Practice 1.5 The origin of cells with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Which of the following characteristics found in a structure necessarily indicates that it is alive?
Which statement provides evidence for endosymbiosis?
Which pair of features is correct for both a human liver cell and an Escherichia coli cell?
| Human liver cell | Escherichia coli cell | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | contains DNA associated with protein | contains naked DNA |
| B. | has 70S ribosomes | has 80 S ribosomes |
| C. | contains mitochondria | contains mitochondria |
| D. | contains DNA enclosed by a membrane | contains DNA associated with protein |
Draw a labelled diagram of the molecular structure of DNA, comprising of four nucleotides.
Outline the therapeutic use of stem cells.
Giving one specific example, discuss genetic modification in organisms including the potential benefits and possible harmful effects.
Which statement is part of the cell theory?
The electron micrograph shows a section through a cell and refers to questions 1 and 2.
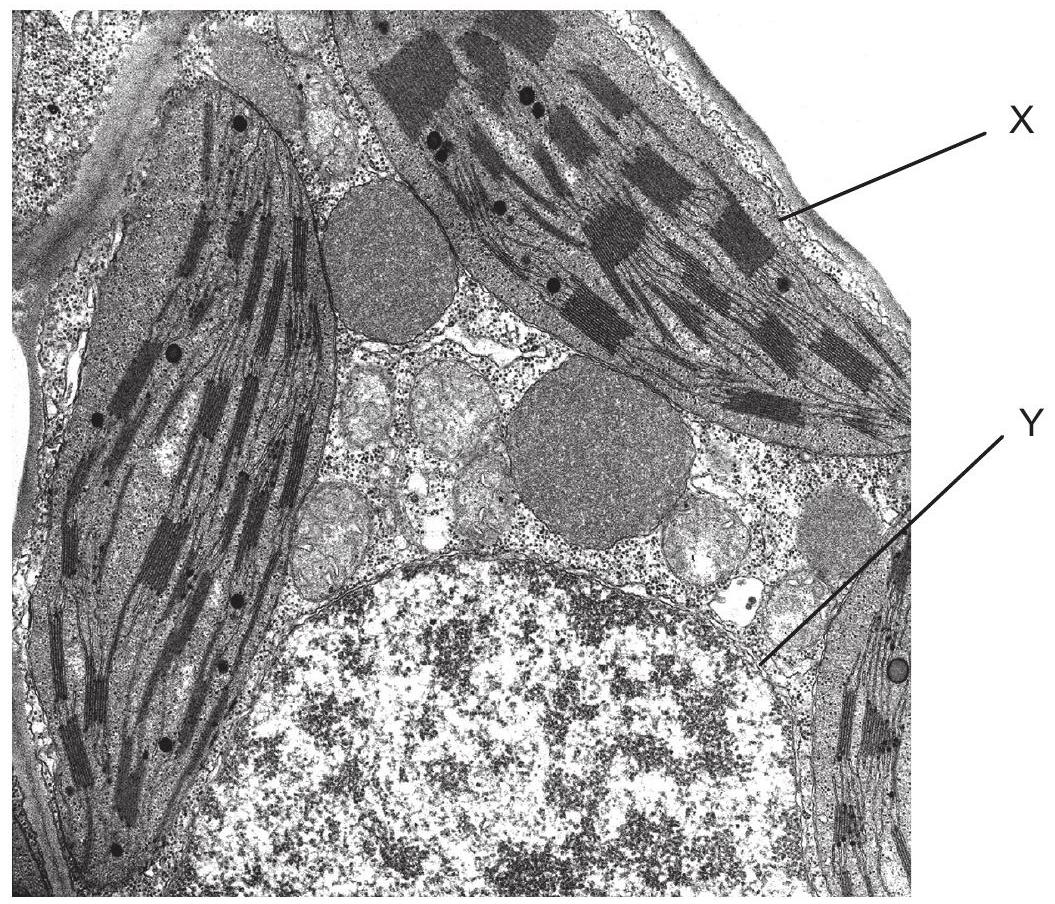
Which feature of the cell in the micrograph is consistent with the endosymbiotic theory?
What distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
| Prokaryotic cells | Eukaryotic cells | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | no plasma membrane | plasma membrane |
| B. | 80 S ribosomes | 70 S ribosomes |
| C. | Golgi apparatus | mitochondria |
| D. | no internal membrane compartments | internal membrane compartments |
A cell contains chloroplasts, plasma membrane and 80 S ribosomes. What type of cell could it be?
What is evidence for the endosymbiotic theory?
State the property of stem cells that makes them useful in medical treatment.
Explain how multicellular organisms develop specialized tissues.
Outline some of the outcomes of the sequencing of the human genome.