Practice Amines with authentic CBSE Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of CBSE examiners.
When Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol, it forms a dye. This reaction is called
An Organic compound (A) with molecular formula C3H7NO on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound (B). Compound (B) on heating with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces a foul smelling compound (C) and on reacting with C6H5SO2Cl forms a compound (D) which is soluble in alkali.
Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Which of the two is more basic and why? CH3NH2 or C6H5NH2
Write the main products of the following reactions:
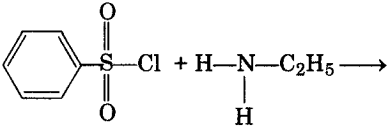
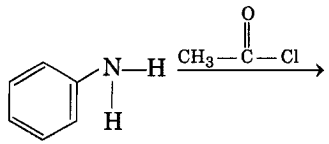
Complete the following reaction:
CHCHNH + CHCl + \text{alc.} \text{KOH} \longrightarrow
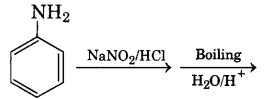
Give a chemical test to distinguish between aniline and ethylamine.
An aromatic compound A (C7H6O2) on reaction with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound B. B on heating with Br2 and alcoholic potash forms a compound C of molecular formula C6H7N.
Write the reactions involved and identify A, B, C.
Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecule by alkyl/aryl groups. Amines are usually formed from nitro compounds, halides, amides, etc. They exhibit hydrogen bonding which influences their physical properties. Alkyl amines are found to be stronger bases than ammonia. In aromatic amines, electron releasing and withdrawing groups, respectively increase and decrease their basic character. Reactions of amines are governed by availability of the unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen. Influence of the number of hydrogen atoms at nitrogen atom on the type of reactions and nature of products is responsible for identification and distinction between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Reactivity of aromatic amines can be controlled by acylation process.
Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions:
I. C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O → A + N2 + HCl + H3PO3
II. CH3CH2CONH2 → A → B Br2/alc.KOH CH3COCl/Pyridine
Give the structures of A and B in the following sequence of reactions:
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation reaction is given by: