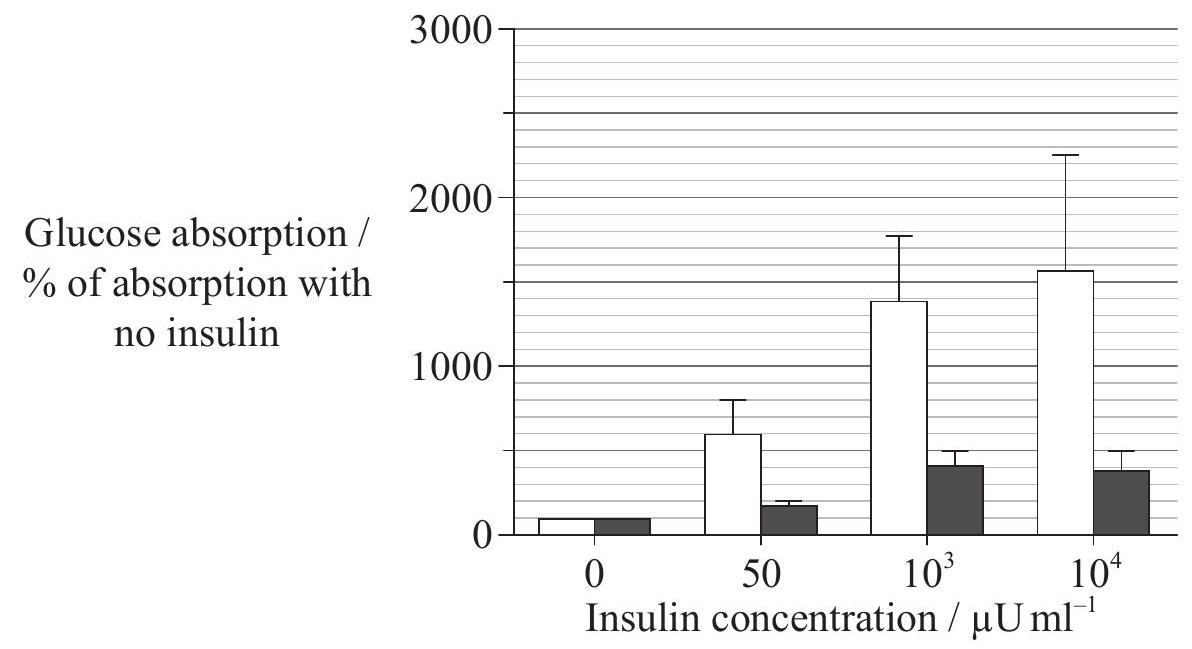 Key: □ control muscle with no lipid ■ muscle bathed in lipid [Source: Chunli Yu, et al. (2002), The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, pages 50 230-50 236]
Key: □ control muscle with no lipid ■ muscle bathed in lipid [Source: Chunli Yu, et al. (2002), The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, pages 50 230-50 236]
Distinguish between type I and type II diabetes.
State the relationship between plasma fatty acid level and enzyme activity.
Calculate the percentage change of enzyme activity after 5 hours exposure to lipids.
Discuss, using the data, whether the effect of lipids on this enzyme is reversible.
Calculate the increase in glucose absorption when insulin is increased from 0 to 10³ μUml⁻¹ for the muscle bathed in lipid.
% of absorption with no insulin
Comment on the effect of increased insulin concentration on glucose absorption in the muscle bathed in lipid.
Some investigators suggest that there is a strong relationship between high lipid diet and the body's response to insulin. Using the data provided, evaluate this hypothesis.
Which correctly describes the role of the epididymis in semen production?
The diagram shows organs that produce hormones in a female human. Which organ is the source of the hormone used in IVF treatment to produce many ova?
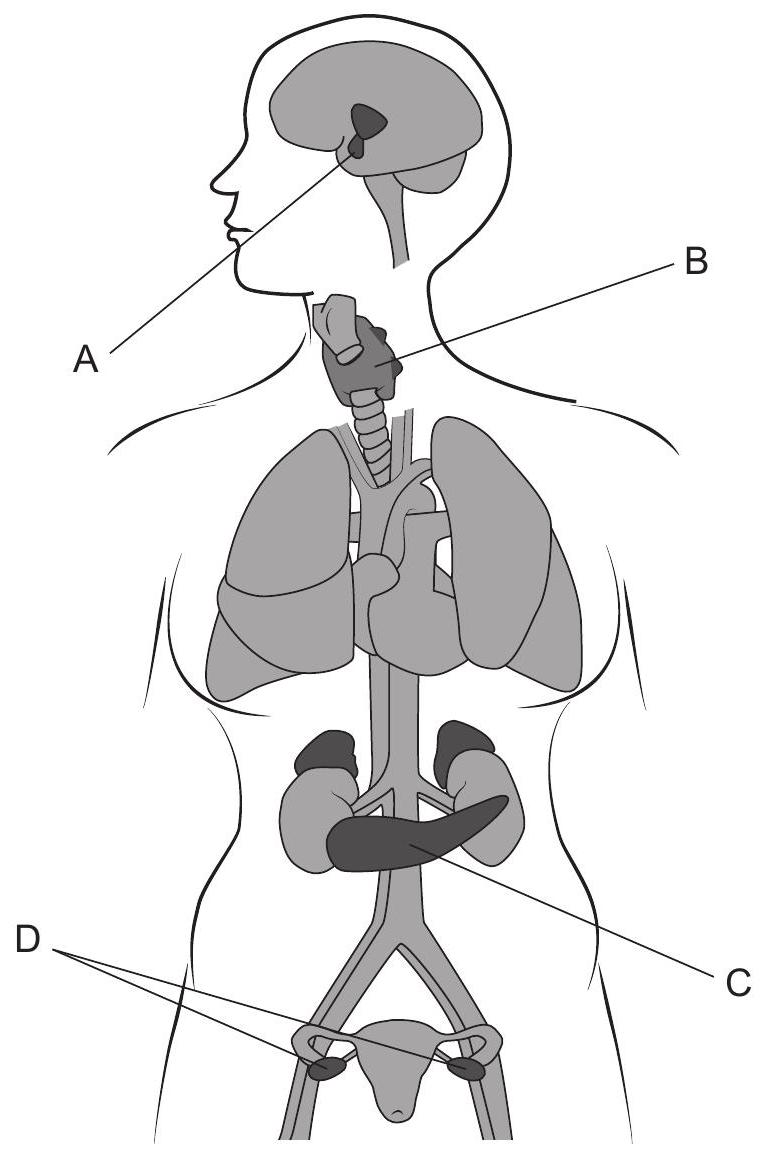
What effect would the continued presence of estrogen and progesterone have in the human female?
What is most likely to increase in the presence of insulin?
Outline what is meant by homeostasis.
Describe how body temperature is maintained in humans.
Explain the processes occurring in the kidney that contribute to osmoregulation.
Describe the structure of the DNA molecule.
Outline the role of three enzymes used in the replication of DNA.
Insulin is produced in β cells of the pancreas and not in other cells of the human body. Explain how differentiation of cells and regulation of gene expression allow proteins such as insulin to be produced in only certain types of body cell.
LH causes the rupture of a follicle and release of an egg cell. What is this process called?
Which hormone controls circadian rhythms?