Practice 2.4 Proteins with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The equation below shows the production of glucose and galactose from lactose. 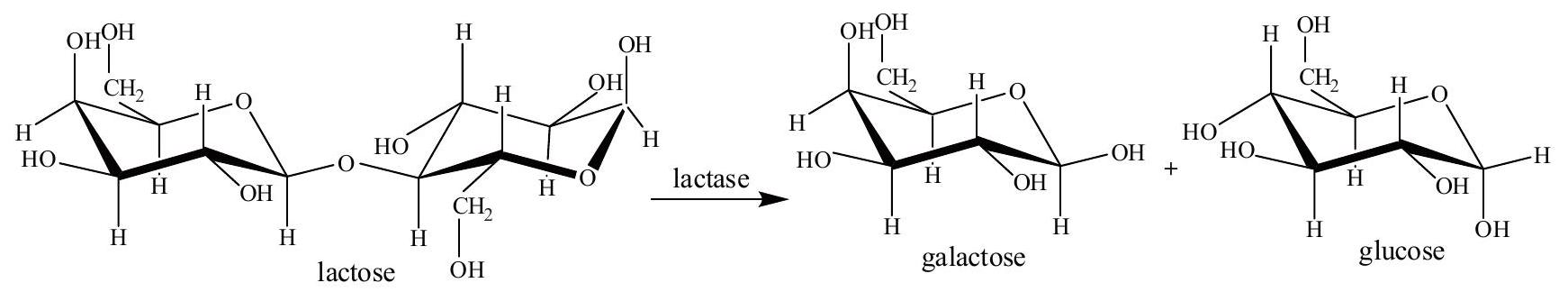
Glucose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. State one other example of a monosaccharide.
There are several different types of carbohydrate. State which type of carbohydrate lactose is.
State the type of chemical reaction that occurs when lactose is digested into glucose and galactose.
Lactase is widely used in food processing. Explain three reasons for converting lactose to glucose and galactose during food processing.
Simple laboratory experiments show that when the enzyme lactase is mixed with lactose, the initial rate of reaction is highest at 48°C. In food processing, lactase is used at a much lower temperature, often at 5°C. Suggest reasons for using lactase at relatively low temperatures.
Which protein is identified with its function?
| Protein | Function |
|---|---|
| collagen | provides strength and support for tissues and organs |
| rhodopsin | enzyme found in tears |
| insulin | raises blood glucose concentrations |
| immunoglobulin | helps in blood clotting |
Outline the first three levels of protein structure, including the types of bonding within each and the significance of each level.
Using a table, compare competitive and non-competitive inhibition and give one named example of each.
Explain the production of antibodies.
The graph shows the results of an investigation into the activity of turnip peroxidase. The accumulation of the product of the reaction catalysed by the enzyme is shown at different pH values.
