Practice C2.1 Chemical signalling (HL) with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Refer to the diagram showing epinephrine binding to a beta-adrenergic receptor and subsequent activation of intracellular signalling.
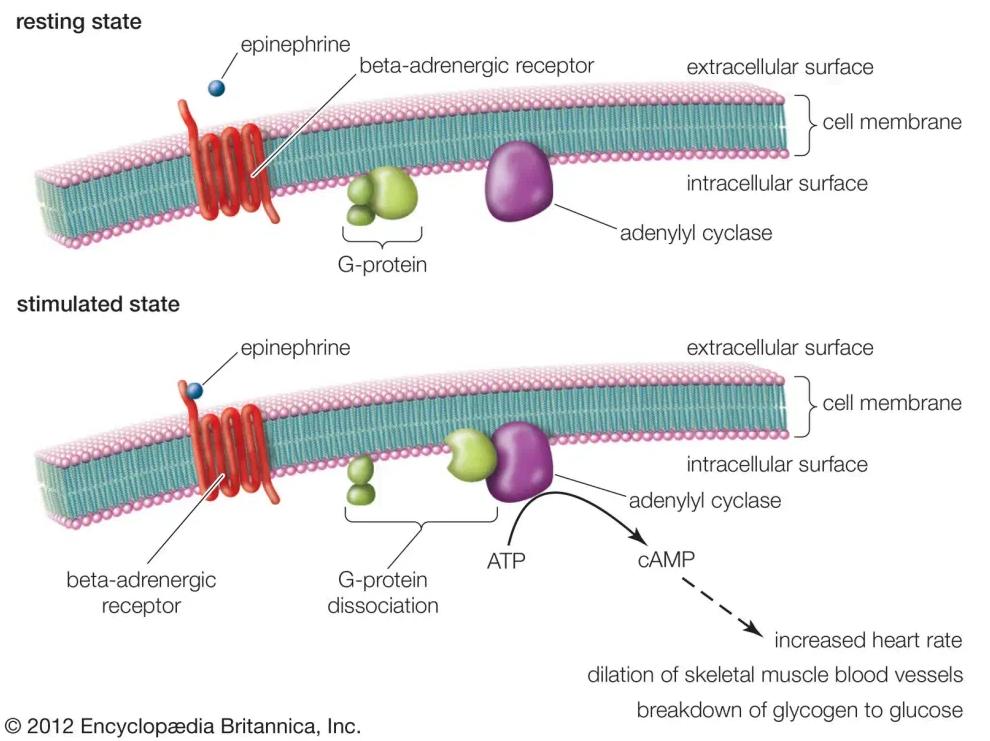
Epinephrine-stimulated cAMP synthesis
Which process best explains how signal transduction begins following epinephrine binding to the receptor?
Refer to the image showing membrane-bound ATPases.
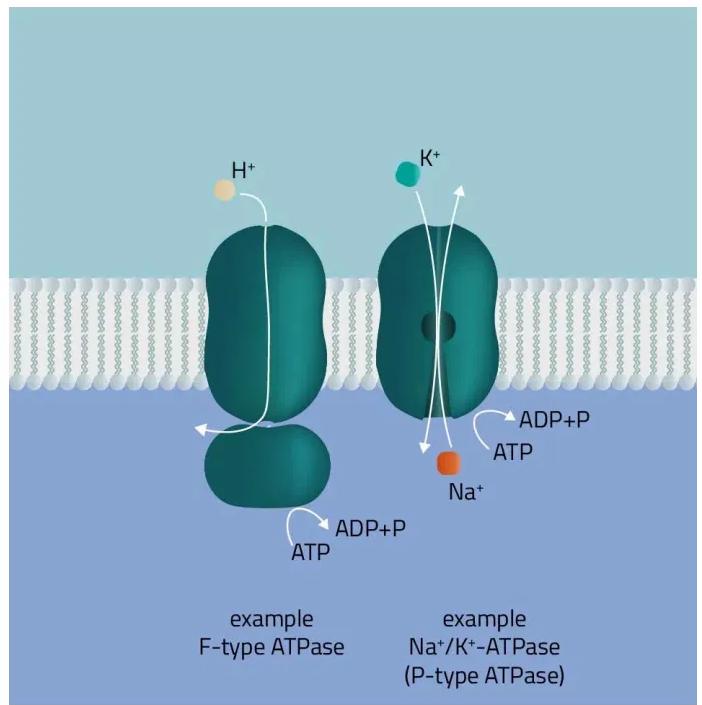
Why do these ATPases require transmembrane regions?
The table below shows Vibrio fischeri bacteria at different cell densities and their production of quorum-sensing signals.
| Cell density (cells/mL) | Quorum signal concentration (µM) | Light emission (relative units) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0 | |
| 1.5 | 5 | |
| 12 | 100 |
Based on the table, what explains the sudden increase in bioluminescence at high cell densities?
Explain how quorum sensing leads to bioluminescence in Vibrio fischeri.
A researcher measured the effect of a ligand binding to a GPCR on cAMP production in liver cells. The data is shown below:
| Ligand Concentration (nM) | cAMP Production (pmol min) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 3.8 |
| 10 | 7.5 |
| 25 | 15.2 |
| 50 | 18.5 |
| 100 | 19.0 |
Describe the relationship between ligand concentration and cAMP production using the data provided.
