Practice 3.4 Inheritance with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
In cats, black coat colour is dominant over gray. A female black cat, whose mother is gray, mates with a gray male. What is the predicted ratio of phenotypes in the offspring?
Which of the following is an inherited disease that is due to a base substitution mutation in a gene?
Creeper in chickens is a condition in which the chickens are born with very short legs. The creeper allele (C) is dominant over the normal allele (c). Embryos which are homozygous for the dominant allele fail to develop into viable chickens and die before they hatch. What phenotypic ratio would you expect in the live offspring of a cross between two creeper chickens?
Which of the following involves complementary base pairing?
I. Transcription II. Translation III. Replication IV. Denaturation
The blood groups of a mother and four children are indicated on the pedigree chart below.
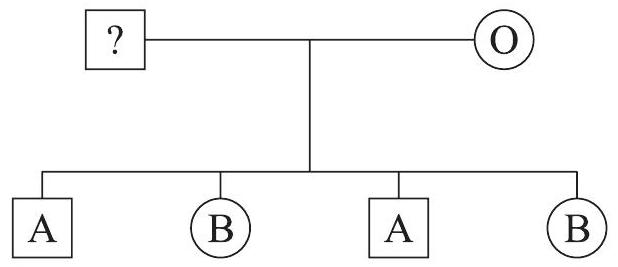
What are the possible blood groups of the father?
If 15% of a sample of DNA is thymine, what percentage of the DNA is guanine?
What is a difference between two alleles of a gene?
Which disease is an example of sex-linked (X-linked) inheritance?
Palomino horses are the result of crosses between horses with black coats and white coats. The alleles for black coats and white coats are codominant.
Which of the following crosses could give palomino offspring?
I. palomino × palomino II. palomino × white III. white × white
What is the effect of dominant alleles?
I. They mask the effect of recessive alleles. II. They become more frequent than recessive alleles in a population. III. They have a joint effect with recessive alleles when characteristics are co-dominant.