Practice 2.8 Cell respiration with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Which row in the table describes the first stage of cellular respiration?
| Substrate | Location | Product | Product | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. | pyruvate | mitochondria | oxygen | water |
| B. | pyruvate | cytoplasm | carbon dioxide | ATP |
| C. | glucose | mitochondria | pyruvate | water |
| D. | glucose | cytoplasm | pyruvate | ATP |
Describe the genetic code and its relationship to polypeptides and proteins.
Outline the role of proteins in active and passive transport of molecules through membranes.
Many cell functions, like synthesis of macromolecules and transport, require energy in the form of ATP. Explain how ATP is generated in animal cells.
The electron micrograph below shows part of several pancreatic islet cells. 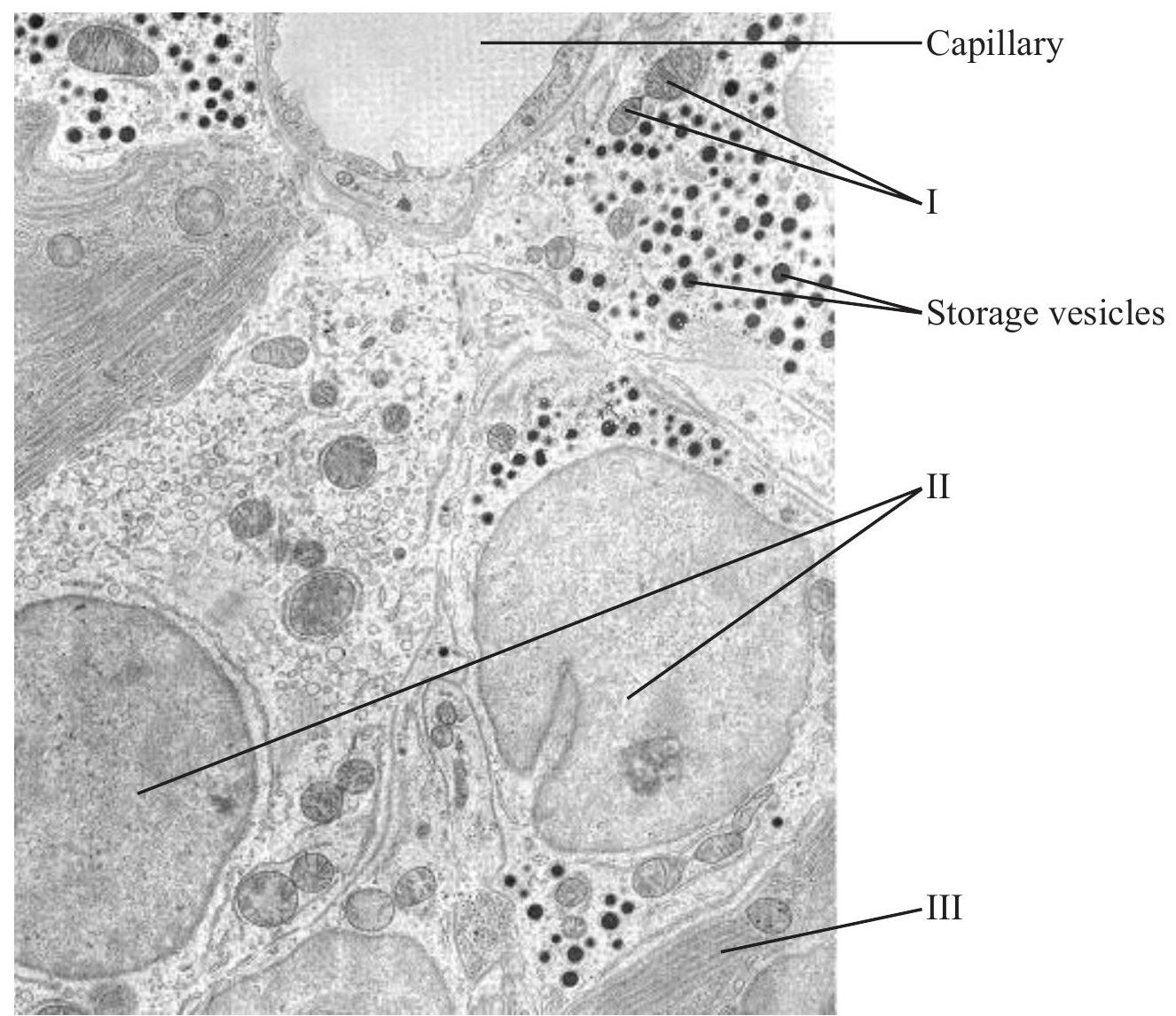
Identify the structures labelled I, II and III in the micrograph above and give a role for each one.