Explain why cAMP production reaches a maximum level when ligand concentration exceeds 50 nM.
Researchers investigated the effects of oxytocin (OT) on cognitive recovery after ischemic stroke in a mouse model. The figure below summarizes several interacting molecular pathways influenced by OT, including calpain-1, NF-B, GDNF, VEGF, AQP4, and cytokines such as TGF- and IL-.
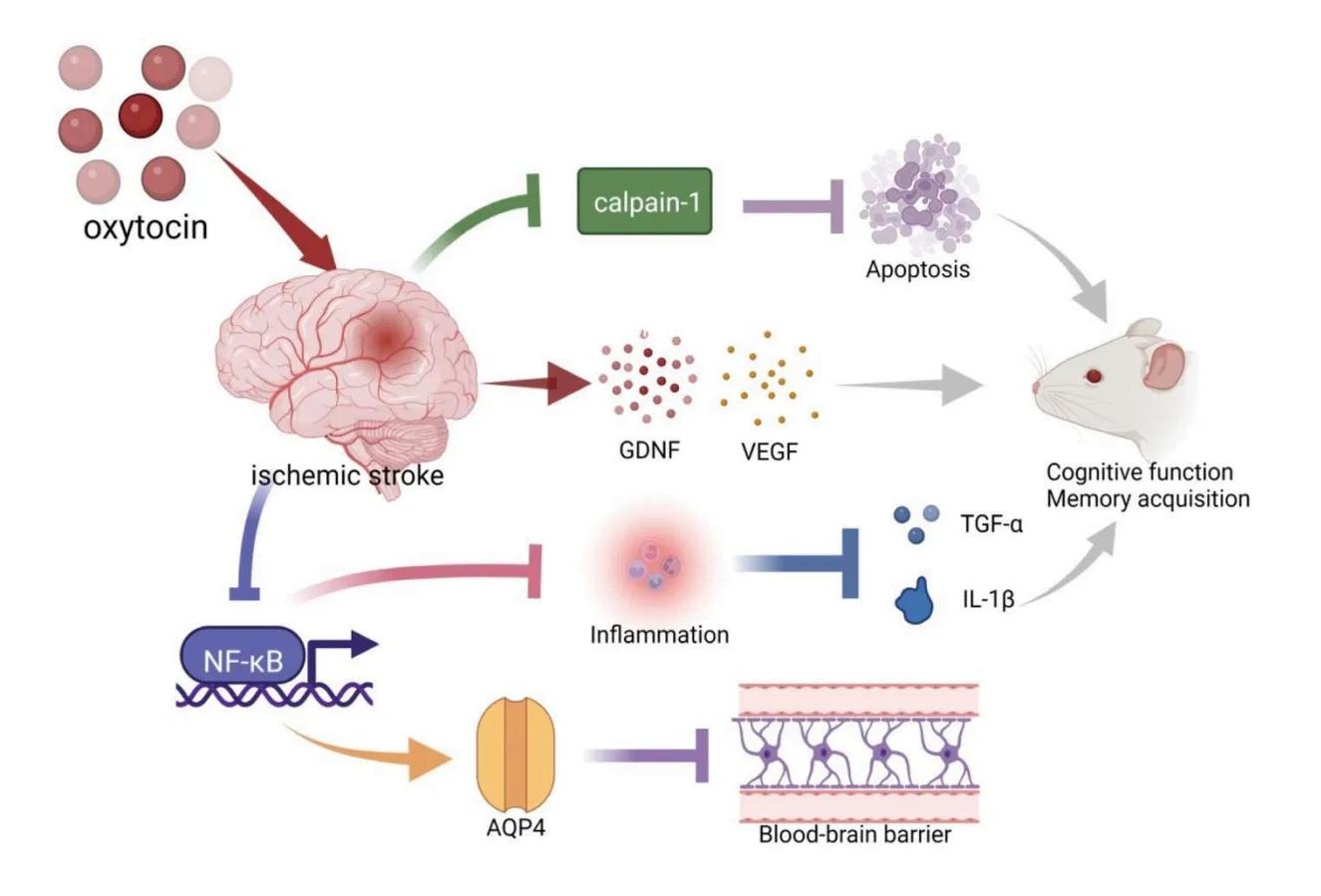
Identify which type of signalling molecule oxytocin belongs to and explain why it can exert distant effects after release into the body.
Explain why cytokines such as TGF- and IL- are classified separately from hormones and neurotransmitters.
Based on the diagram, list one signalling molecule that acts locally (near its release site) and one that acts at distant sites, and explain your reasoning.
State one reason why animals use a wide range of chemical substances (such as amines, proteins, peptides, and steroids) for signalling.
The signalling pathway shown in the diagram involves the activation of Calpain-1, which is a calcium-dependent enzyme. Describe the role of calcium ions () in intracellular signalling and explain their importance in the nervous system.
What type of receptor is associated with the hormone insulin?
Which of the following signaling molecules are involved in synaptic transmission?
How do neonicotinoid pesticides cause paralysis and death in insects?
I. Acetylcholine receptors are blocked.
II. Cholinesterase fails to break down the pesticide.
III. The pesticides bind to presynaptic receptors.
Which of the following describes the function of neurotransmitter receptors in the post-synaptic membrane?