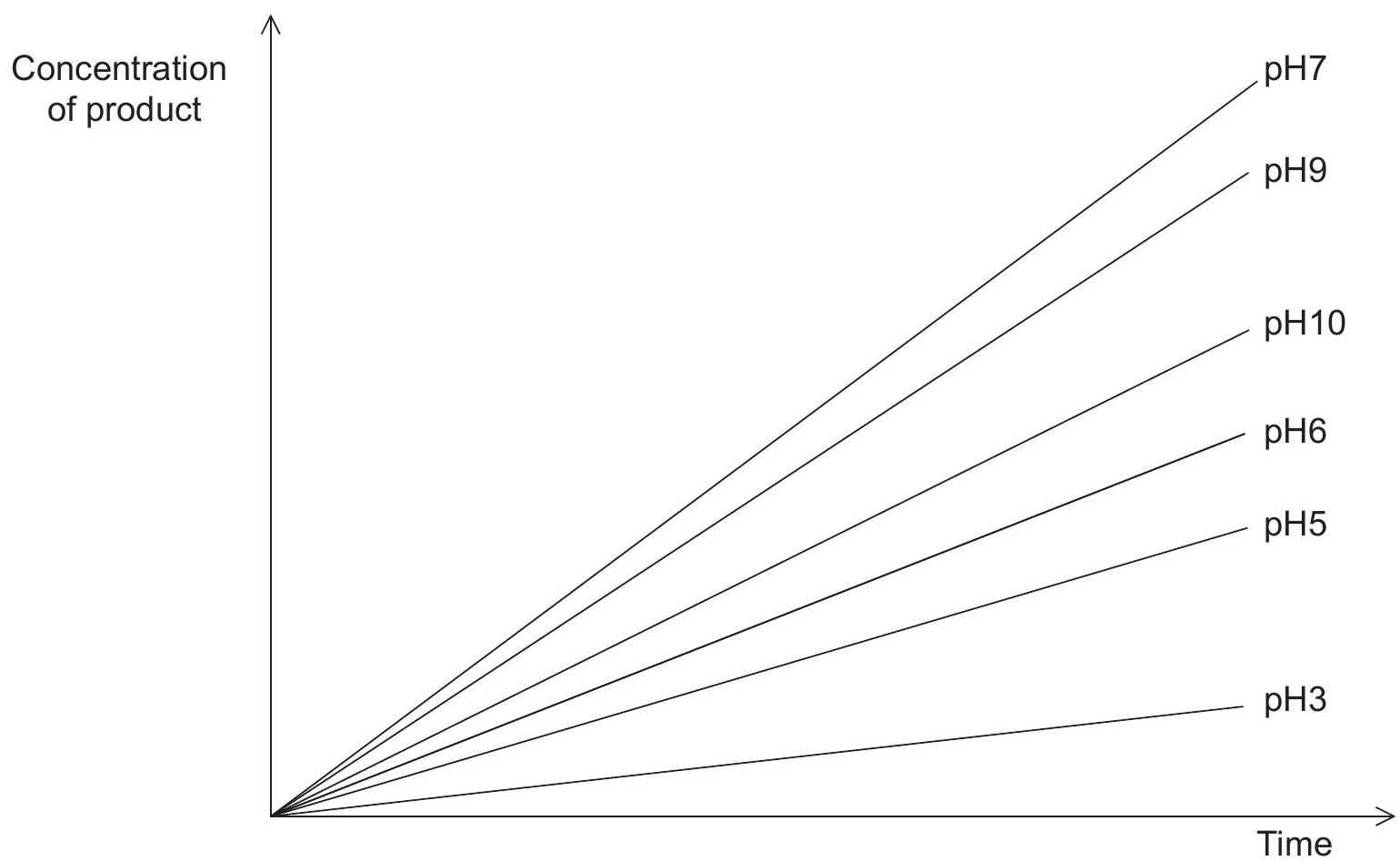
Based on the data in the graph, what is most probably the optimum pH for turnip peroxidase?
Describe the genetic code and its relationship to polypeptides and proteins.
Outline the role of proteins in active and passive transport of molecules through membranes.
Many cell functions, like synthesis of macromolecules and transport, require energy in the form of ATP. Explain how ATP is generated in animal cells.
How is the sequence of DNA conserved?
Outline the structure of proteins.
Cells produce a large variety of proteins with different sequences of amino acids. Explain how this is done.
Outline the range of functions of proteins in cells.
Living organisms produce a wide variety of organic compounds.
Define the term organic.
State the three most commonly occurring elements.
Some organic compounds contain other elements. State one substance, or group of substances, that contains nitrogen.
Some organic compounds contain other elements. State one substance, or group of substances, that contains phosphorus.
What are the most frequently occurring elements in living organisms?
State four functions of proteins, giving a named example of each.
Explain the process of translation.
In a given population some variations of a protein are expressed more frequently than others. Outline how evolution through natural selection can lead to the expression of one version of a protein rather than another.