Practice 2.1 Molecules to metabolism with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Which carbon compound produced by living organisms is inorganic?
Living organisms produce a wide variety of organic compounds.
Define the term organic.
State the three most commonly occurring elements.
Some organic compounds contain other elements. State one substance, or group of substances, that contains nitrogen.
Some organic compounds contain other elements. State one substance, or group of substances, that contains phosphorus.
What is the source of carbon for the following organisms?
| Autotrophs | Heterotrophs | Saprotrophs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. | Organic | Inorganic | Organic |
| B. | Inorganic | Organic | Organic |
| C. | Organic | Organic | Organic |
| D. | Inorganic | Inorganic | Inorganic |
What are the most frequently occurring elements in living organisms?
What is involved during oxidation?
Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in metabolic reactions involving carbohydrates.
Metabolic reactions are catalysed by enzymes. Explain how enzymes catalyse reactions and how a change in pH could affect this.
Describe the digestion of food in the human digestive system.
What is needed in photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules?
Glucose is absorbed through protein channels in the plasma membrane of epithelium cells in the small intestine. Which characteristics of glucose prevent its diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer?
Where in the mitochondrion does the formation of acetyl CoA occur?
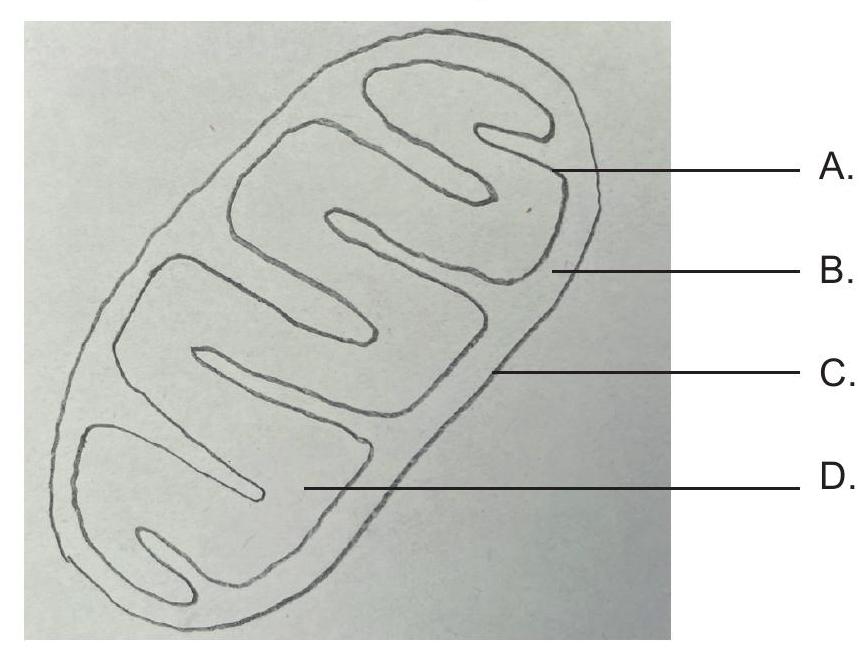
Organisms have evolved a great diversity of cell types.
Describe the endosymbiotic theory.
Explain the need for halving the chromosome number during a sexual life cycle and how this is done.
Outline the binomial system of classification.