Using the letter A, identify one location on the micrograph where transcription takes place.
Using the letter B, identify one location on the micrograph where chemiosmosis occurs.
Suggest what product each cell is likely to be making.
Explain how the products are transported from the site of production and released from the islet cells.
Which of the following is the best definition of cell respiration?
What happens during the pathway of glycolysis?
Draw and label a diagram of the carbon cycle.
Outline the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis and how this can be measured by carbon dioxide uptake.
Explain how carbon dioxide is produced in anaerobic and in aerobic respiration.
Which process produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose?
How much energy is stored in 1 kg of body fat compared to 1 kg of glycogen?
The graph shows the activity of an enzyme at various temperatures. The pH of the experiment was kept constant at pH 8.
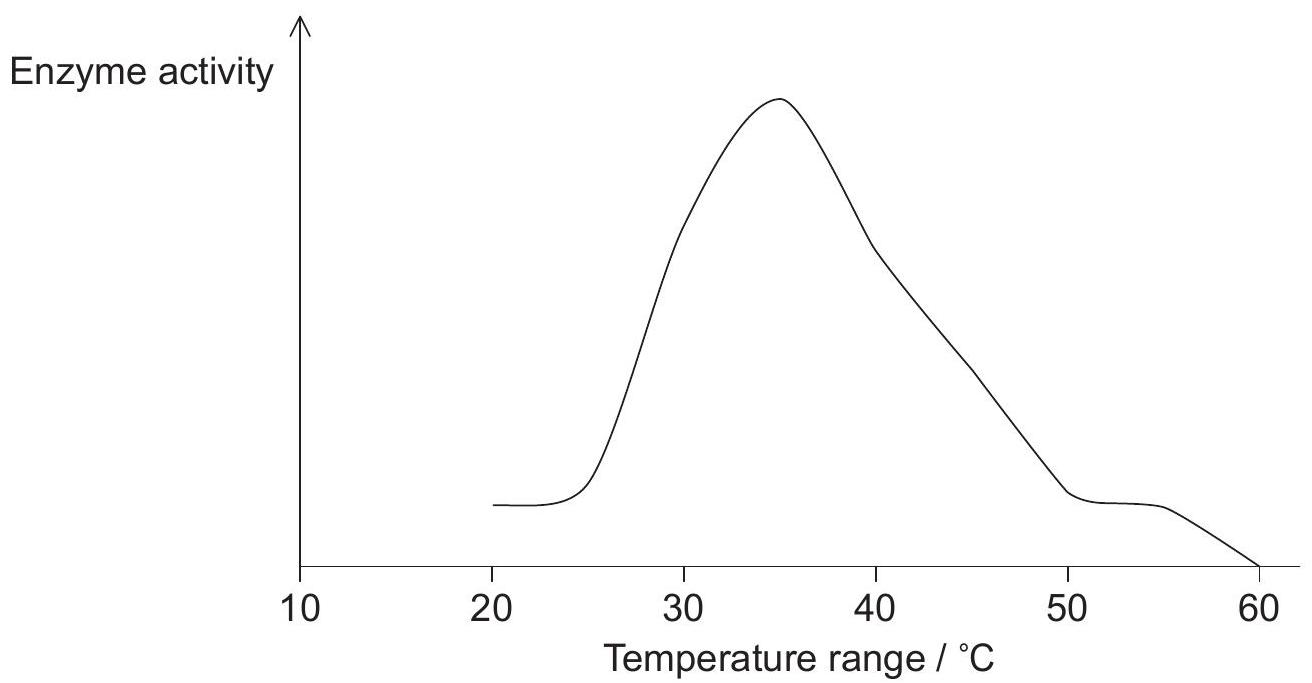
Based on the data, what would the result be if the experiment was repeated at pH 9?
All organisms take in and also release carbon compounds. Draw a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle.
Describe how the rate of photosynthesis can be measured.
Explain the mechanism of ventilation in humans.